Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
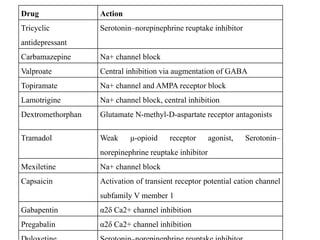 |  |
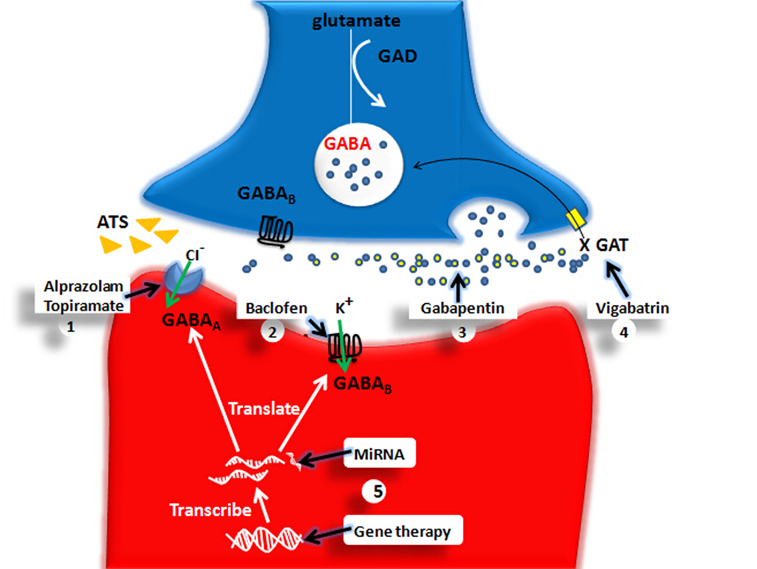
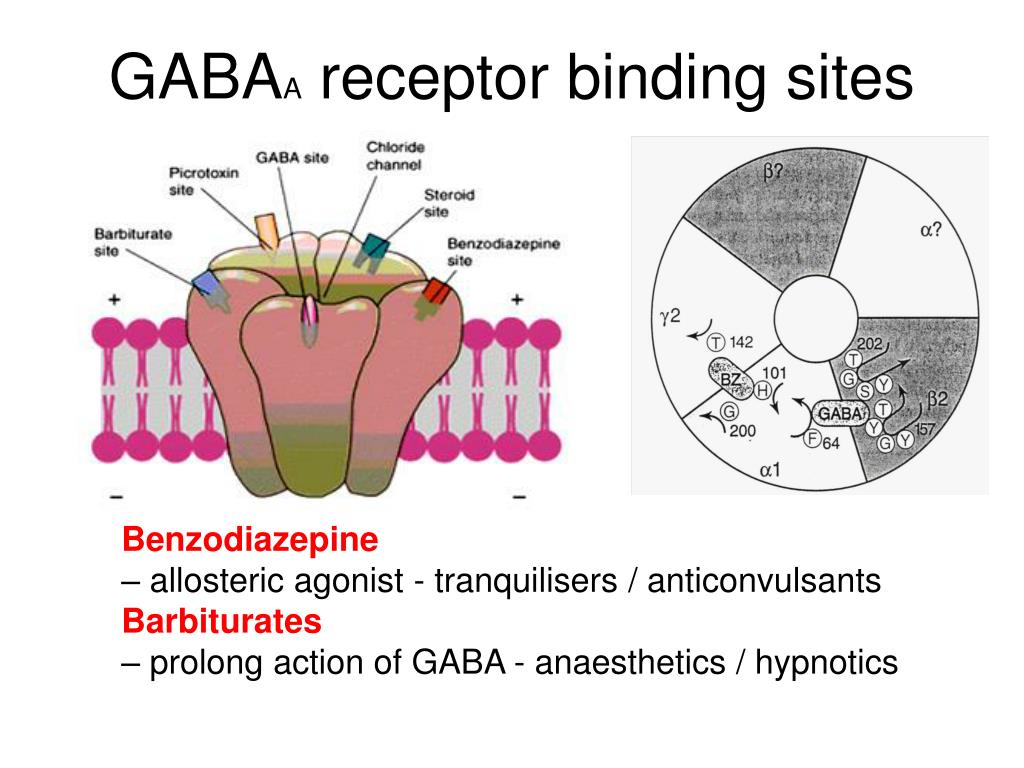
A GABA reuptake inhibitor (GRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) by blocking the action of the gamma-Aminobutyric acid transporters (GATs). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of GABA and therefore an increase in GABAergic neurotransmission. [1] Gabapentin is a GABA agonist and anticonvulsant that increases GABA concentrations in the central nervous system, possibly via inhibition of GABA-transaminase (Cai et al., 2012). While more commonly trialed in combination with flumazenil, as described above, one double-blind RCT ( Heinzerling et al., 2006 ) examined gabapentin as an individual Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions including the cerebellum and hippocampus. Although gabapentin is a GABA analogue, it does not bind to and modulate the GABA receptors nor does it affect GABA transport or metabolism. Gabapentin is a gabapentinoid, which acts as an inhibitor of the α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) that are linked to neurotransmitter release. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) but it does not modify GABA A or GABA B radioligand binding, it is not converted metabolically into GABA or a GABA agonist, and it is not an inhibitor of GABA uptake or degradation. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) but it does not modify GABA A or GABA B radioligand binding, it is not converted metabolically into GABA or a GABA agonist, and it is not an inhibitor of GABA uptake or degradation. Gabapentin was tested in radioligand binding assays at concentrations up Gabapentin (1, Fig. 15.8), originally designed as a lipophilic GABA analogue, is an anticonvulsant with as yet an uncertain mechanism of action. Despite its structural analogy with GABA, gabapentin does not interact with any of the GABA receptors, nor is it an inhibitor of GABA uptake or degradation. Gabaculine – neurotoxin; GABA-T inhibitor and GABA reuptake inhibitor; Gabapentin – anticonvulsant; inhibitor of α 2 δ subunit-containing VGCCs Gabapentin enacarbil – used for the treatment of restless legs syndrome and postherpetic neuralgia; same mechanism of action as gabapentin; Gaboxadol – GABA A receptor agonist Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibitors, or GABA antagonists, are drugs that inhibit the action of GABA, the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system. They predominantly work at the GABA receptor. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin and was designed to overcome the limitations of gabapentin (gabapentin is poorly absorbed and only lasts for a short duration of time). Liver enzymes convert gabapentin enacarbil it into its active form, gabapentin. Gabapentin works along a similar mechanism but appears to affect the calcium currents after chronic dosing and not in the acute stages. Tiagabine: is a GABA reuptake inhibitor; Topiramate: This has a wide range of actions on voltage-gated sodium channels, high-voltage-activated calcium channel, GABA-A receptors and carbonic anhydrase receptors Even though gabapentin is a structural GABA analogue, and despite its name, it does not bind to the GABA receptors, does not convert into GABA Tooltip γ-aminobutyric acid or another GABA receptor agonist in vivo, and does not modulate GABA transport or metabolism within the range of clinical dosing. [85]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |