Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 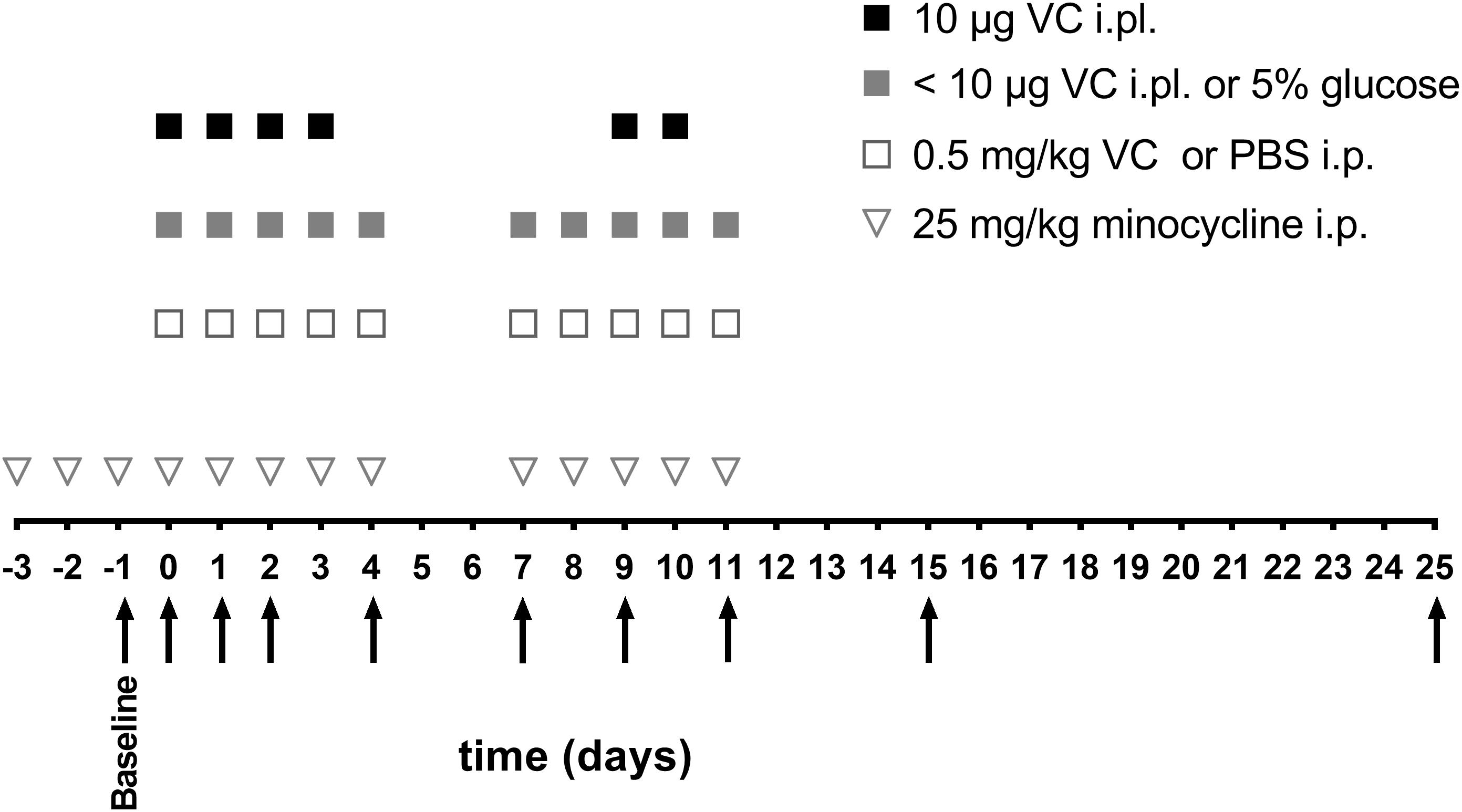 |
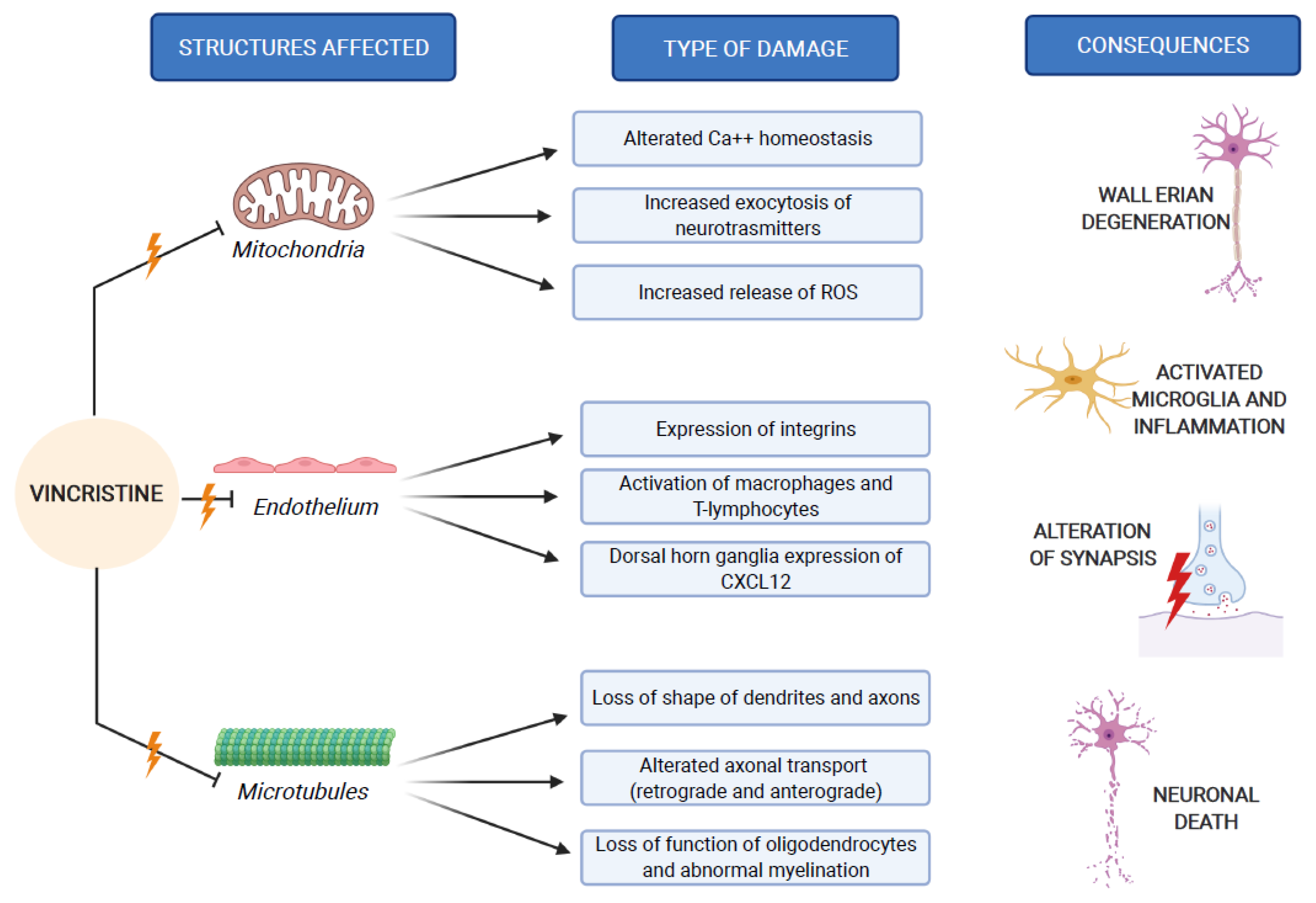
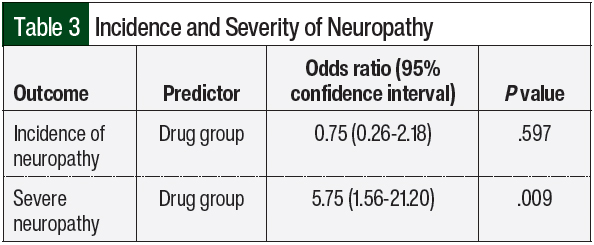
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common adverse effect of cancer therapy that can have a profound impact on quality of life and survivorship [1]. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Vincristine-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (VIPN) is a very common side effect of vincristine chemotherapy among pediatric patients with cancer. Neuropathy may be sensory, motor and/or autonomic, with consequent reduction, delay or discontinuation of vincristine-chemotherapy, but also pain, disabi Vincristine (VCR), an alkaloid extracted from vinca, is often used in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs to treat a variety of cancers, such as acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), malignant lymphoma, and neuroblastoma. However, VCR possesses dose-dependent neurotoxicity, which is the mai Vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy (VIPN) is particularly challenging to detect and monitor in pediatric patients, in whom the side effect can diminish long term quality of life. This review There is a lack of consensus about the prophylaxis and treatment of VIPN among pediatric oncologic patients, despite several molecules (such as gabapentin, pyridoxine and pyridostigmine, glutamic acid and glutamine) having been already investigated in clinical trials. A powerful analgesic effect of both gabapentin and pregabalin on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel and oxaliplation has been reported. However, gabapentin did not affect vinctistine-induced allodynia [51, 52]. To evaluate the clinical efficacy of gabapentin, 115 patients with symptomatic CIPN were randomly selected to receive Patients experiencing peripheral neuropathy due to vincristine may experience pain, tingling, numbness, and reduced sensation in the hands and feet. Management of peripheral neuropathy In this population of children with vincristine-related neuropathic pain, opioid consumption and pain scores were higher in the gabapentin group than in the placebo group. Future randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies should test gabapentin given longer or at a higher dose. Children aged 1-18 years who developed vincristine-induced neuropathy on a St Jude frontline acute lymphoblastic leukemia trial were prospectively enrolled on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial with two treatment arms: gabapentin plus opioid versus placebo plus opioid. Gabapentin (20 mg/kg/day) increased the pain scores and opioid consumption in pediatric patients with vincristine-induced neuropathy . Treatment with pregabalin (75 mg) twice daily showed a trend to reduce numbness, but not any other paclitaxel-induced neuropathy symptoms [ 71 ]. The potentiating interaction between vincristine and posaconazole was witnessed in our patient's case during an overlap of therapy in which the patient experienced significant constipation, peripheral neuropathy, and jaw pain. Vincristine follows a triphasic serum decay pattern after intravenous injection, with initial, middle, and terminal In this study, paclitaxel and oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia was responsive to oral doses of gabapentin, whereas vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy was not , possibly explaining the results seen in the randomized controlled trial in humans. gabapentin in the treatment of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in children with ALL reported a higher opioid consump-tion and pain scores in the gabapentin group compared to the placebo group [14]. Although the failure of the analgesic ben-efit of gabapentin may be multifactorial, the authors reported Vincristine (VCR) induces peripheral neuropathy. We aimed to assess the efficacy of modafinil on VCR-induced neuropathy in rats. Neuropathy was induced by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of VCR (0.1 mg/kg). Neuropathic groups received modafinil (5, 25 and 50 mg/kg); gabapentin (20 mg/kg); and a co Vincristine-induced neuropathy (VIN) spans a broad spectrum of dysfunctions that fall into three categories: sensory, motor, and autonomic neuropathy (Table 1). The most common is peripheral sensory and motor nerve neuropathy characterized by numbness, paresthesia, impaired balance, weakened tendon reflexes, and altered gait [9]. VCR: vincristine, VIPN: Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy, ALL: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, CTCAE: national cancer institute Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events, FLACC: Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability scale, NPS: Neuropathic Pain Scale, CCG: Children’s Cancer Group, DFCI: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, NCI CTC Children aged 1 to 18 years who developed vincristine-induced neuropathy on a St. Jude frontline acute lymphoblastic leukemia trial were prospectively enrolled on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial with two treatment arms: gabapentin plus opioid versus placebo plus opioid. Vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy (VIPN) not only limits the dose of VCR and leads to the discontinuation of treatment but also triggers serious damage to the physical and mental health of patients. With the initiation of neuropathy, gabapentin was given at 100 mg twice per day. Clinicians could increase gabapentin to 100 mg 3 times daily if the lower daily dose did not resolve symptoms. The abstract reported there was a disappearance of neuropathy symptoms, which continued even with the use of up to 14 total oxaliplatin doses.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |