Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
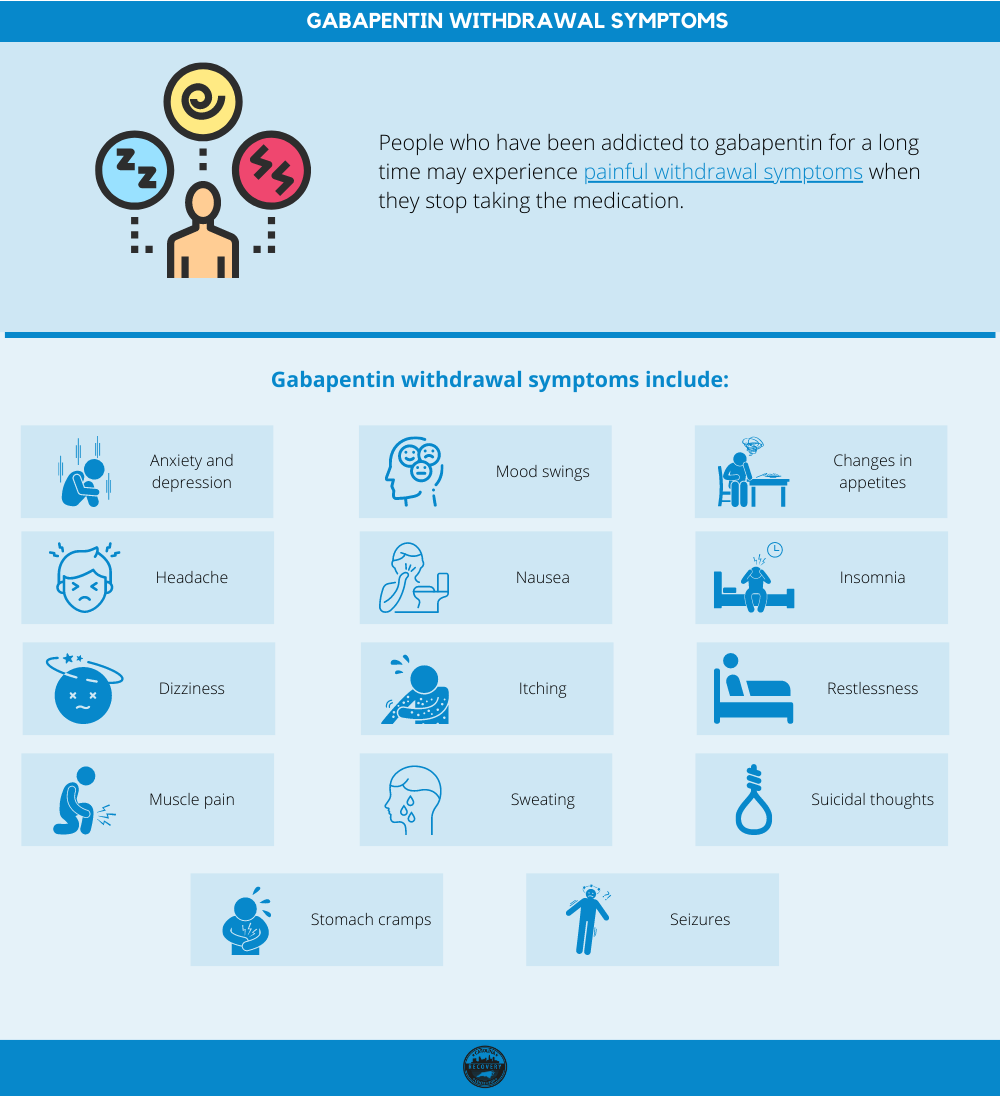
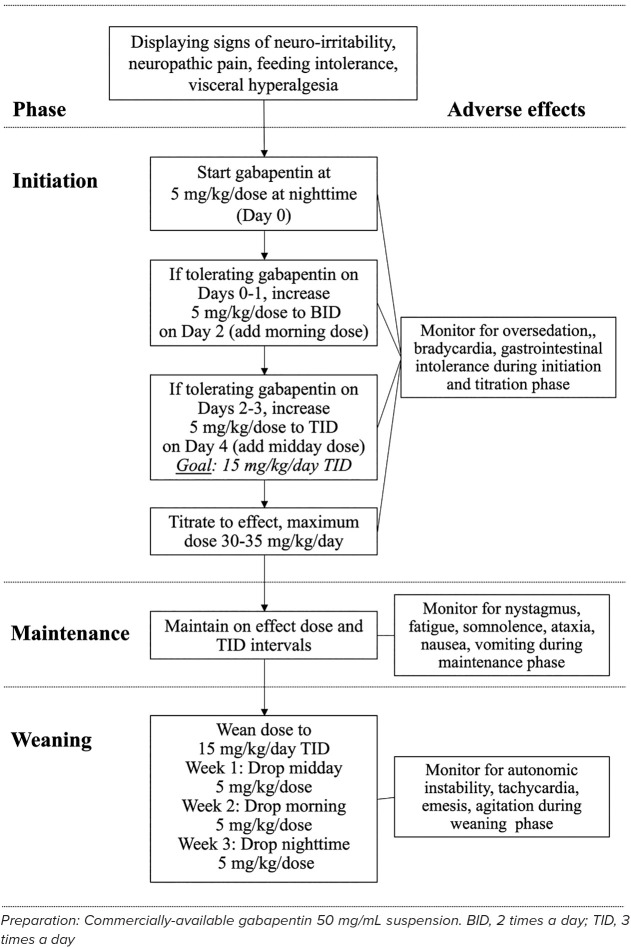
Will it cause withdrawal symptoms in my baby after birth? Studies have not been done to see if gabapentin use alone can cause withdrawal in a newborn. One study found that when gabapentin is combined with opioids late in pregnancy, withdrawal can occur. %PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 112 0 obj > endobj xref 112 123 0000000016 00000 n 0000003281 00000 n 0000003486 00000 n 0000003527 00000 n 0000003562 00000 n 0000004020 00000 n 0000004126 00000 n 0000004241 00000 n 0000004349 00000 n 0000004463 00000 n 0000004571 00000 n 0000004686 00000 n 0000004791 00000 n 0000004906 00000 n 0000005013 00000 n 0000005128 00000 n 0000005235 00000 n 0000005350 00000 n Similar to most of the published studies with gabapentin in neonates and infants, no patients in our study were noted to have withdrawal symptoms after gabapentin discontinuation. Edwards et al 7 noted 3 children with withdrawal attributed to gabapentin including tachycardia, emesis, and irritability upon abrupt discontinuation. Infant #9 received intermittent lorazepam for persistent agitation, which caused him to be sleepy and not participate in oral feedings. Within 24 hours of initiating gabapentin, the infant no longer required lorazepam, and he was noted to have improved sleep at night and participated more consistently in oral feeding. Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) is a postnatal drug withdrawal syndrome that primarily occurs after in utero exposure to opioids. In the US, it is estimated that 1 infant is born every 25 minutes with NAS, representing $1.5 billion in additional hospital charges. 1,2 NAS is increasing in frequency and can represent as many as 50% of admissions to some neonatal intensive care units. 3 Request PDF | Neonatal Gabapentin Withdrawal Syndrome | Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, neuroleptic, and pain medication, is widely used in both adults and children for management of epilepsy Gabapentin was well tolerated in infants. Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin. Keywords: gabapentin, infants, irritability, neonates, pain, visceral hyperalgesia. OBJECTIVE: Although gabapentin use is deemed safe during pregnancy, no clinical reports of gabapentin withdrawal syndrome in a neonate have been described. RESULTS: We present a newborn who showed signs of withdrawal after prolonged in utero exposure to gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant, neuroleptic, and pain medication frequently used in adults and children with epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and neurological impairment. 2 Of note, there is no literature available on withdrawal symptoms in infants of gabapentin treated mothers, nor has the treatment of a newborn with signs of drug withdrawal from Figure Neonatal abstinence scores were monitored using the Finnegan scoring system in the neonatal intensive care unit starting at 24 hours of life. Gabapentin treatment was initiated at approximately 124 hours of life (day of life 6) and the gabapentin dose was further escalated within the next 24 hours, as depicted by black arrows. Emerging concern exists regarding possible neonatal gabapentin withdrawal 31 after several studies contend a possibility of fetal retention following maternal exposure. 32–34 Huybrechts et al. 35 reported in utero co-exposure to opioids and gabapentin was associated with both an increased risk of neonatal withdrawal and more severe withdrawal We report a retrospective case series of 19 infants exposed to both opioids and gabapentin prenatally. We describe a unique behavioral phenotype in 15 of these infants and report a treatment strategy. Emerging concern exists regarding possible neonatal gabapentin withdrawal 31 after several studies contend a possibility of fetal retention following maternal exposure. 32-34 Huybrechts et al. 35 reported that in utero co-exposure to opioids and gabapentin was associated with both an increased risk of neonatal withdrawal and more severe Larger randomized controlled trials are needed to determine what role gabapentin may serve in neonatal withdrawal, particularly in infants with poor oral feeding and those exposed to concomitant psychoactive medications. I need to take gabapentin throughout my entire pregnancy. Will it cause withdrawal symptoms in my baby after birth? Studies have not been done to see if gabapentin use alone can cause withdrawal in a newborn. One study found that when gabapentin is combined with opioids late in pregnancy, withdrawal can occur. Results: We present a newborn who showed signs of withdrawal after prolonged in utero exposure to gabapentin. Clinical implications: Clinicians should be aware of possible withdrawal symptoms from drugs such as gabapentin, administered to mothers during pregnancy. There is one case study in which an infant was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit because she was born in gabapentin withdrawal. If you are pregnant, talk to your obstetrician about the safety of gabapentin and the possibility of tapering down before your baby is born. We present a newborn who showed signs of withdrawal after prolonged in utero exposure to gabapentin. Clinicians should be aware of possible withdrawal symptoms from drugs such as gabapentin, administered to mothers during pregnancy. We present a newborn who showed signs of withdrawal after prolonged in utero exposure to gabapentin. Clinicians should be aware of possible withdrawal symptoms from drugs such as gabapentin, administered to mothers during pregnancy. Results The absolute risk for neonatal drug withdrawal ranged from 1.0% in infants exposed in utero to prescription opioids alone to 11.4% for those exposed to opioids co-prescribed with gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |