Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
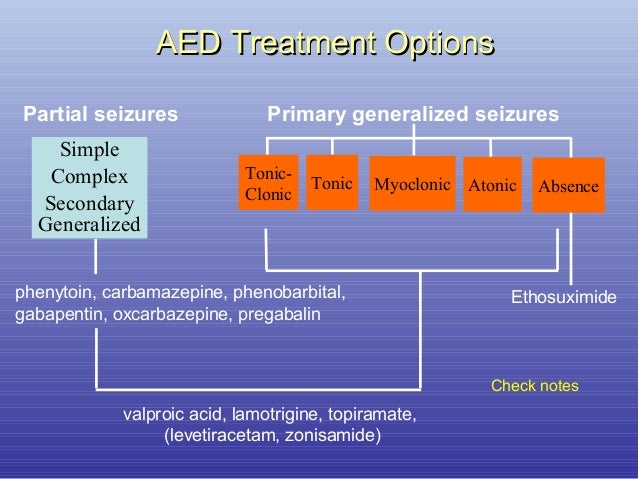
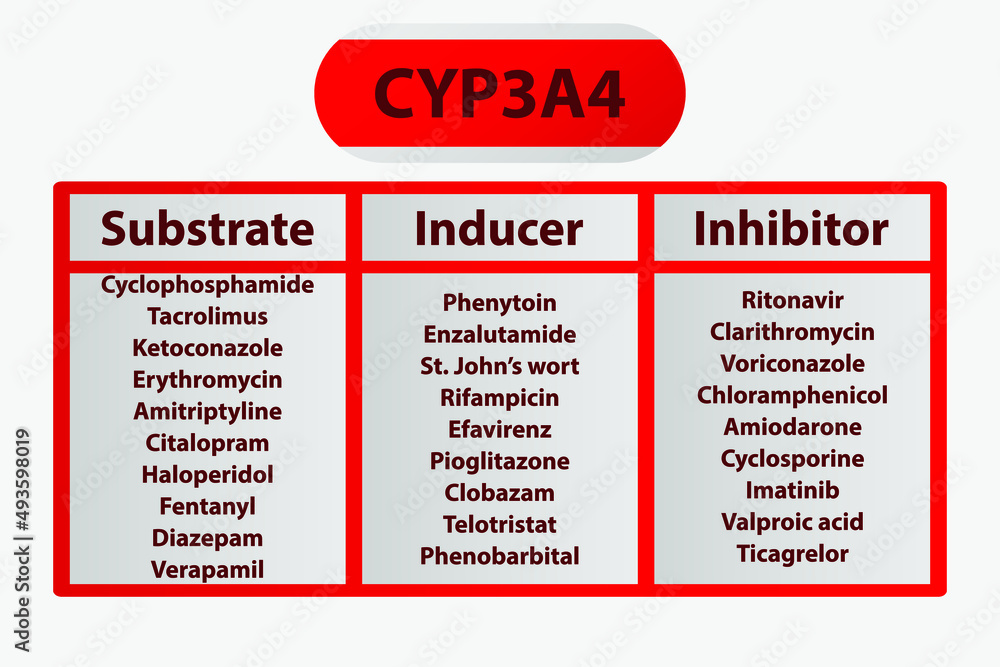
This class, which includes gabapentin and pregabalin, is not metabolized by the liver. Therefore, risks in patients with advanced liver disease are not greatly increased. However, there are case reports of pregabalin‐induced hepatoxicity. 4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are renally excreted, so dosages need to be adjusted for renal failure. Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. However, there are a few descriptions of gabapentin-related Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Metabolism of gabapentin in rats. The metabolism of gabapentin, a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug, has been extensively studied in rats. Gabapentin is primarily eliminated from the body through renal excretion, with only a small portion being metabolized by the liver. When gabapentin is administered to rats, it undergoes minimal metabolism Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant that is also used off-label to treat neuropathic pain. It is not metabolized by the liver, and there have been few reports of hepatotoxity associated with it. We present a rare case of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurring in a young male. Case Description/Methods: Hi, Gabapentin is exclusively excreted by the Kidneys and undergoes no appreciable metabolism by the Liver. As to whether it is toxic to your Kidneys is probably a question that you should be asking your prescribing doctor. No cases of acute liver failure or chronic liver injury due to gabapentin have been described. There is no information about cross reactivity with other compounds having similar structure (pregabalin). Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver and is excreted unchanged in the kidneys after circulating in the blood. It affects nerves and chemicals involved in pain and seizures. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for the liver or kidneys, but in rare instances, it can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). Gabapentin/pregabalin: not metabolized by the liver or bound by proteins, but consider renal dysfunction in cirrhosis patients, as well as other relevant side effects (e.g. sedation, dizziness); minimal data on safety of these agents. Morphine: Morphine is considered to have a high hepatic extraction on first-pass metabolism, making it only 30% to 40% bioavailable following oral dosing in healthy patients. 4,5 Morphine is metabolized by the liver to morphine-6-glucuronide (active metabolite) and morphine-3-glucuronide (inactive metabolite with potential neurotoxic effects Moreover, there is a paucity of high-quality, prospective data that examine the pharmacology and adverse effect profile of many analgesics in patients with advanced liver dysfunction. Drug metabolism in general occurs in the liver via 3 mechanisms: (1) oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis reactions of the hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme The liver is the organ that is responsible for breaking down (metabolizing) most of the substances in a person’s system. However, gabapentin is one of the few drugs that is not metabolized by the liver; instead, it is primarily metabolized by the kidneys. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). It is extensively metabolized in the liver and only a small percent of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. 19, 20 Since ESM undergoes significant liver metabolism, it has potential interactions with other enzyme-inducing AEDs, though the clinical importance of these drug–drug interactions is unclear. Gabapentin's effects seem to be associated with NMDA receptors, although the mechanism for its action is unknown. Gabapentin has been used to decrease seizure activity, as an analgesic for the prevention of allodynia, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain (see Table 26-1). Gabapentin is not metabolized and is excreted in the urine unchanged. Gabapentin has minimal direct effects on the liver, as it undergoes minimal hepatic metabolism before excretion. However, liver health remains important because any existing liver disease could indirectly alter how gabapentin is processed in the body. They are not metabolised by the liver and do not affect the cytochrome P450 system, major cytochrome P450 system isoenzymes; however, drug-induced hepatotoxicity has been described in case reports. 16 Elimination is mostly done by the kidney and is proportional to the creatinine clearance. Accumulation can cause renal failure resulting in Gabapentin is not protein-bound. A high volume of distribution indicates greater concentration in tissue than in plasma. It is not metabolized and does not induce hepatic enzymes or inhibit metabolism of other antiepileptic drugs. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |