Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
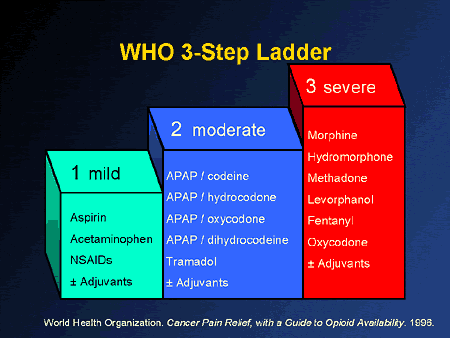 |  |
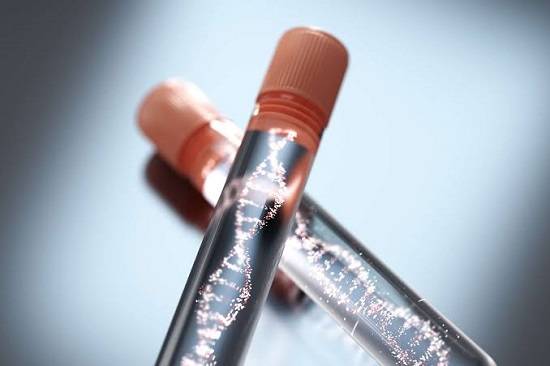
American Family Physician Community Blog on the topic, Substituting gabapentin for opioids has significant downsides, written by Kenny Lin, MD, MPH. Gabapentin is a medication for nerve pain and seizures. It’s not a controlled substance by the federal government, but some states have made it a schedule V substance due to its potential for misuse and addiction. Officials ruled that gabapentin was a cause of death in almost 3000 of these cases. The number of fatal overdoses in which gabapentin was detected or involved increased from 2019 to 2020, apparently tracking with the overall increase in overdose deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic. Opioids can impair the immune system, increasing risk of infection. 11; Opioid use, particularly in high doses or for a long period of time, can cause changes in a person’s body that can actually make them more sensitive to pain. 12,13; Opioid use also has been associated with mental disorders like depression or sexual dysfunction. 15,16,17 Gabapentin is a prescription drug for neuropathic pain and seizures, but it is also a Schedule V controlled substance in some states. It may be abused, diverted, or combined with opioids to increase euphoria and risk of overdose. Experts say gabapentin is now being mixed with other opioids in an apparent effort to get a stronger "high." Even before gaining recent attention for its role in the opioid epidemic Gabapentin, a purportedly nonaddictive painkiller primarily used to treat shingles and control seizures, has landed on the radar of beleaguered health officials and law enforcement already Gabapentin is a prescription medication that mimics the effects of GABA, a brain chemical that reduces nerve excitability. It is not an opioid, but it can interact with opioids and cause serious breathing problems. Prescription opioid use is highly associated with risk of opioid-related death, with 1 of every 550 chronic opioid users dying within approximately 2.5 years of their first opioid prescription. Although gabapentin is widely perceived as safe, Gabapentin is not an opioid, but it may be used as an alternative to opioids for some types of pain. Learn how gabapentin and opioids differ in FDA-approved uses, controlled substance status, and potential side effects. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medicine that can treat some types of nerve pain, but it is not an opioid or painkiller. Learn about its uses, side effects, interactions, and the FDA alert on serious breathing problems with gabapentin and other drugs. Opioids are a class of drugs that derive from, or mimic, Anticonvulsants such as gabapentin or pregabalin; Other adverse effects. Low sex hormone levels Gabapentin is a non-opioid medication that can be used for acute pain relief, but it can also increase the risk of opioid-use disorder and opioid-related overdose when prescribed with opioids. Learn about the mechanisms, data, and recommendations from Epic Research and Pharmacy Times. Opioid medication significantly reduces low back pain, but opioids should not be used in combination with gabapentin (Neurontin) because of their limited effectiveness and potential for abuse, according to the authors of a small new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pain Medicine. Gabapentin is a prescription drug for epilepsy, nerve pain, and restless leg syndrome. It is not an opioid, but it can have some similar effects and risks, especially when combined with opioids. Opioid medicines travel through the blood and attach to opioid receptors in brain cells. This blocks pain messages and can boost feelings of pleasure. When opioid medicines are dangerous. What makes opioid medicines effective for treating pain also can make them dangerous. At lower doses, opioids may make you feel sleepy. Some neurologists believe that stricter gabapentin regulation may lead to greater opioid use and make it harder for people with neuropathic pain to receive proper care. Gabapentin is not an opioid. It’s an anticonvulsant medication with important uses in managing seizures, nerve pain, and other conditions. Understanding the differences between gabapentin and opioids is crucial for safe and effective medication use. In case of an opioid overdose, individuals who take opioids, or their caregivers, should always have a rescue medication called naloxone within reach. This medication can block the effects of opiates to help reverse an overdose (an opioid antagonist). Opioids are powerful pain-relieving drugs with medical uses and side effects, and factors that may increase the risk of opioid use disorder.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |