Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
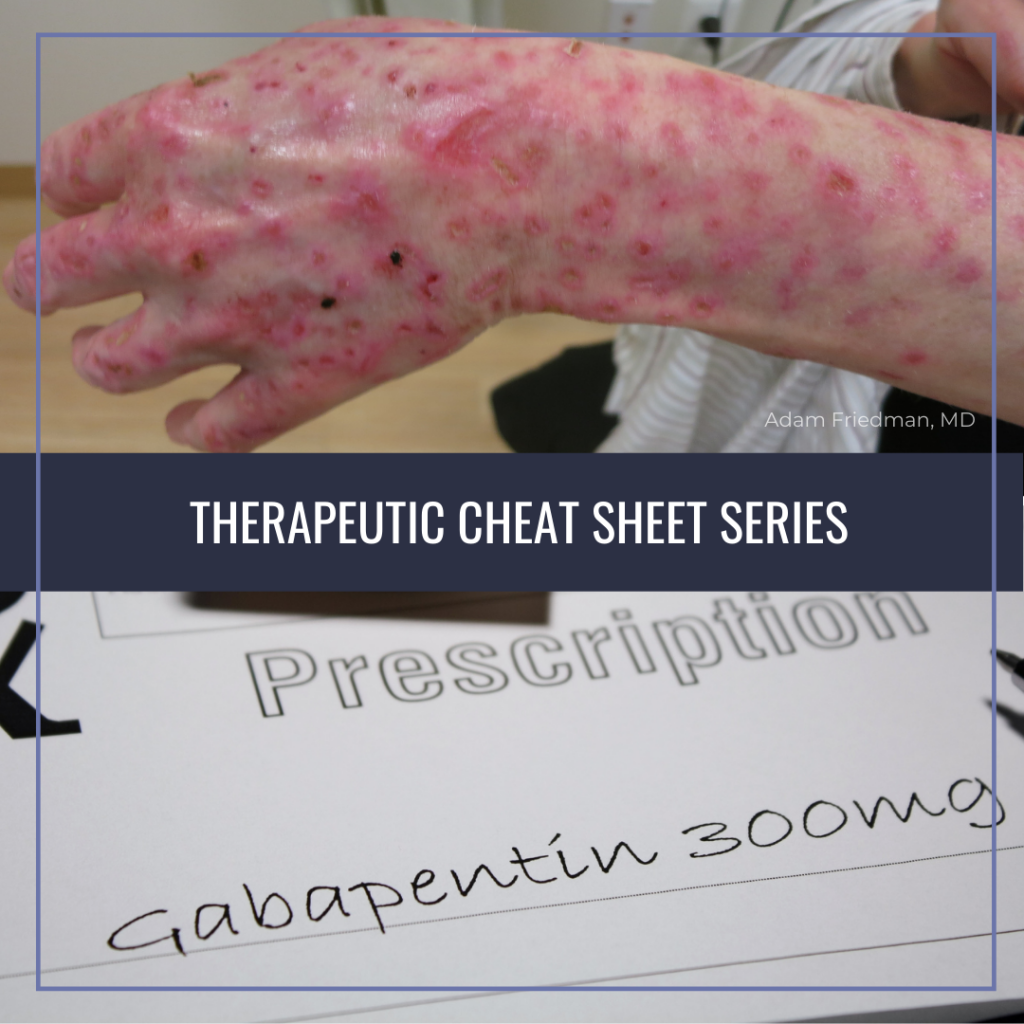
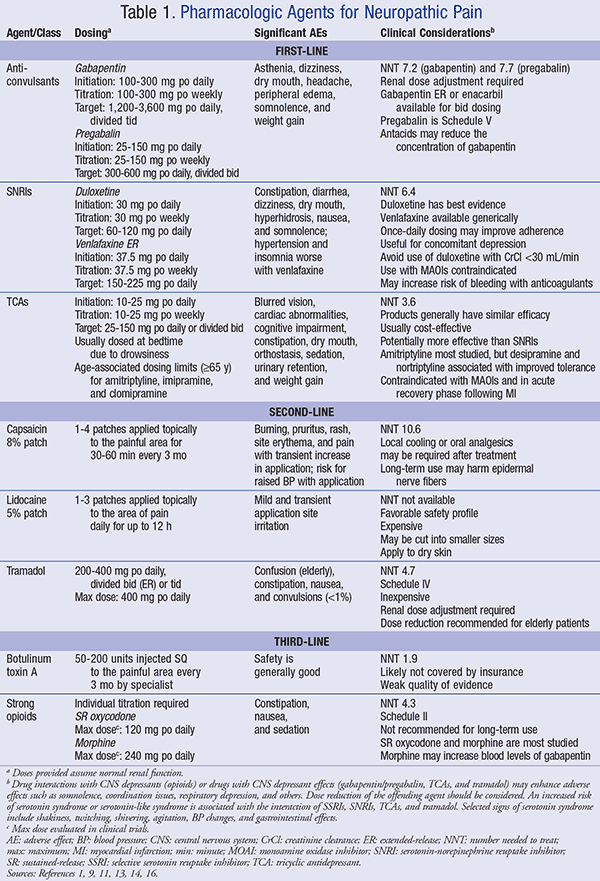
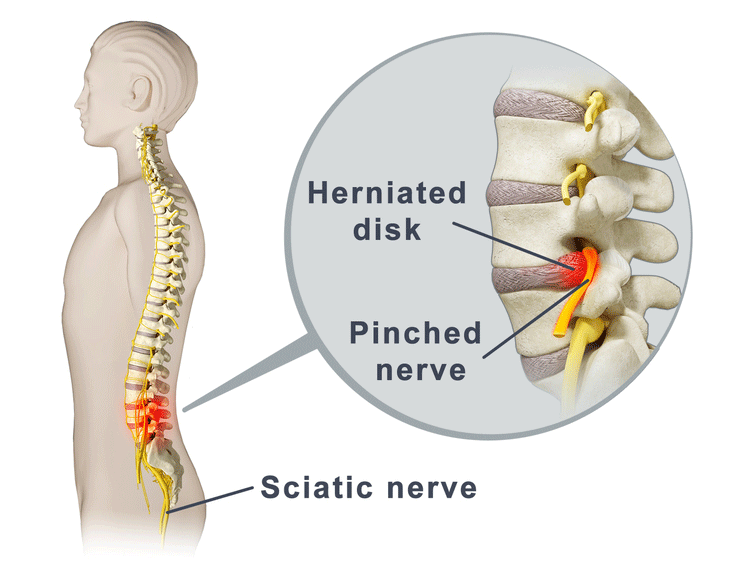
Fourteen of 15 comparisons found anticonvulsants were not effective to reduce pain or disability in low back pain or lumbar radicular pain; for example, there was high-quality evidence of no effect of gabapentinoids versus placebo on chronic low back pain in the short term (pooled mean difference [MD] −0.0, 95% confidence interval [CI] −0.8 A 2016 double-blind RCT (N = 108) investigated gabapentin as a treatment for chronic low back pain with and without a radicular component. 2 This RCT was included in the 2017 meta-analysis but is Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Despite no clear rationale, they are increasingly used for nonspecific CLBP. They necessitate prolonged use and are associated with adverse effects and increased cost. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and Gabapentin for back pain could be a good choice, as it’s the best treatment for neuropathic back pain. However, it should not be taken without consulting a doctor. Let’s explore more. Background: Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of enormous value. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Background and objective: Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of enormous value. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. Additionally, we considered the domains for chronic pain studies as suggested by Moore et al. and added the domains of outcome assessment time (12 weeks or more as low risk), outcome assessment threshold (>30% improvement in pain relief as low risk), and potential for publication bias based on the sample size threshold (>50 as low risk) to Although providers often prescribe gabapentin, high-quality studies show that gabapentin does not work well to treat all types of back pain. Evidence suggests that gabapentin works best for nerve pain caused by diabetes and shingles. Back pain can have a huge effect on your day-to-day life. Can Gabapentin 300mg be effective for back pain? Yes, gabapentin is frequently employed off-label for various types of nerve pain, including back pain. It was originally designed to manage seizures and nerve pain from shingles; however, many studies have proved this medicine effective in back pain treatment. Are anticonvulsants an effective treatment for low back pain? The use of anticonvulsants like gabapentin (Neurontin) for painful conditions has increased greatly in recent years. There are three main categories: benzodiazepines, antispasticity medications, and non-benzodiazepine muscle relaxers. A recent review of studies found that benzodiazepines and spasticity medications aren’t effective for short-term relief from back pain. The others can help with pain initially but aren’t effective after 2 weeks. Introduction: Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a common condition and causes significant pain, distress and disability across the world. It is multifactorial in aetiology and is challenging to manage. Although the underlying mechanism of pain is predominantly non-specific, many argue that there is a substantial neuropathic pain element. for low-back pain. National Conference of State Legislatures. (2024). State medical cannabis laws. Oliveira, C. B., et al. (2018). Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: An updated overview. European Spine Journal. Parke-Davis Div of Pfizer Inc. (2022). Neurontin- gabapentin [package insert]. Back pain has an impact on daily life and drives individuals to seek effective treatments, leading many healthcare providers to turn to gabapentin. Originally designed as an anti-seizure medication, gabapentin has found application beyond its initial purpose, addressing not only back pain but also nerve pain, postsurgical discomfort, and Gabapentinoids are not a good substitute for opioids in the management of chronic low back pain that does not include neuropathic pain, study finds.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |