Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 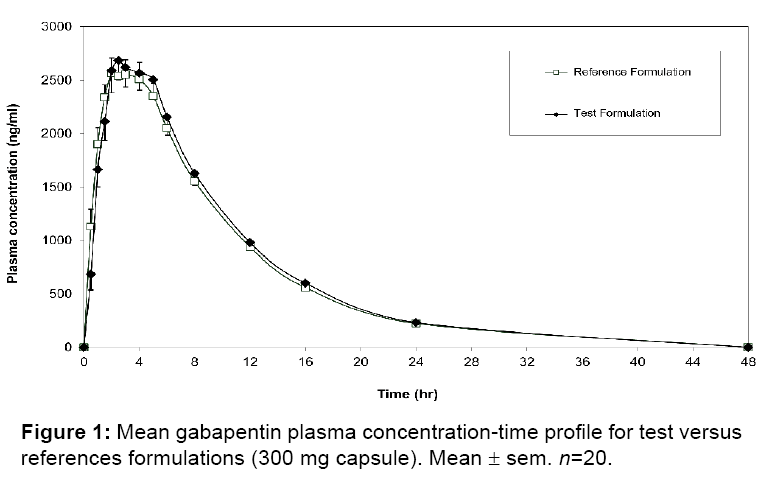 |
Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are Half-life. The elimination t 1/2 of gabapentin in patients with normal renal function is 5-7 hours. 16,17,5 In patients with reduced renal function, the elimination t 1/2 may be prolonged - in patients with a creatinine clearance of 30 mL/min, the reported half-life of gabapentin was approximately 52 hours. 16,17. Clearance For example, one report documented that among 11 individuals with renal failure, just one 400 mg oral gabapentin dose had a half-life of 132 hours (on average). Should you have renal failure and take just one dose of gabapentin, it could take over 30 days for complete systemic excretion. Gabapentin lasts between 6 and 8 hours per dose for most people. In general, it needs to be taken consistently for optimal effect. Neurontin (gabapentin) has a relatively short half-life and duration of action. unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Based on AUC and half-life, multiple-dose pharmacokinetic profiles of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of tablets containing 2.5 mg of norethindrone acetate and 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol were similar with and without coadministration of gabapentin (400 mg three times a day; N=13). Apply patient-centered approaches to gabapentin prescribing, tailoring dosage adjustments and treatment plans based on individual needs and preferences. In adult patients, the half-life of gabapentin is about 5 to 7 hours. In other words, it takes the body about 5 to 7 hours to eliminate its gabapentin concentration by half. This estimate can be altered by many factors including but not limited to kidney function. Pediatric Patients. Half-life for pediatric patients is roughly 4.7 hours. In adult patients, the half-life of gabapentin is about 5 to 7 hours. In other words, it takes the body about 5 to 7 hours to eliminate its gabapentin concentration by half. This estimate can be altered by many factors including but not limited to kidney function. Half-life for pediatric patients is roughly 4.7 hours. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are Mean half-life increased from 6.5 h (CrCl >60 mL/min) to 52 h (CrCL <30 mL/min) Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis Bioavailability is not proportional to dose (i.e. bioavailability of gabapentin ≅ 60% (900mg), 47% (1200mg), 34% (2400mg), 33% (2600mg), and 27% (4800mg) per day, given in 3 divided doses. Based on AUC and half-life, multiple-dose pharmacokinetic profiles of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of tablets containing 2.5 mg of norethindrone acetate and 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol were similar with and without coadministration of gabapentin (400 mg three times a day; N=13). Adults, normal: 5 to 7 hours; increased half-life with decreased renal function; anuric adult patients: 132 hours; adults during hemodialysis: 3.8 hours. <3% In CrCl <30 mL/minute, half-life is approximately 52 hours (immediate release). In patients with Cl cr <30 mL/minute, half-life of 52 hours reported with conventional (immediate-release) gabapentin; in anuric patients, half-life reported to be 132 hours on nondialysis days and 3.8 hours during hemodialysis. Based on AUC and half-life, multiple-dose pharmacokinetic profiles of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of tablets containing 2.5 mg of norethindrone acetate and 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol were similar with and without coadministration of gabapentin (400 mg three times a day; N=13). Gabapentin has a half-life of 5 to 7 hours, but it can vary by dosage, formulation, and individual factors. Gabapentin’s half-life and how long it stays in the body influence how long the effects last and possible risks. This gabapentin half life calculator shows how gabapentin accumulates and how long it stays in your body. Get dose and frequency with ease! Oral Contraceptive Based on AUC and half-life, multiple-dose pharmacokinetic profiles of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of tablets containing 2.5 mg of norethindrone acetate and 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol were similar with and without coadministration of gabapentin (400 mg three times a day; N=13). The Cmax of Administer gabapentin three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 11 Years. Factors Affecting Gabapentin half life. Several factors can influence the gabapentin half life, making it longer or shorter depending on the person. These include: Dosage: Higher doses of gabapentin can lead to a longer half life of gabapentin because the drug accumulates in the system. Regular, high-dose usage may result in longer detection times.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |