Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
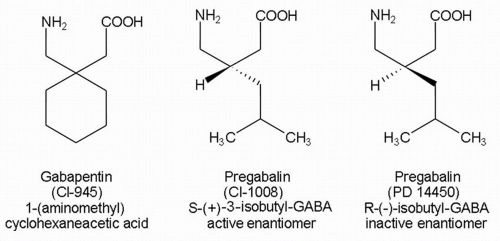
Several studies reviewing conversion of gabapentin to pregabalin predict that a rough ratio for conversion is about 6:1 gabapentin to pregabalin. In addition, a direct switch from gabapentin to pregabalin seems to be well tolerated, making the conversion simple. In this context, the objective of this meta-analysis is to evaluate and compare pregabalin vs. gabapentin in terms of efficacy and safety in the treatment of neuropathic pain, aiming to provide a solid foundation for clinical decision-making and improve the management of this condition in medical practice. 2. Methods 2.1. Eligibility criteria No, combining Gabapentin and Pregabalin is not recommended as it can exaggerate side effects like drowsiness and dizziness and raise the risk of falls or accidents. It can also cause breathing problems in individuals [4]. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both antiepileptic medications used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but they have some differences. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic and is typically taken three times a day, while pregabalin is also available as a generic but is usually taken two or three times a day. Gabapentin: Dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, peripheral edema, and weight gain. Pregabalin: Similar side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, and potential for weight gain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Pregabalin is used in the treatment of nerve pain and also to prevent seizures. Yes, Lyrica (pregabalin) can cause extreme drowsiness (somnolence) and may affect your ability to drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities. This may lead to an injury or fall. In studies, up to 20% of children and 35% of adults experienced drowsiness as a side effect. Gabapentin vs Pregabalin. Gabapentin was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 for treating seizures. Side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and coordination problems. Pregabalin was first approved by the FDA in 2004 for treating neuropathic pain and seizures. Both Pregabalin and Gabapentin can help with sleep by reducing pain and anxiety, but pregabalin is generally faster-acting and may be more effective for improving sleep quality. However, gabapentin may be preferred in some cases due to its milder side effect profile. The results of the meta-analysis showed that the PGIC score for pain in patients taking pregabalin and gabapentin was significantly improved compared with the placebo group, with the RR of the pregabalin group being 0.44 (95% CI 0.33–0.56, P < 0.05), as shown in Fig. 4A, and that of the gabapentin group being 0.18 (95% CI 0.12–0.23, P < 0. Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Gabapentin is not federally controlled, but some states have begun monitoring its use due to rising misuse cases. Side Effects and Risks. Both gabapentin and Lyrica come with side effects. The severity and likelihood depend on the person, their dosage, and any underlying health conditions. Common Side Effects of Gabapentin. Drowsiness 6. Houghton, K. T., et al. (2017). Comparing the efficacy of pregabalin and gabapentin for neuropathic pain in adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Pain Research, 10, 2767-2776. 7. Bockbrader, H. N., et al. (2010). A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are generally well-tolerated, with the most common side effects being drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, dry mouth and swelling (edema). However, there may be some slight differences in their adverse events profiles. How Do These Drugs Work? Lyrica vs Gabapentin. Lyrica is the brand name for the drug pregabalin, and gabapentin is the name of the medication that is used in drugs such as Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. All of these drugs are prescribed as anticonvulsant or antiepileptic medications. There is also a positive impact of gabapentin on sleep (P = 0.002) compared with pregabalin (P = 0.003). This may be attributed to the most frequently reported adverse effect, sedation due to gabapentin. Evaluation of 5-D itch scale before after drug therapy for gabapentin and pregabalin is given in [Tables 1 and 2]. When comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin, they work in similar ways but pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and fully. Common side effects of both medications include dizziness, drowsiness, and fluid buildup. * Both Lyrica and gabapentin can cause dizziness and sleepiness. Be careful with any tasks that require concentration or focus, such as driving, until you become used to the effects of Lyrica (pregabalin) is both chemically and structurally similar to gabapentin. It does however, have a unique way of being absorbed and has much better bioavailability than gabapentin does. Lyrica is almost totally absorbed (~90%) very quickly after taking by mouth. Differences Between Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both anticonvulsants used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but they have key differences in potency, absorption, and usage. Potency and Effectiveness. Pregabalin binds more strongly to calcium channels, making it more potent and requiring lower doses for the same effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |