Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 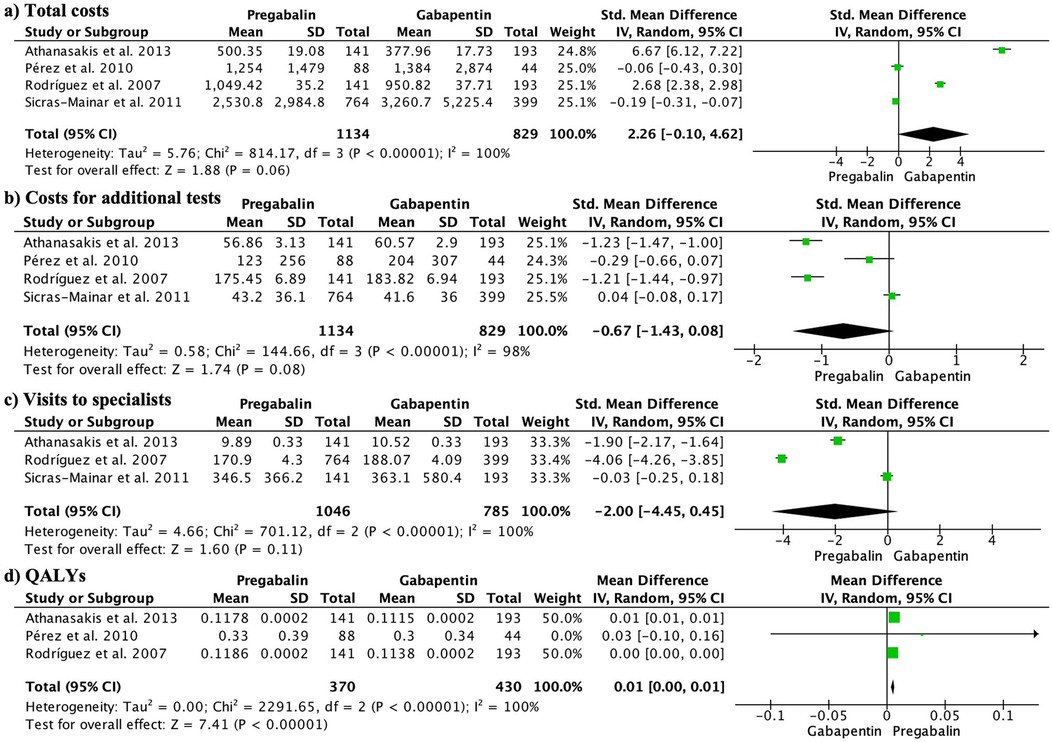 |
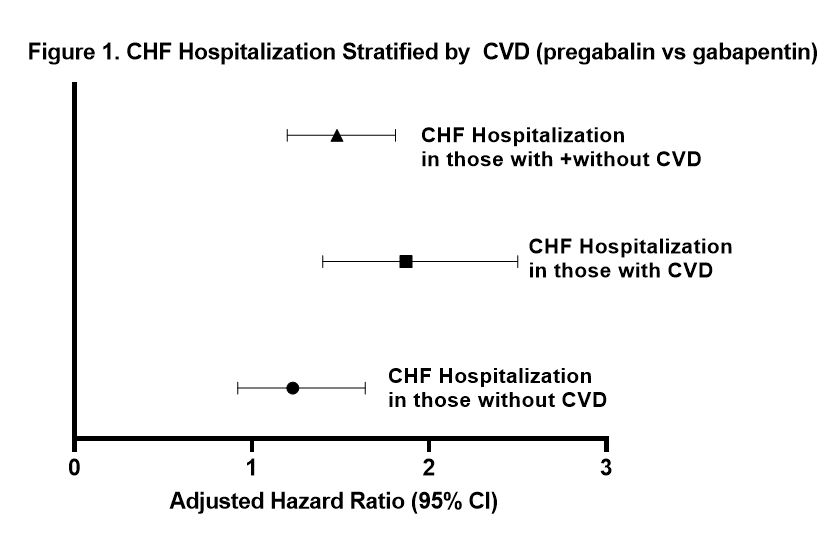
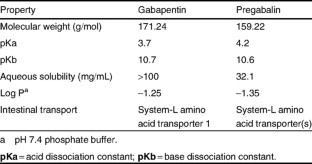
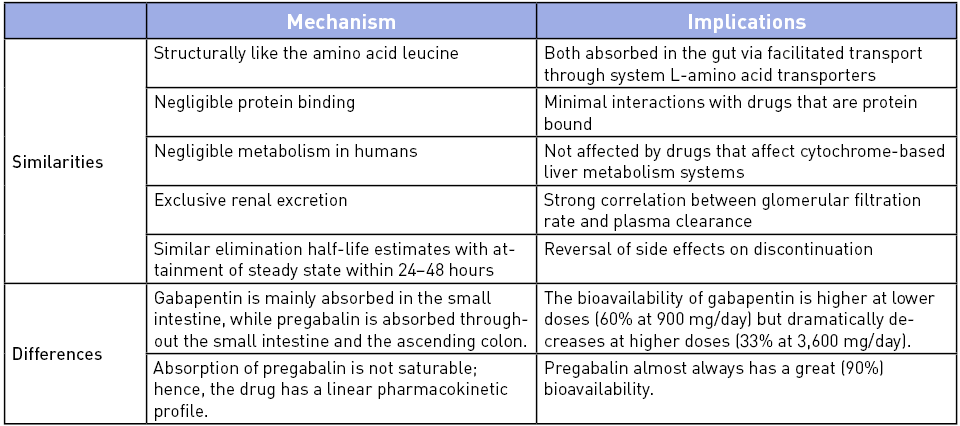
Gabapentin and pregabalin are analogs of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and share a similar mechanism of action, although they differ in some aspects. Both drugs bind to the α2δ subunit of calcium channels in neurons, but pregabalin exhibits greater affinity and potency in its binding (5, 6). Pregabalin Vs Gabapentin For Anxiety. Pregabalin and gabapentin are sometimes used off-label to manage anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Both drugs work by altering the activity of neurotransmitters to reduce neural excitability and lower anxiety symptoms. Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. Nonetheless, because standard pregabalin doses are more potent than standard gabapentin doses for similar medical conditions like postherpetic neuralgia (e.g. pregabalin 300 mg/day vs. gabapentin 900 mg/day – making the former dose approximately double as potent as the latter), it’s reasonable to expect that pregabalin users might From the minimal head-to-head studies we have, Lyrica (although potentially more expensive) does show stronger binding to receptors, leading to increased potency, and a better response for neuropathic pain than gabapentin. Lyrica potentially has fewer side effects than gabapentin and may be better tolerated as well. Pregabalin exhibits a six-fold higher binding affinity for the α2δ-1 calcium channel subunit compared to gabapentin. 10,13 The increased binding affinity explains the greater potency and subsequent analgesic effect of pregabalin. 10 These pharmacodynamic and aforementioned pharmacokinetic characteristics of pregabalin translate into clinical ben First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology. Introduction. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The Pregabalin has a more favorable side effect profile, faster onset of action, and greater potency than gabapentin. However, gabapentin has been associated with a higher risk of respiratory depression and withdrawal symptoms. Results of comparison of analgesic benefits of gabapentin vs pregabalin for postoperative analgesia 7: Keyhanfar F. Relative potency of pregabalin, gabapentin When comparing pregabalin and gabapentin, potency is one major factor to look into, especially in treating pain and seizure disorders. The main difference between these two medications is that pregabalin tends to show more strength and effectiveness than the gabapentin. This can be because of the rate at which pregabalin is absorbed by the body. Gabapentin is more slowly and variably absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations around 3 hours post-dose. Pregabalin is quickly absorbed, with the maximum rate of absorption being 3 times that of gabapentin. It reaches peak blood concentrations within an hour after ingestion. Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Pregabalin and gabapentin are members of a unique class of compounds characterized by high affinity binding to the alpha-2-delta (α2δ) protein in the CNS. Both have been shown to be effective as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures and neuropathic pain disorders. Clinical pharmacology studies conducted to characterize the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and drug-drug interaction Main Differences Between Gabapentin and Pregabalin. The binding affinity and potency of gabapentin and pregabalin differ. Gabapentin has a weaker sensitivity to the alpha-2-delta enzyme when compared to pregabalin, and hence pregabalin provides more significant relief from acute nerve pain. Gabapentin outperforms pregabalin in reducing leg pain Though gabapentin and pregabalin share a similar mechanism of action, pregabalin’s higher bioavailability and faster absorption may account for its perceived potency in managing symptoms more quickly than gabapentin. Gabapentin vs. Pregabalin for Anxiety Disorders 150 mg Lyrica (pregabalin) and gabapentin are widely prescribed medications that share similarities in treating nerve-related conditions, but they differ in potency and pharmacodynamics. Patients switching between these medications often need clarity on equivalent dosing to ensure effective symptom management without adverse effects. One of the primary differences between pregabalin and gabapentin is their relative potency and the corresponding dosing requirements. Pregabalin is generally considered to be more potent than gabapentin, binding to calcium channels in the central nervous system (CNS) with greater strength. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. Pregabalin has been found to have distinct pharmacokinetic advantages over gabapentin. 3 . Pregabalin has shown greater potency than gabapentin in pain and seizure disorders. 6 J. Fehrenbacher et al stated that pregabalin has been shown to have greater analgesic activity in rodent models of neuropathic pain. 2 Further, D. Wesche et al noted
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |