Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
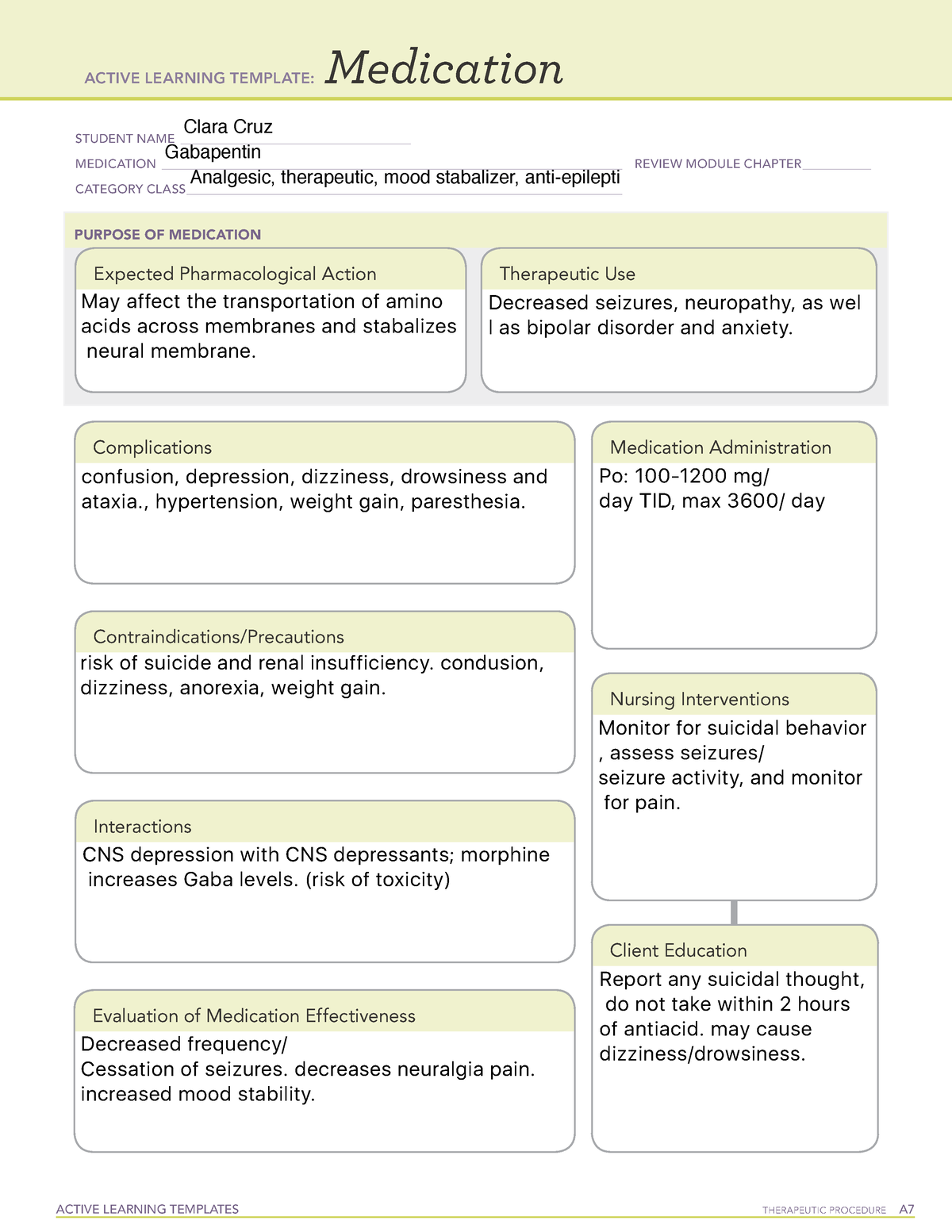 |  |
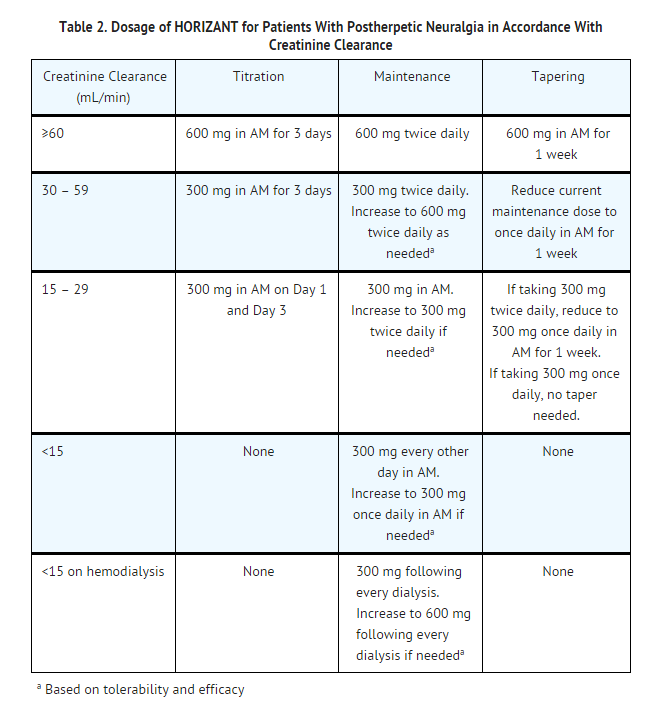
Use a CIWA protocol (see below) to administer benzodiazepines with or without adjunctive haloperidol. Can also start adjunctive gabapentin (300-600 TID) to decrease benzodiazepine requirements. Limited data for gabapentin in alcohol use disorder treatment. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. • No stairs, no jumping, no driving for cats on sedative doses of gabapentin. • Gabapentin has analgesic effects in cats, and reducing pain may be one of the ways it helps reduce fear. • Gabapentin is typically used prior to sedation/premedication protocols (see below). Gabapentin does not replace in-clinic sedation/premedication protocols. The protocol consists of at-home administration of gabapentin, melatonin, and oral transmucosal (OTM) acepromazine (10 mg/mL injectable formulation) prior to a medical appointment (see Treatment at a Glance: Chill Protocol). Gabapentin and melatonin can be given with a small amount of food, and acepromazine should be administered oral In this retrospective, single-center cohort study, we evaluated patients admitted for alcohol withdrawal and an underlying alcohol use disorder initiated on the CIWA-Ar protocol with or without scheduled gabapentin. Use of nonopioid analgesics has been shown to decrease PONV in patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Lidocaine, 11 gabapentin, 12 ketamine, 13 pregabalin, 14 acetaminophen, 15 as well as regional 16 and neuraxial 5 techniques have all been shown to decrease the incidence of PONV in colorectal surgery patients compared with opioid-based Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Use of a gabapentin-based, benzodiazepine-sparing protool began in early 2015 by the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry Service. Objective: A retrospective chart review was conducted to detect any safety concerns with use of a gabapentin protocol for alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin’s anxiolytic and sedative properties along with its overall safety profile suggest that it may be a viable adjuvant to lorazepam in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal. Objectives: Recent literature suggests that gabapentin may be an alternative treatment to standard management of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). CANINE PRE-EUTHANASIA SEDATION PROTOCOLS CALM PATIENT REACTIVE PATIENT 7-10 mg/kg TRAZODONE Preappointment ORAL sedation 10-40 mg/kg GABAPENTIN 50-150 mcg/kg PENTOBARBITAL In-clinic ORAL sedation 60 mg/kg DEXMEDETOMIDINE or DETOMIDINE OR + BLESSED SLEEP DOGGIE MAGIC ABK 0.22 mg/kg x 0.3 mg/kg ACEPROMAZINE 10 mg/ml 0.1 mg/kg 0.2-0.5 mg/kg 0.3 mg Use of a gabapentin-based, benzodiazepine-sparing protool began in early 2015 by the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry Service. A retrospective chart review was conducted to detect any safety concerns with use of a gabapentin protocol for alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Originally developed for opioids and adapted to benzodiazepines, the use of the Bravo Protocol provides a framework for a gabapentin taper. For patients in whom gabapentin treatment leads to severe dependence and withdrawal, the BRAVO Protocol provides a practical, patient-centered framework for tapering. A retrospective review of 50 patients who received at least 1800 mg per day of gabapentin in the first 48 hours of AWS compared with 50 propensity-matched patients who received benzodiazepines found that the gabapentin group required lower benzodiazepine doses and had a shorter LOS. 15 In contrast, 3 other retrospective studies16, 17, 18 used Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. No stairs, no jumping, no driving for cats on sedative doses of gabapentin. Gabapentin has analgesic effects in cats, and reducing pain may be one of the ways it helps reduce fear. Gabapentin is typically used prior to sedation/premedication protocols (see below). Gabapentin does not replace in-clinic sedation/premedication protocols. A retrospective review of 50 patients who received at least 1800 mg per day of gabapentin in the first 48 hours of AWS compared with 50 propensity-matched patients who received benzodiazepines found that the gabapentin group required lower benzodiazepine doses and had a shorter LOS. 15 In contrast, 3 other retrospective studies 16-18 used The strategy of postoperative minimization of opioid use reduces nausea and vomiting, impairment of bowel function, delayed mobilization, and pulmonary morbidity 54. Regimens designed to minimize postoperative opioid use also may include the use of scheduled acetaminophen, gabapentin, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |