Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
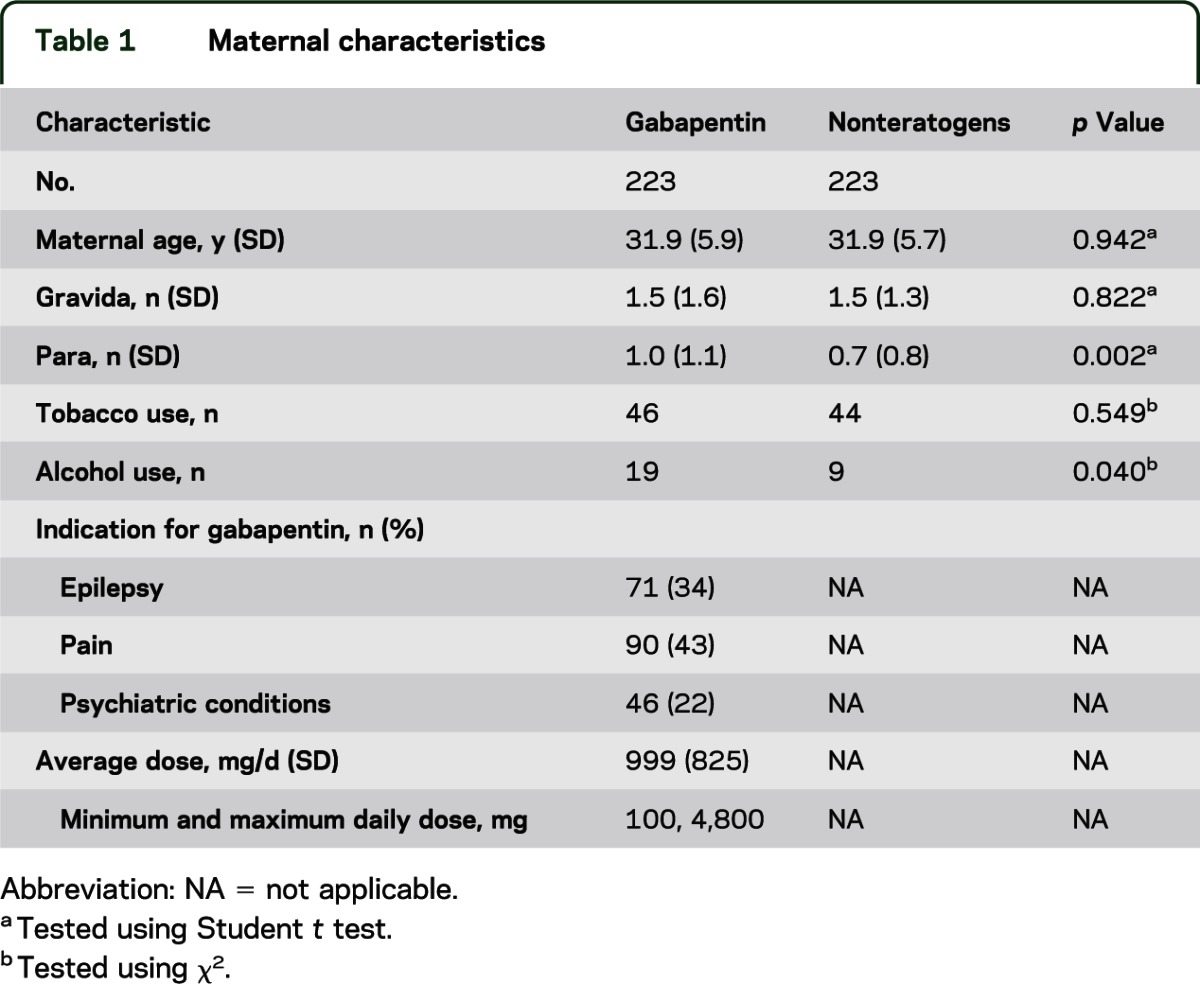
Our results add to the current understanding of the safety of gabapentin prenatal use and provide pregnant women with pain conditions and epilepsy and their providers with important information, which can guide clinical decisions during pregnancy. If you're trying to get pregnant or have become pregnant while taking gabapentin, it is recommended to take a high dose of folic acid (5mg a day). You can get this from your doctor or midwife. Ideally you'll take high dose folic acid for 3 months before you start trying to get pregnant and for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Maternal use of gabapentin, particularly late in pregnancy, was associated with a higher risk of PTB, SGA, and NICUa. While gabapentin (Neurontin) is now used in a wide variety of clinical settings — for epilepsy, pain management, restless leg syndrome, anxiety, and sleep disturbance – there is relatively little information regarding its reproductive safety. Most recently, a prospective study from researchers at the Motherisk program reports on the outcomes of 223 pregnancies exposed to gabapentin We have data on 223 pregnancy outcomes exposed to gabapentin and 223 unexposed pregnancies. The rates of major malformations were similar in both groups (p = 0.845). There was a higher rate of preterm births (p = 0.019) and low birth weight <2,500 g (p = 0.033) in the gabapentin group. This article summarizes the current literature regarding gabapentin use during pregnancy and related prenatal and neonatal exposure outcomes with special consideration for interactions between gabapentin and opioid use. Data on gabapentin use in pregnancy are mixed—some studies suggest it can result in increases in birth defects and other pregnancy complications, while other studies suggest it’s safe. Since decisions about gabapentin use in pregnancy are complex, it’s important to talk with your doctor about whether starting or continuing use is right Pregnancy-related problems, such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth) have been reported in some studies looking at the use of gabapentin during pregnancy. It is not known if gabapentin can make it harder to get pregnant. Sexual dysfunction (including loss of desire to have sex and loss of ability to have an orgasm) has been reported among women who take gabapentin. With maternal doses up to 2.1 g/day, estimated doses for fully breastfed infants are 0.2 to 1.3 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 1.3 to 3.8% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose). An expert panel has deemed this drug is an acceptable choice for refractory restless leg syndrome during lactation. Prenatal exposure to pregabalin is associated with an increased risk of congenital anomalies and long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes while gabapentin exposure was associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia, preterm birth and small-for-gestational age. Larger studies are needed to confirm these data and explore additional outcomes. Pregnancy-related problems, such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth) have been reported in some studies looking at the use of gabapentin during pregnancy. Despite the widespread use, only sparse information is available on the safety of gabapentin during pregnancy. We sought to evaluate the association between gabapentin exposure during pregnancy and risk of adverse neonatal and maternal outcomes. Gabapentin, a commonly prescribed medication for treating seizures and nerve pain, has recently raised concerns regarding its safety during pregnancy. Studies have shown a potential link between gabapentin use during pregnancy and an increased risk of certain birth defects. What are the risks? Is gabapentin dangerous in pregnancy? Because the risks of taking gabapentin while pregnant in humans are not fully understood, use of gabapentin during pregnancy is determined on a case-by-case basis to determine if the benefits outweigh the risks. Gabapentin is a pregnancy category C, which means risk cannot be ruled out. Gabapentin should only be used during pregnancy where benefits of treatment are considered to outweigh any potential risks. In view of the limited human pregnancy data, close monitoring of mother and fetus should be considered with use of gabapentin in pregnancy. use disorders. However, new empirical efforts are revealing concerns regarding the safety of widespread gabapentin use, particularly in pregnancy and for individuals with a propensity toward substance misuse. The Food and Drug Administration’s full prescribing information report on gabapentin provides concerning preclinical data and then states that gabapentin is potentially The last decade has seen a significant increase in gabapentin prescriptions among pregnant people, particularly for off-label use, despite limited evidence of its safety during pregnancy. 6-8 Despite the lack of reports on the teratogenicity of gabapentin, it has been associated with the potential risk of congenital malformations, including All pregnant women in the UK will be offered a very detailed anomaly scan at around 20 weeks of pregnancy as part of their routine antenatal care. No extra monitoring for major birth defects is required following gabapentin use in pregnancy. Babies exposed to gabapentin before delivery may experience withdrawal symptoms for a few days after birth.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |