Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
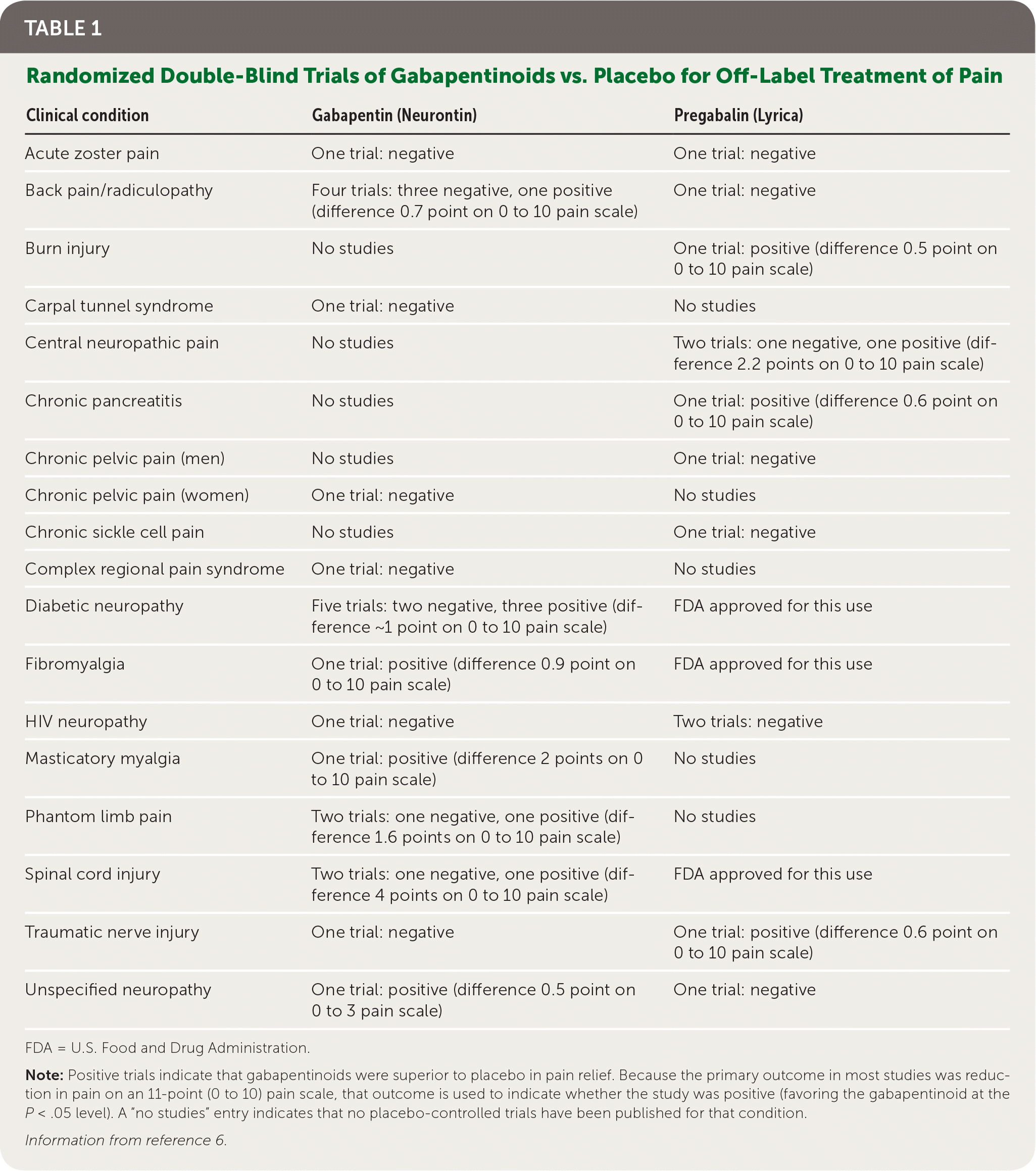
OPIOIDS and GABAPENTINOIDS for chronic pain in adults Chronic pain (sometimes known as long-term pain or persistent pain) is pain that lasts for more than 3 months. Pain can be secondary to (caused by) an underlying condition (for example, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, endometriosis). Chronic pain can also be primary. Gabapentin is helpful for some people with chronic neuropathic pain. It is not possible to know beforehand who will benefit and who will not. Current knowledge suggests that a short trial is the best way of telling. Thirty-seven studies (5633 participants) studied oral gabapentin at daily doses of 1200 mg or more in 12 chronic pain conditions; 84% of participants were in studies of postherpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuropathy or mixed neuropathic pain. A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak . Chronic pain is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as ongoing or recurrent pain that lasts beyond the usual course of acute illness or injury or more than three to six Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Several case reports note analgesia when gabapentin was used for treatment of chronic pain. 14,15 And in a clinical study on postoperative pain in dogs undergoing mastectomy, although pain scores did not differ, dogs receiving NSAIDs plus gabapentin required fewer opioid rescue doses than dogs receiving NSAIDs alone; thus, the gabapentin did Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Background: This review updates parts of two earlier Cochrane reviews investigating effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). ). Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burn Chronic pain results from combined biologic, psychologic, and social factors, and most often requires a multifactorial approach to management. In addition to nonpharmacologic therapies, many patients require medications to manage pain. The general approach to the management of chronic non-cancer pain and nonpharmacologic therapies for chronic pain are discussed separately. Evaluation of chronic pain and the use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain are also discussed separately. (See "Approach to the management of chronic non-cancer pain in adults".) Gabapentin is prescribed for long-term pain control. It isn't used to treat short-term pain. Researchers aren't sure exactly how it works, but it may change how your body feels Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. NSAIDs are most effective for mild to moderate pain that occurs with swelling, known as inflammation. These medications are commonly used for arthritis and pain resulting from muscle sprains, strains, back and neck injuries, or menstrual cramps. Generic (brand) names. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others); naproxen sodium (Aleve); others. But the evidence shows that it doesn’t work that well to ease back pain, particularly chronic low back pain. For chronic low back pain, physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) tend to work better. Gabapentin for sciatica The cause of sciatica back pain is compression of the sciatic nerve. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Bottom line. There is moderate‐quality evidence that oral gabapentin at doses of 1200 mg daily or more has an important effect on pain in some people with moderate or severe neuropathic pain after shingles or due to diabetes. Background. Neuropathic pain comes from damaged nerves. This review updates parts of two earlier Cochrane reviews investigating effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burning. Gabapentin is widely used off-label for various chronic pain conditions and for the treatment of acute pain, making it now one of the most commonly described analgesic drugs; The liberal use of gabapentin for both acute and chronic pain management has created quite some controversy. The concurrent use with chronic opioids, especially in older
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |