Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
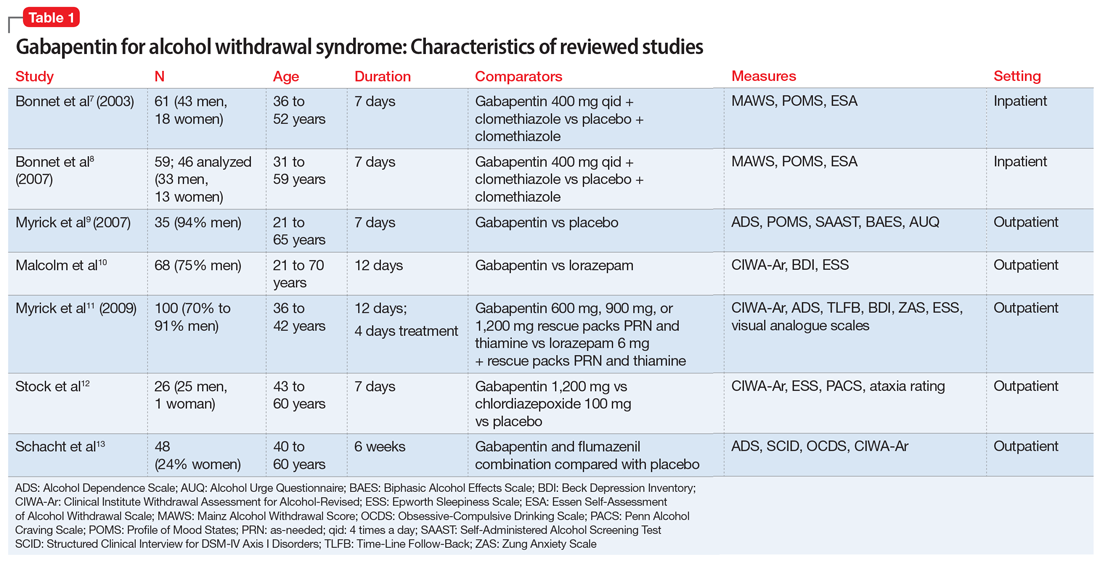
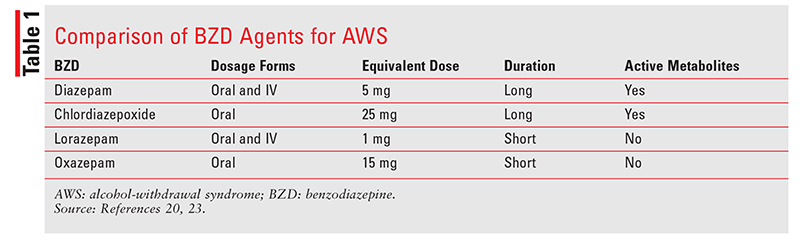
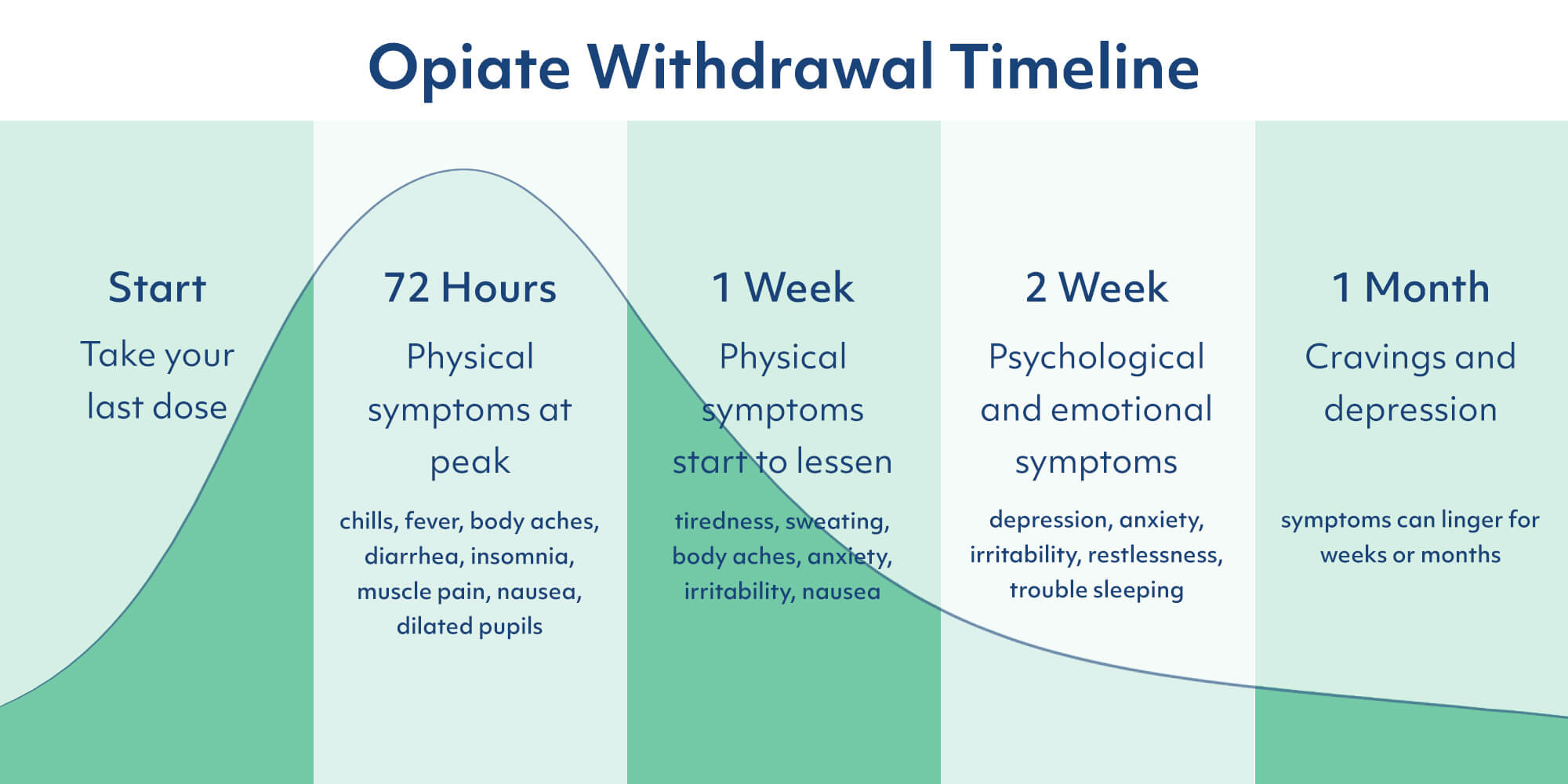
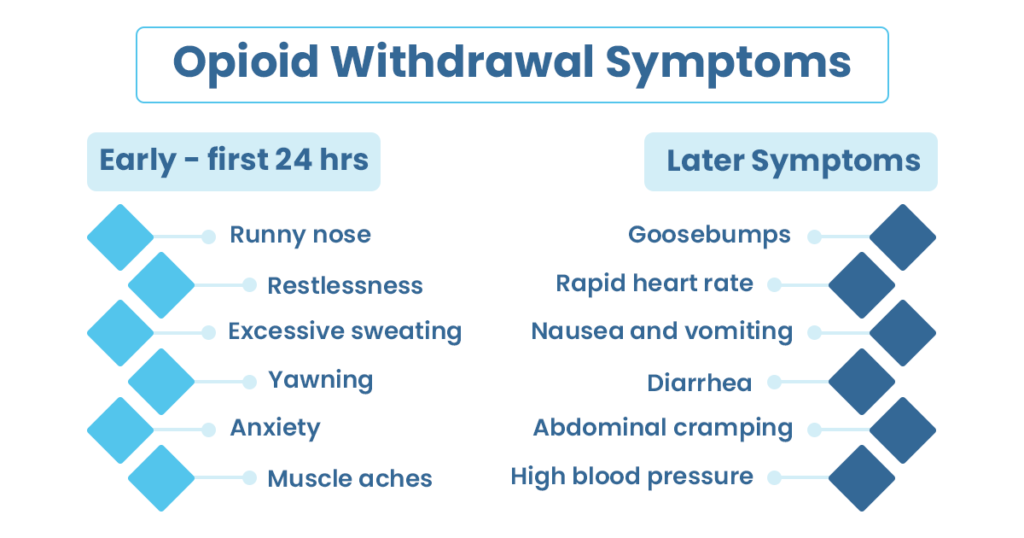
Withdrawal effects are more likely where someone is on high dose gabapentinoid or has been taken for more than 6 weeks. Where a gabapentinoid has to be discontinued due to medical reasons it is recommended this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week independent of the indication3. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric For patients in whom gabapentin treatment leads to severe dependence and withdrawal, the BRAVO Protocol provides a practical, patient-centered framework for tapering. View details for DOI 10.1080/10550887.2021.1907502 ⦁ The patient must be willing to abort the outpatient protocol and go to the emergency department or an inpatient withdrawal treatment program if you determine that the withdrawal syndrome is worsening and your patient’s safety is at risk Mild Outpatient Withdrawal With Gabapentin ⦁ Prescribe gabapentin 300 mg #30, no refills Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. UpToDate safety profile, gabapentin may be a viable ad-juvant because emerging data may suggest a potential role in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal.12,14,15 Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal at VAPORHCS Although not currently included in the alcohol withdrawal protocol at Veterans Affairs Port-land Health Care System (VAPORHCS), gaba- The mean PAWSS scale for these patients was 4.7 ± 1.4 with 62 (80.5%) of patients having a PAWSS score of at least 4 indicating a high risk for complicated withdrawal. In this gabapentin protocol group 51.9% of patients received a mean of 2.3 ± 1.6 mg of lorazepam equivalents in the measures included total average benzodiazepine and gabapentin dosage used during hospitalization and the development of severe complications of withdrawal including seizures or delirium. Results: The gabapentin protocol utilized in the MMDU was similar to that . of the GMU (mean time to the primary outcome of interest between both alcohol withdrawal delirium (DTs), yet some signs of early withdrawal may be present Alcohol Withdrawal Delirium (DTs) Usually appear 1–3 d after cessation; peak intensity on 4–5th day w5% In most cases (80%) the symptoms of DTs resolve within 72 h, in those that do not, the mortality rate in cases of DTs has been reported between 1% and 15% The best method of controlling gabapentin withdrawal symptoms is gradually tapering gabapentin doses. The tapering protocol used for opioids can be individualized to meet the needs of the person discontinuing gabapentin. Typically, a doctor will advise gradually tapering gabapentin to avoid dangerous side effects and withdrawal symptoms. This advice applies to both generic gabapentin and brand name Alcohol is believed to potentiate the actions of GABA, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, and suppress the actions of glutamate, a major excitatory neurotransmitter. Rapid cessation of alcohol use results in overall CNS hyperactivity and lower seizure threshold. There are no clinical protocols designed to manage gabapentin withdrawal. You and your healthcare provider can work together to figure out the best way forward. The general consensus seems to be that tapering off the drug can help prevent severe gabapentin withdrawal symptoms. Tapering off Gabapentin is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms due to its CNS effects. Withdrawal can include agitation, confusion, seizures and should be managed by healthcare professionals. Tapering schedules are personalized, often reducing the dose no more frequently than once a week. Gabapentin is one medication shown in small studies to reduce the need for benzodiazepines in the setting of alcohol withdrawal. The continuation of gabapentin after alcohol withdrawal appears to be safe during early sobriety and may aid in reducing alcohol-related cravings or returning to alcohol consumption. Tapering or slowly reducing your dose is recommended to stop taking gabapentin. Tapering off will help you avoid side effects. The timeline to reduce gabapentin depends on the individual A fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol appears to be an effective and safe alternative to CIWA-driven benzodiazepines in patients hospitalized with alcohol withdrawal syndrome, though further research is necessary to define the potential subpopulations that benefit most. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |