Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
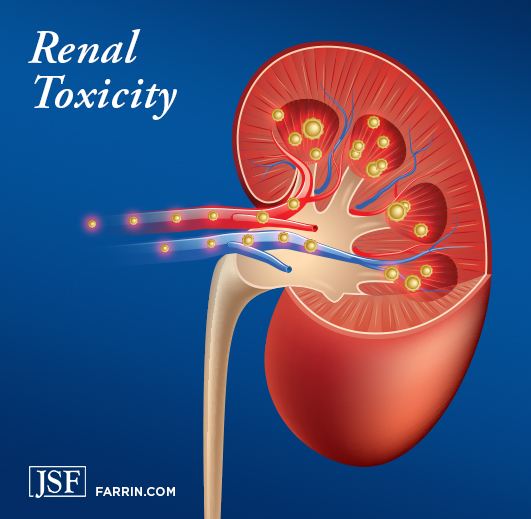
This accumulation can increase the risk of side effects and potential toxicity. Therefore, anyone with stage 3 kidney disease considering gabapentin needs to do so under close medical supervision and with a carefully adjusted dosage. Never self-medicate with gabapentin, especially if you have kidney issues. Understanding Gabapentin and Kidney When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Limited data are available on the hepatotoxicity of gabapentin. In clinical trials in diabetic neuropathy and epilepsy, therapy with gabapentin was not associated with an increased frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations or liver toxicity. Gabapentin is generally considered safe for the liver and kidneys when taken at prescribed doses. However, certain considerations are important for individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions, as gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys and not metabolized significantly by the liver. Gabapentin is approved by the FDA for treating seizure disorders and neuropathic pain, except for trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is frequently used off-label to treat other pain conditions and psychological disorders, such as anxiety. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Moreover, gabapentin administration caused structural changes in the hepatic and renal architecture with a weak Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction that reflects glycogen deposition in the liver and kidney and a positive immunoreaction for BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) that reflects activated apoptosis. This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabapentin toxicity has been underrecognized. Gabapentin (C 9 H 17 NO 2 ) is a water-soluble 1-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexaneacetic acid and a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin is not absolutely contraindicated in kidney disease, but it demands meticulous management. The key to its safe use is careful dose adjustments, rigorous monitoring for toxicity, and an open dialogue with your healthcare provider. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Gabapentin toxicity and side effects are well-known among nephrologists and fully described in the literature as myoclonic twitches, myopathy, neurotoxicity, etc., particularly in dialysis patients. 2,4. Rhabdomyolysis with associated acute renal failure is an uncommon side effect, but it has been described in earlier cases. 1,3 The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. However, there are a few descriptions of gabapentin-related Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Hi, Gabapentin is exclusively excreted by the Kidneys and undergoes no appreciable metabolism by the Liver. As to whether it is toxic to your Kidneys is probably a question that you should be asking your prescribing doctor. Our literature search found only 2 population-based studies examining the association between gabapentin use and risk of toxicity in patients with CKD (our search strategy is shown in Table S2 and the results in Table S3). 11, 14 Only one study examined the risk of toxicity by initial gabapentin dose in new users, 14 and, in a subgroup analysis Many antiretroviral medications have the potential for liver toxicity. But the incidence is much lower with contemporary treatment regimens. The risk of liver damage is higher for people with other liver infections, like hepatitis B, who have alcohol use disorder or who take other medicines that
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |