Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
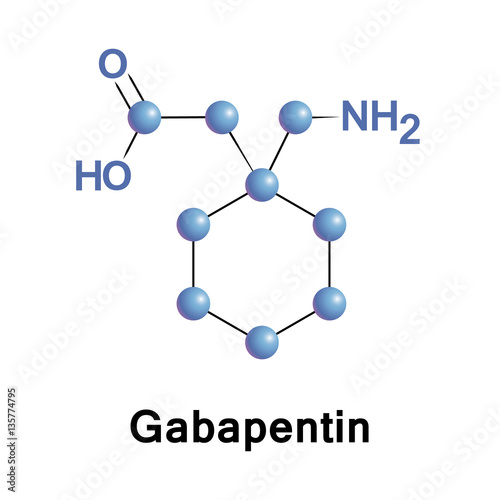 |  |
gabapentin? Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve pain. It also reduces menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin in higher doses has been shown to be as effective as estrogen in reducing the severity and frequency of hot flushes. Before you take gabapentin Tell your doctor if you are taking other A 2005 study by Pandya et al. randomized 420 women with breast cancer and experiencing at least 2 hot flashes in 24 hours to one of three groups: gabapentin 300 mg daily, gabapentin 900 mg daily, or placebo 23. After 8 weeks, the 300 mg dose group showed a modest 20% reduction in hot flashes, but the 900 mg dose group showed a reduction of The hot flashes almost stopped completely after just 1 week of taking this medicine. The study lasted for 6 months, and then I was taken off cold turkey. The withdrawal was horrible. Hot flashes, couldn't sleep, and just overall irritable to say the least. I went to my regular doctor and was prescribed gabapentin 600mg. Again the hot flashes Several clinical studies have shown that gabapentin becomes effective at reducing hot flashes within around 4 weeks of taking it consistently. And while some may feel a benefit sooner Gabapentin has a short half life, meaning it is removed from the body quickly, so ideally it is taken three times a day. The dosing for hot flashes ranges from 300 mg three times a day (900 mg/day total) to 800 mg three times a day (2,400 mg/day total). earched the PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases for English-language articles published until June, 2018. The following search terms were used: “menopause,” “hot flushes,” “vasomotor symptoms,” “gabapentin,” and “non-hormonal therapy.” Primary outcomes were frequency, duration, and composite score of hot flushes. Secondary outcomes were adverse effects and It works in the brain to treat hot flashes and night sweats." Fezolinetant is the generic name of the medication. Dr. Kling says it offers patients a choice. "For people who can't take hormone therapy or choose not to, it's a good option for them, potentially, to treat their hot flashes and night sweats," she says. Gabapentin Helps Hot Flashes. In BREEZE 3, 600 postmenopausal women (mean age, 54.0 years; mean time since last menstrual period, 114 months; mean body mass index, 29.4 kg/m²) were randomized to Gabapentin 300 mg/day could be useful to relieve hot flashes in women for whom hormone therapy is not suitable or when hot flashes do not respond to other therapies. Further researches are needed to determine the efficacy of gabapentin use for longer periods or at higher doses. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has emerged as an effective non-hormonal treatment for menopausal hot flashes, with doses ranging from 600 to 2400 mg/day showing significant reduction in both frequency and severity. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). This antiseizure medicine helps ease hot flashes. Side effects can include being drowsy, dizzy or tired and swelling in the arms and legs, called edema. Although the studies were few, all showed gabapentin to be safe and effective in the treatment of hot flashes. At doses used to control hot flashes, gabapentin was well tolerated, with drowsiness as its most reported adverse effect. Gabapentin can be considered effective in the treatment of hot flashes and should be considered a reasonable Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. In a recently published clinical trial in men with prostate cancer who were treated with GnRH analogues and antiandrogens, the disabling hot flashes were successfully treated with gabapentin. 32 Unfortunately, gabapentin has been associated with anorgasmy in both men and women. 33 Nonetheless, a thorough study of gabapentin in rigorous clinical Studies have found gabapentin to be effective in relieving severe hot flashes after just 12 weeks of treatment. Other treatments for hot flashes include: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) Gabapentin was associated with reductions in the severity and frequency of hot flashes in menopausal women, but there was substantial variation in the results across the included trials. The authors' conclusions appear to be reliable based on the evidence presented. The efficacy of gabapentin was assessed by three measures of hot-flash symptoms: frequency (total number of mild, moderate, severe, and very severe hot flashes), severity score (calculated by assigning scores of 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively, to mild, moderate, severe, and very severe hot flashes and adding the scores), and mean duration. For the 9 patients taking antidepressants at baseline compared with those not taking antidepressants at baseline, there was no substantial difference in their baseline hot flashes (mean hot flash score of 16.7 vs 19.7 per day, mean hot flash frequency of 8.8 vs 10.3 per day). to reduce hot flushes? The non-hormonal medicines used to reduce hot flushes in women include gabapentin, clonidine, venlafaxine or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The treatment option depends on the individual. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® available as 100mg, 300mg, 400mg, 600mg and 800mg capsules. Also available in To make the most of Gabapentin for managing hot flashes, consider these useful tips: Take at Bedtime: Administering Gabapentin at bedtime can help minimize daytime drowsiness and dizziness. Gradual Dosage Increase: Start with a low dose and gradually increase it. This approach helps your body adjust and reduces the risk of side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |