Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 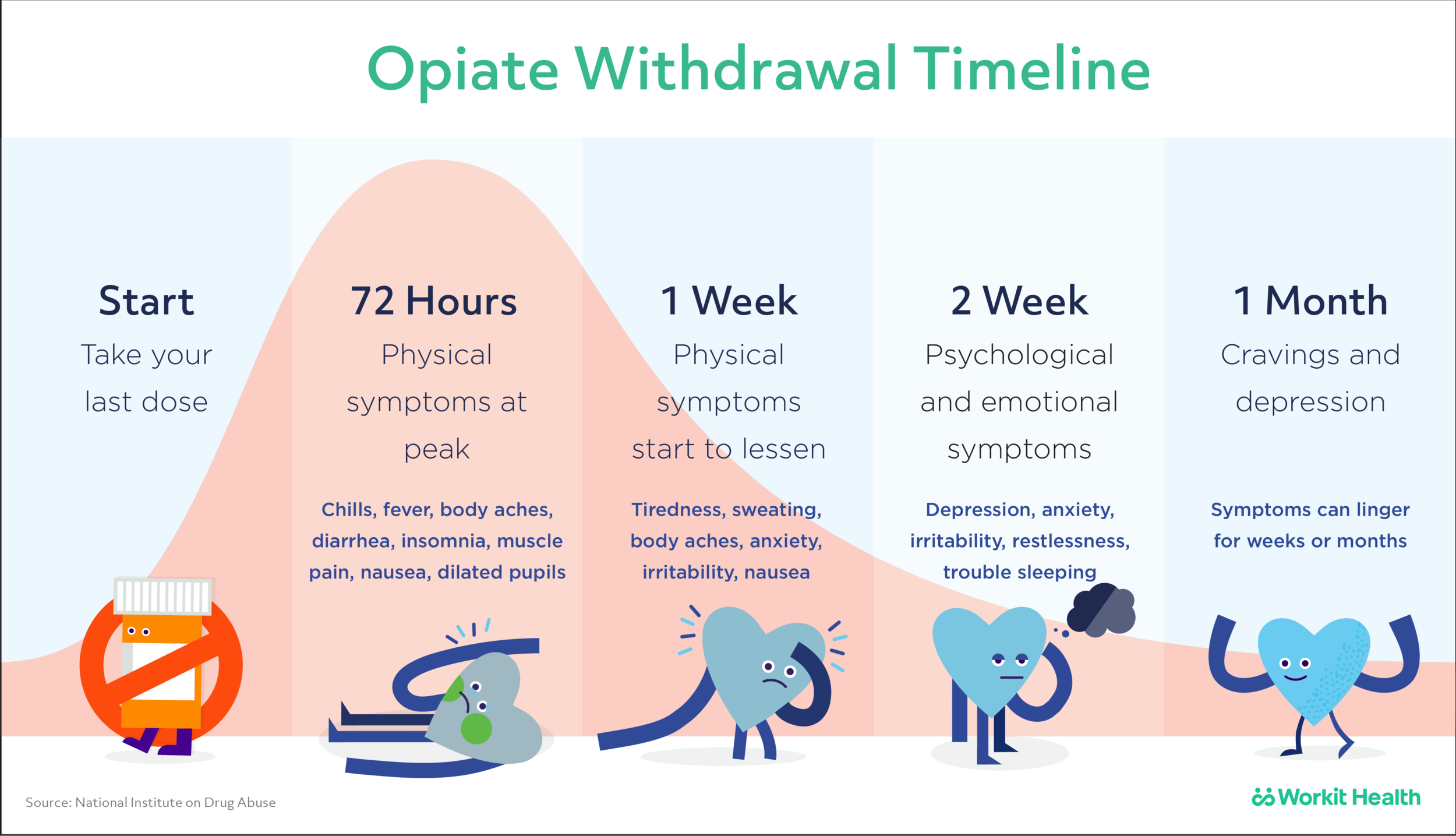 |
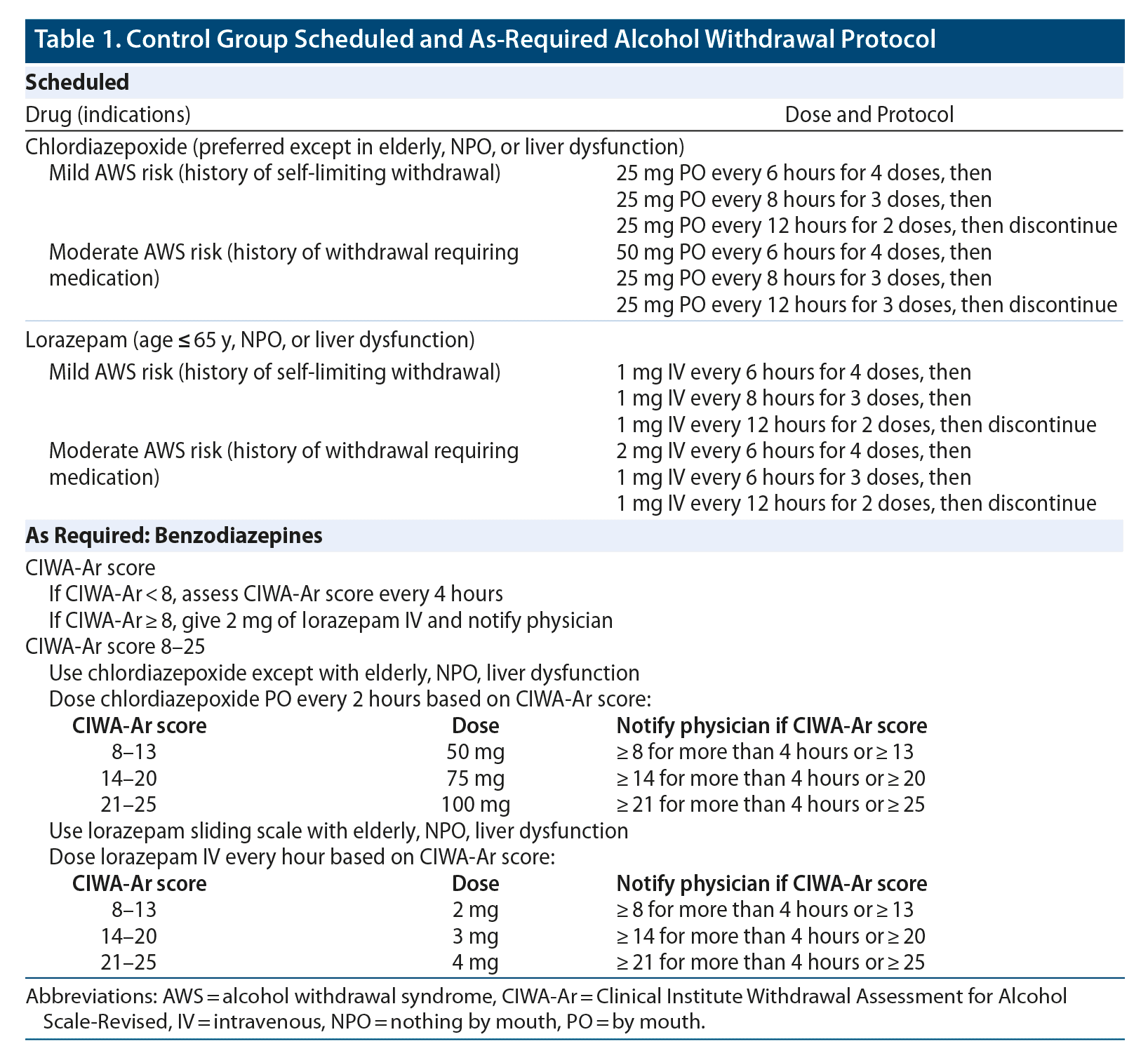
Gabapentin and pregabalin are the safest, but contraindicated if severe renal insufficiency is present. In detail, gabapentin is a structural analogue of GABA, and it has been approved for adjunctive treatment of patients (12 years or older) with partial seizures and mixed seizure disorders and refractory partial seizures especially in children. ing gabapentin (Neurontin) after 3 days of abstinence had fewer heavy drinking days (defined as 5 or more drinks for men and 4 or more drinks for women) and greater rates of Secondary objectives included identifying the number of patients requiring antipsychotics (Step 3), the gabapentin regimen, comparison of Échelle de Douleur et d'Inconfort du Nouveau-né (EDIN), Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium (CAPD), and Withdrawal Assessment Tool-1 (WAT-1) scores 72 hours pre- and post-gabapentin initiation, and This unusual case of gabapentin dependence and abuse involved toxic delirium, intense cravings, and a prolonged post-withdrawal confusional state reminiscent of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin is a central nervous system inhibitory agent with likely gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic and non-GABAergic mechanisms of action. More and more evidence has questioned the ability of gabapentin to reduce postoperative delirium, our study found that although the risk of delirium was not demonstrated in model 4, an increased risk of delirium was found in models 1, 2, and 3, and it can also provide evidence support for future research. Gabapentin abuse, and delirium tremens upon gabapentin withdrawal J Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Mar;68(3):483-4. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n0320a. Authors Christopher Common treatable causes of delirium, most often: [1] Medication/substance withdrawal: Review alcohol use and home medications. Consider resumption of home psychiatric medications, especially if these may cause withdrawal (e.g., gabapentin, baclofen). [2] Wernicke encephalopathy: If this is possible, give empiric thiamine 500 mg IV q8hr. %PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 112 0 obj > endobj xref 112 123 0000000016 00000 n 0000003281 00000 n 0000003486 00000 n 0000003527 00000 n 0000003562 00000 n 0000004020 00000 n 0000004126 00000 n 0000004241 00000 n 0000004349 00000 n 0000004463 00000 n 0000004571 00000 n 0000004686 00000 n 0000004791 00000 n 0000004906 00000 n 0000005013 00000 n 0000005128 00000 n 0000005235 00000 n 0000005350 00000 n Guiding diagnostic clues include recognizing the timing of symptom onset, ruling out other possible causes, and reviewing outpatient medications. Here we present a case of psychotic symptoms associated with a delirium, possibly due to gabapentin withdrawal. The case described here involved a 38-year-old male physician with substance intoxication delirium and psychoactive substance dependence due to high self-administered doses of gabapentin, which had been prescribed at lower doses in combination with buspirone and bupropion for depression and anxiety. This unusual case of gabapentin dependence and abuse involved toxic delirium, intense cravings, and a prolonged post-withdrawal confusional state reminiscent of ben-zodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin is a central nervous system inhibitory agent with likely gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic and non-GABAergic mechanisms of action. How addictive are gabapentin and pregabalin? A systematic review . European Neuropsychopharmacology, Vol. 27, Issue. 12, p. If you or someone you love is experiencing serious signs of gabapentin withdrawal, such as confusion or delirium, do not hesitate to seek emergency medical attention. If you are planning to stop taking gabapentin, you will want to make an appointment with your prescribing doctor or a primary care doctor who can help see you through the tapering It is especially important to recognize gabapentin withdrawal in critically ill patients because its symptoms overlap with common ICU syndromes such as ICU delirium, severe sepsis, drug reactions, pain, stroke, or serotonin syndrome. Delirium after gabapentin withdrawal. Case report Can J Neurol Sci. 2013 Jan;40(1):126-7. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100017418. Authors Roberto Di Withdrawal symptoms from gabapentin can appear anywhere from 12 hours to seven days after discontinuation of this anticonvulsant medication. 5 A clear withdrawal timeline for gabapentin hasn’t yet been documented, but reports have indicated that symptoms may gradually worsen over a 10-day period. 7 Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. Alcohol withdrawal delirium (delirium tremens): agitation, diaphoresis, disorientation, hallucinations (predominantly visual), hypertension, low-grade fever, tachycardia are appropriate The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Withdrawal symptoms have occurred even in patients prescribed normal doses of gabapentin for a short period of time (as little as 3 weeks). 14 The onset of withdrawal symptoms can be as early as 12 hours or may take as long as seven days. 15 Case reports of patients taking gabapentin and tapering off or stopping the medication abruptly describe
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |