Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
+and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
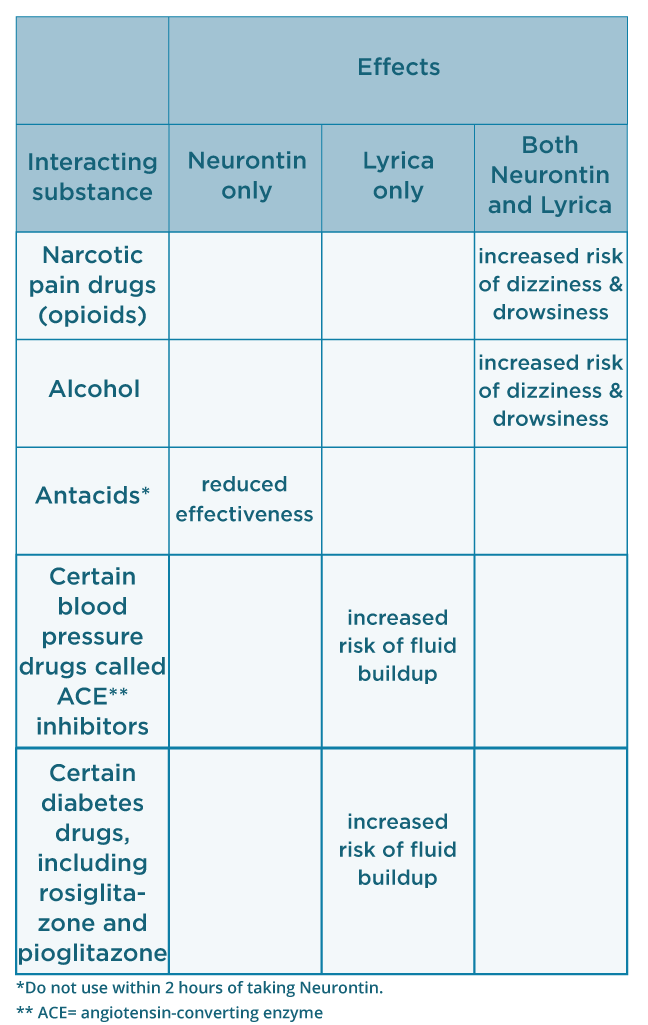
It was suggested that the analgesic action of pregabalin in PHN was six times that of gabapentin in terms of effectiveness in dosage conversion. Regarding the side effects, although the incidence of the peripheral edema was higher with pregabalin compared with gabapentin, this finding is not conclus Gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs commonly used for neuropathic pain management and pain reduction in adults. Both medications are classified as antiepileptic medications, but they have differences in pharmacokinetics, safety profile, and clinical applications. Peripheral edema in a 76-year-old woman taking pregabalin for neuropathic pain. Pregabalin is used to treat neuropathic pain. The drug’s likely mechanism of action is binding to the α 2 δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels in presynaptic neurons, thereby reducing the release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. Everything considered, standard Lyrica capsules are cheaper than standard Neurontin capsules/tablets at moderate-to-high doses (e.g. 300 mg/day of Lyrica vs. 1800 mg/day Neurontin) – whereas standard Neurontin capsules/tablets are cheaper than standard Lyrica capsules at low doses (100 mg/day of We hypothesize that there is an increased risk of heart failure or edema in individuals receiving pregabalin compared to placebo or gabapentin. To investigate this further, we will conduct a systematic review of pregabalin across all available studies. Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. Gabapentinoids can cause concentration-dependent peripheral edema of early onset. The primary mechanism of non-cardiogenic peripheral edema is vasodilatory edema secondary to altered myogenic tone, independent of Ca<sub>v</sub>1.2 blockade under the experimental conditions tested. When comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin, pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and more fully by the body. Pregabalin is a controlled substance in every state, while gabapentin is controlled only in some states. Both medications have common side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and edema. But pregabalin is more likely to cause weight gain. Pregabalin Vs Gabapentin For Anxiety. Pregabalin and gabapentin are sometimes used off-label to manage anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Both drugs work by altering the activity of neurotransmitters to reduce neural excitability and lower anxiety symptoms. This is not the case however. Gabapentin is the generic of a different medication, Neurontin. Nevertheless, the chemical structures of Lyrica and gabapentin are nearly identical to one another. The main difference between the two medications is that Lyrica is more potent, and lasts longer per dose than gabapentin. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin and pregabalin, are both indicated in partial seizure and neuropathic pain. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also approved pregabalin for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder and fibromyalgia, respectively. Dizziness, headaches, sleepiness, and edema (fluid retention) References for Gabapentin vs Pregabalin. Siler AC, et al. J Pain 12(4):407-415, 2011. Free Report; Pooled risk ratio (RR) of pregabalin (PGB) vs. gabapentin (GBP) for adverse events (AEs). There was no significant difference between two drugs for AEs. CI: confidence interval, df: degree of freedom. PGB vs. placebo: Drowsiness, dizziness, edema, and peripheral edema were the most common AEs in the selected studies [41,43,44]. Unlike pregabalin, gabapentin is not scheduled as a controlled substance. Gabapentin is not associated with peripheral edema 9 . Gabapentin is more effective in controlling pain in patients with painful bladder syndrome 14 . All cases of peripheral edema or HF involving gabapentin or pregabalin were reported to the French Pharmacovigilance Centers between January 1, 1994 and April 30, 2020 [4]. A total of 58 reports were included (gabapentin n = 5, pregabalin n = 53). In this context, the objective of this meta-analysis is to evaluate and compare pregabalin vs. gabapentin in terms of efficacy and safety in the treatment of neuropathic pain, aiming to provide a solid foundation for clinical decision-making and improve the management of this condition in medical practice. 2. Methods 2.1. Eligibility criteria Gabapentin increased the risk of HF by 14% over a 5-year period compared to not using gabapentin, and pregabalin increased such risk by 20% (Table 1). Table 1. All cases of peripheral edema or HF involving gabapentin or pregabalin were reported to the French Pharmacovigilance Centers between January 1, 1994 and April 30, 2020 [4]. In 2008, after the decompression surgery, the patient was given pregabalin (titrated to 300 mg, twice daily) for ongoing neuropathic pain. Increasing peripheral edema in the patient’s legs was documented from that time on. In 2011, chronic wounds with serous drainage developed on the patient’s legs. Dizziness and somnolence are the most common side effects in both drugs (>20% seen in gabapentin). 3-5 Confusion and peripheral edema have also been reported with gabapentin. 4
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
+and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |