Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
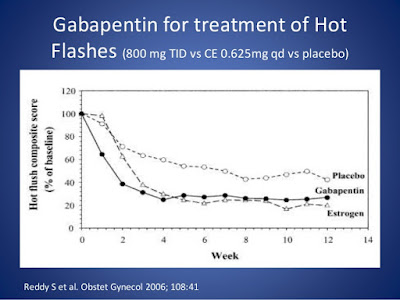
Clinicians have been using gabapentin off-label to help relieve hot flashes in postmenopausal women. A new extended-release formulation of gabapentin has also shown efficacy in treating hot flashes and improving sleep quality with potentially fewer side effects than regular gabapentin. 12–18. Gabapentinhas undergone investigation for treating hot flashes, after patients taking it for other indications incidentally noted improvement of hot flashes. Although it is an analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and is used to treat neurologic disorders such as seizures and neuropathic pain, gabapentin does not affect Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown that when compared with placebo, gabapentin is effective at reducing hot flash frequency by 54% and hot flash composite score (combined hot flash frequency and severity score) by 31% to 51%. This review investigated the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin for the treatment of hot flashes in menopausal women. Gabapentin was associated with reductions in the severity and frequency of hot flashes in menopausal women, but there was substantial variation in the results across the included trials. The authors' conclusions appear to be reliable based on the evidence presented. Menopausal hormone therapy is the most effective tool for treating hot flashes and night sweats associated with menopause. It also can help to prevent osteoporosis. "This new medication shouldn't replace hormone therapy," says Dr. Kling. "Hormone therapy remains the most effective treatment for hot flashes and night sweats. How effective is gabapentin for hot flashes? Gabapentin appears to be effective for reducing hot flashes, although potentially not as effective as estrogen therapy. Gabapentin can be considered effective in the treatment of hot flashes and should be considered a reasonable alternative when estrogen therapy is not desired. Hot flashes occur frequently in menopausal women and in women with breast cancer, diminishing their quality of life. In one, albeit small, clinical trial 2,400 mg of gabapentin divided three times a day was as effective as 0.625 mg of Premarin a day (which is a standard dose for hot flashes). How to Take Gabapentin? Hot flashes affect approximately 75% of postmenopausal women and 40% of perimenopausal women. Women who experience hot flashes have higher rates of sleep and mood disturbances than do women unaffected by hot flashes. 1, 2, 3 Although hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is highly effective in reducing hot flashes, there is growing concern that long-term HRT is associated with an increased risk of Studies on these agents are summarized in Table 3. 44 – 52 Belladonna/ergotamine tartrate/phenobarbital combination and gabapentin were more effective than placebo in reducing hot flashes in two Gabapentin 300 mg/day could be useful to relieve hot flashes in women for whom hormone therapy is not suitable or when hot flashes do not respond to other therapies. Further researches are needed to determine the efficacy of gabapentin use for longer periods or at higher doses. Gabapentin is effective in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes, particularly for those experiencing menopausal symptoms. Originally used for epilepsy and neuropathic pain, it has been found to offer significant relief from hot flashes. Higher, open-label gabapentin dosing was associated with 54% and 67% reductions in hot flash frequency and composite score from baseline, respectively. Conclusion: Gabapentin is effective in reducing hot flash frequency and severity in postmenopausal women. Gabapentin is effective in the control of hot flashes at a dose of 900 mg/day, but not at a dose of 300 mg/day. This drug should be considered for treatment of hot flashes in women with breast cancer. Gabapentin at 900 mg/day is an effective and well-tolerated treatment for hot flashes. Older nonhormonal means of treating hot flashes (eg, a combination of belladonna alkaloids, ergotamine tartrate, and phenobarbital [Bellergal], clonidine, α-methyldopa, and vitamin E) are associated with limited efficacy and/or toxicity. 4 Recently, one of the newer antidepressants, venlafaxine, was proved to be helpful in substantially Talk to your healthcare professional about the pros and cons of treatments for hot flashes. If hot flashes don't bother you much, you likely don't need treatment. For most people, hot flashes go away slowly, even without treatment. But it can take several years for them to stop. A 2005 study by Pandya et al. randomized 420 women with breast cancer and experiencing at least 2 hot flashes in 24 hours to one of three groups: gabapentin 300 mg daily, gabapentin 900 mg daily, or placebo 23. After 8 weeks, the 300 mg dose group showed a modest 20% reduction in hot flashes, but the 900 mg dose group showed a reduction of How does gabapentin help with hot flashes? As GABA slows down activity in the part of the brain that controls body temperature, it stands to reason that gabapentin could have the same effect. Although the FDA has not approved Neurontin for hot flashes, there’s some good evidence that it’s effective.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |