Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
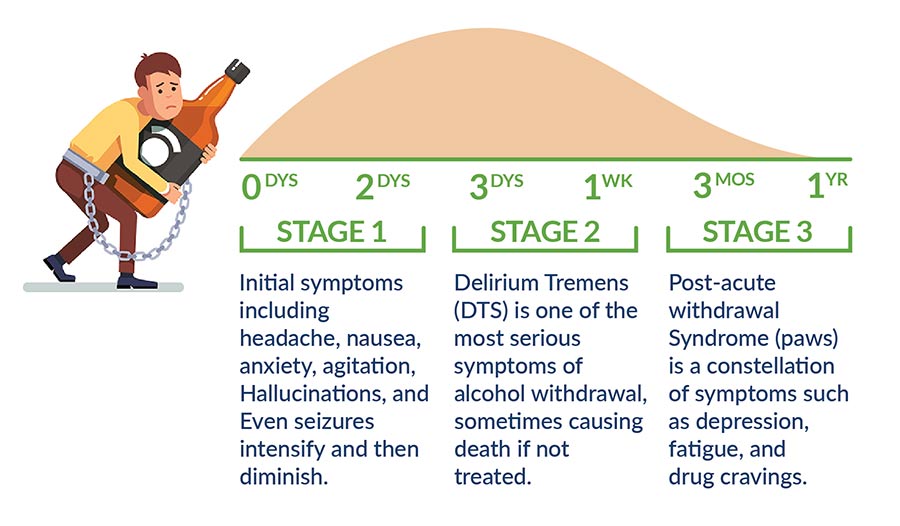 |  |
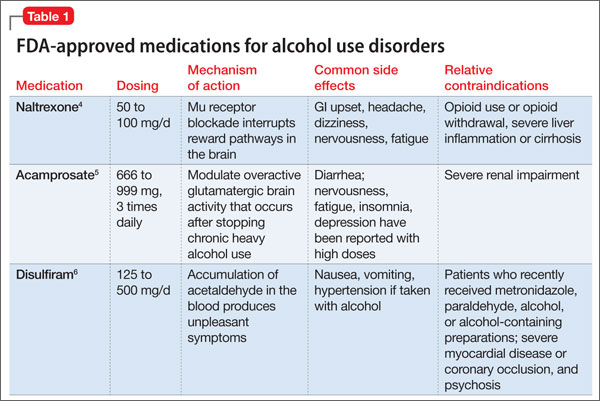
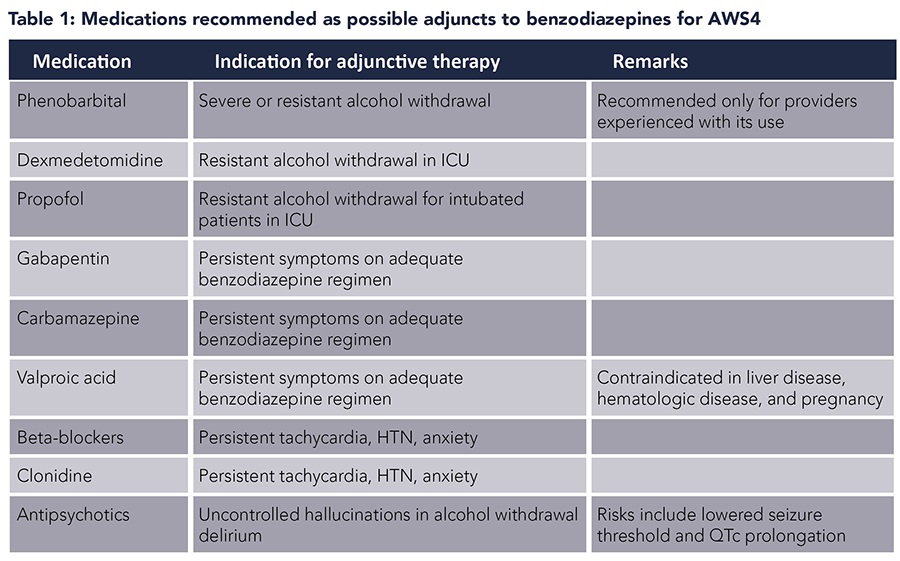
Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or naltrex Many of the same treatment services that work well for gabapentin addiction work just as well for alcohol withdrawal. These services include inpatient detox , the use of certain medications like benzodiazepines to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications like seizures, psychosocial support to address the psychological aspects of addiction Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine if gabapentin can effectively replace/reduce the use of benzodiazepines for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms in hospitalized patients. Time to alcohol withdrawal symptom resolution, amount of benzodiazepines administered, rate of resolution of alcohol Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and pain-relieving medication that has several off-label uses, including the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Learn more here. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) have been used to treat alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol withdrawal, but with inconsistent results. In this meta-analysis, we explored the effects of GBP/PGB treatment on AUD and their effects on withdrawal, craving, depression, and sleep disturbance in AUD patients. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demon-strated effi cacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line al- A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02349477. For instance, studies have highlighted the efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal symptoms (Mariani et al. 2006; Myrick et al. 2009). Additional trials found a benefit of combining gabapentin with naltrexone (Anton et al. 2011) and with flumazenil (Anton et al. 2009; Schacht et al. 2011). These studies consistently Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, Conclusions: Our analysis of pooled data provides evidence that the use of gabapentin to manage alcohol withdrawal symptomatology and related cravings is at least moderately effective. However, given the limited number of available well-designed studies, these findings require further support through more rigorously designed studies. Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4 Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or What is the duration of Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal? Gabapentin is typically used for the acute phase of alcohol withdrawal, often lasting from a few days to several weeks. The exact duration depends on the severity of the withdrawal symptoms and the individual’s response to the medication. treatment of choice for detoxifying patients and managing alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Non-benzodiazepine anticonvulsants (NBACs) are increasingly being used both for alcohol withdrawal management and for ongoing outpatient treatment of alcohol dependence, with the goal of either abstinence or harm reduction. Treatment with gabapentin may benefit alcohol withdrawal inpatients based on its use in Alcohol Use Disorder outpatients and mechanism of action. Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat hospitalized alcohol withdrawal syndrome patients, but are associated with several adverse drug events. Gabapentin is an outpatient antiepileptic medication used to treat alcohol use disorder (AUD). This medication is a structural analog of GABA that binds calcium channels to inhibit calcium influx and reduce the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (Sills, 2006, Mason et al., 2018).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |