Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
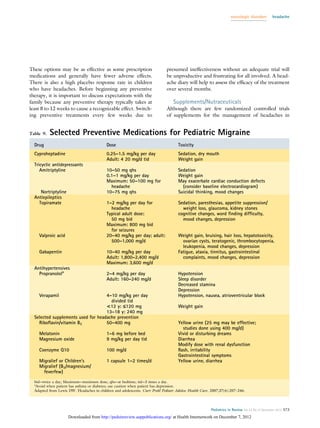
Research indicates that gabapentin has no substantial evidence supporting its effectiveness in treating major depressive disorder. Some studies even suggest that while it may relieve certain anxiety symptoms, it may inadvertently contribute to depressive symptoms in other users. Gabapentin can affect mood and may cause depressive symptoms, though this is considered a rare side effect. While it is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain, some individuals have reported experiencing feelings of sadness or worsening depression during treatment. The truth is, the effectiveness of gabapentin in mental health conditions is a bit of a mixed bag – but with some very promising highlights. Let’s start with anxiety. Several clinical studies have shown gabapentin to be effective in reducing symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety. While studies don’t typically show effectiveness for improving symptoms of depression, there is evidence that gabapentin may have some benefit for anxiety disorders. A rat study found that gabapentin produced behavioral changes suggestive of anxiolysis, or feelings of calmness. Gabapentin and pregabalin are probably not effective for depressive state but may improve some subscales, such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. They may have benefits for anxiety symptoms as do most GABAergic agents and also potential utility for bipolar individuals with comorbid substance use disorders. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Gabapentin requires three times daily administration because of its short duration of effect. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) only requires once-daily dosing. Only effective for partial-onset seizures, not other types of seizure disorders. Some branded and generic forms of gabapentin are not interchangeable. Venlafaxine was therefore initiated. The patient remains on gabapentin and venlafaxine at the time of manuscript submission. 3. Discussion. The potential anxiolytic effect of gabapentin was first observed in animal models . Randomized controlled trials in patients with anxiety disorders found that gabapentin is effective in treating social Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. Furthermore, other measurements of mood, depression, anger-hostility, fatigue, and physical functioning were more effectively managed with gabapentin compared to a placebo. During the same time, Backonja et al reviewed the effect of gabapentin in 165 diabetic neuropathy patients. We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the efficacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these Gabapentin for Depression. When it comes to finding effective treatments for depression, gabapentin has emerged as a potential option. Gabapentin is commonly used as an anticonvulsant and analgesic medication, but recent research suggests that it may also have benefits for individuals struggling with depression. In patients with treatment-resistant depression, augmenting therapy with atypical antipsychotics can be effective. Adding quetiapine (Seroquel) to antidepressant therapy reduces symptoms below the Gabapentin is sold under the brand names Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Because there is limited research on how effective gabapentin is at reducing anxiety symptoms, it’s not typically the first medication a licensed physician will recommend for treating anxiety. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Evidence also suggests gabapentin is more effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and certain types of anxiety than conditions like bipolar disorder, panic disorder, or panic attacks. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |