Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 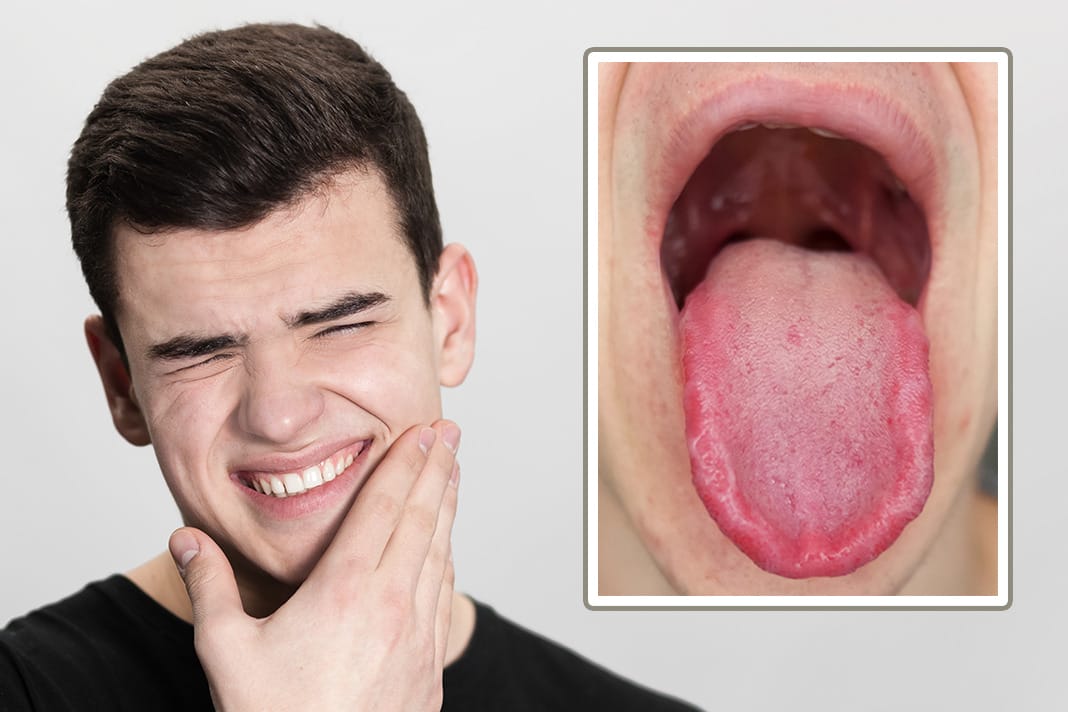 |
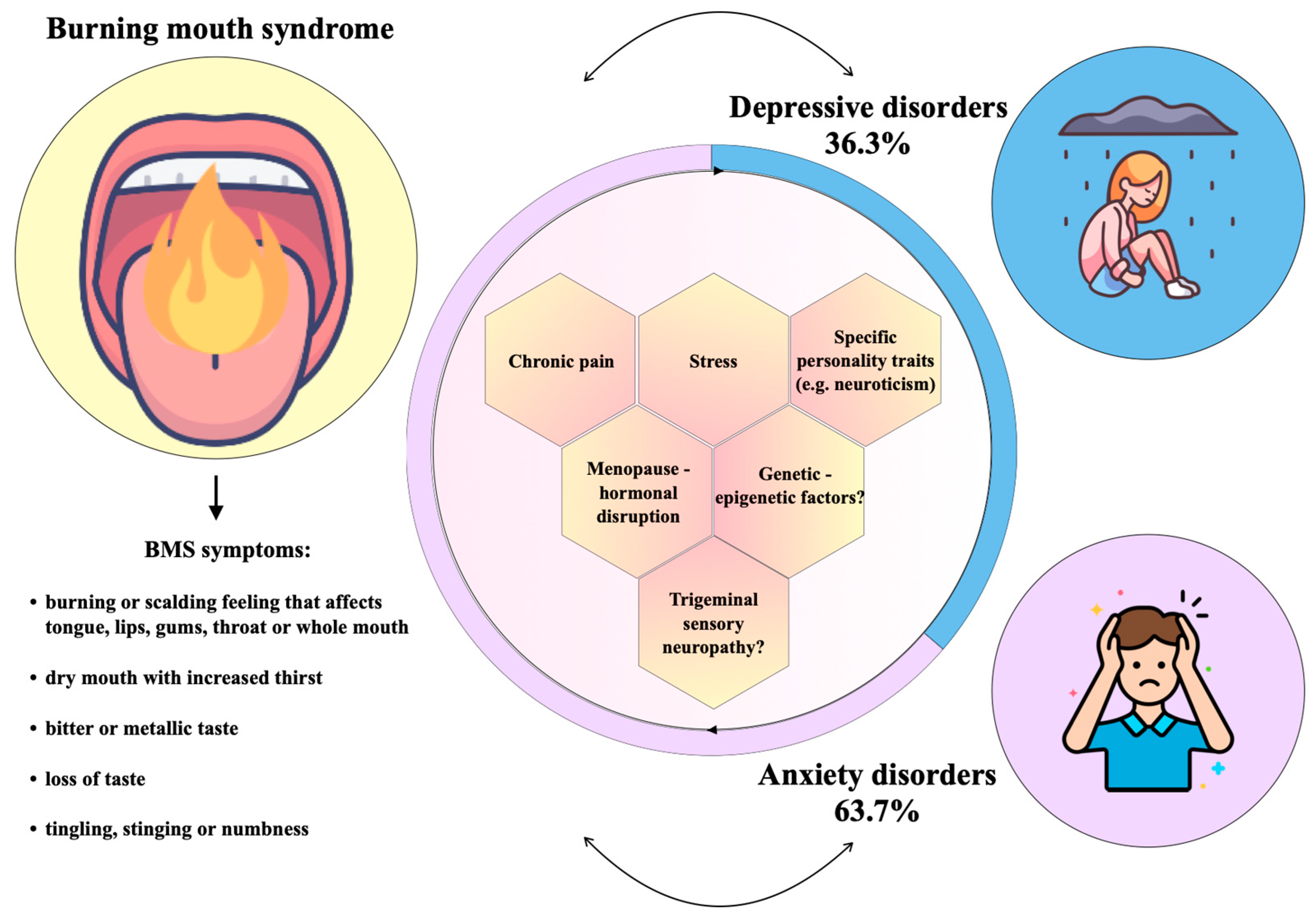
Burning mouth syndrome is a debilitating disorder involving oral pain that may have at least 4 underlying causes. Although several treatments have been proposed, none seems to be universally effective. We report the case of a 67-year-old woman with unremitting oral burning that is increased with the Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a disease that manifests as burning in the tongue or in any area of the oral mucosa, in the absence of clinically verifiable injuries. Objectives: To verify the efficacy of alpha lipoic acid (ALA) and gabapentin (GABA), used individually and jointly, to reduce the burning in patients with burning mouth and Gaba is naturally made, and it exists in the brain, but if you have a low amounts of Gaba it can cause burning mouth syndrome. Hope that helps. Let me know if you have any success, and what you're trying. Initial treatments with nortriptyline hydrochloride and sertraline hydrochloride were contraindicated because of adverse effects, but the administration of gabapentin significantly reduced oral Treatment depends on whether you have primary or secondary burning mouth syndrome. Primary burning mouth syndrome. There's no known cure for primary burning mouth syndrome. And there's no one sure way to treat it. Solid research on the most effective methods is lacking. Treatment depends on what symptoms you have and is aimed at controlling them. Heckmann SM, Heckmann JG, Ungethüm A, Hujoel P, Hummel T. Gabapentin has little or no effect in the treatment of burning mouth syndrome - results of an open-label pilot study. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13:e6–e7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01294.x. Systemic gabapentin has been found to be beneficial in relieving burning symptoms in patients with BMS [12]. However, systemic gabapentin has been associated with various side effects and a potential for misuse and overdose [13, 14]. Certainly, burning mouth syndrome has been associated with psychological disorders, including anxiety. 51-53 However, other studies comparing patients with burning mouth syndrome with the general population have found a lack of evidence for significant clinical elevations on any psychological subscales, including anxiety. 54-56 Practitioners Gabapentin has an average rating of 6.8 out of 10 from a total of 11 reviews for the off-label treatment of Burning Mouth Syndrome. 55% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 18% reported a negative experience. Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a chronic pain condition characterized by the presence of a burning sensation/pain of the oral cavity without any clinically evident signs of lesions or sys-temic causes [1]. Prevalence rates of BMS in the general population range between 0.7% to 15%, with higher rates seen in older females [2]. Initial treatments with nortriptyline hydrochloride and sertraline hydrochloride were contraindicated because of adverse effects, but the administration of gabapentin significantly reduced oral burning. The present case illustrates the effectiveness of gabapentin as a treatment of burning mouth syndrome. Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a term used for oral mucosal pain (burning pain or discomfort in the tongue, lips or entire oral cavity) without identifiable cause. General population prevalence varies from 0.1% to 3.9%. Many BMS patients indicate anxiety, depression, personality disorders and impaired quality of life (QoL). Various studies have shown that the use of ALA did not produce greater benefits on the burning mouth that the use of placebos (13,14). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant whose chemical structure consists of a molecule of gamma-aminobutyric acid covalently linked to a lipophilic cyclohexane ring. Burning mouth syndrome is characterized by a burning sensation in the tongue or other oral sites, usually in the absence of clinical and laboratory findings. Affected patients often present Gabapentin has little or no effect in the treatment of burning mouth syndrome—results of an open-label pilot study. European Journal of Neurology , 13(7). doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01294.x [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ] the mouth, and the inside surface of the lips, although the pattern is highly variable and burning may occur anywhere in the mouth. A patient may feel he/she has burnt the mouth with hot food and there may be a sour, bitter, or metallic taste in the mouth. The mouth may also feel dry. The onset of BMS is usually gradual Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is defined as idiopathic orofacial pain with intraoral burning or dysaesthesia recurring daily for more than 2 hours per day and more than 3 months, without any identifiable causative lesions, with and without somatosensory changes in International Classification of Orofacial Pain, 2020 (1). Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a chronic oral pain syndrome that primarily affects peri- and postmenopausal women. It is characterized by oral mucosal burning and may be associated with dysgeusia, paresthesia, dysesthesia, and xerostomia. The etiology of the disease process is unknown, but is thoug ALA, topical clonazepam, gabapentin, and psychotherapy may provide modest relief of pain in BMS. Gabapentin may also boost the effect of ALA. Capsaicin is limited by its side effects. Catuama showed potential for benefit. Future studies with standardized methodology and outcomes containing more patients are needed. Burning mouth syndrome is characterized by a burning sensation in the tongue or other oral sites, usually in the absence of clinical and laboratory findings. Affected patients often present with
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |