Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-605377259-de566072ac9a44c3a9ae688a8c6027c4.jpg) |
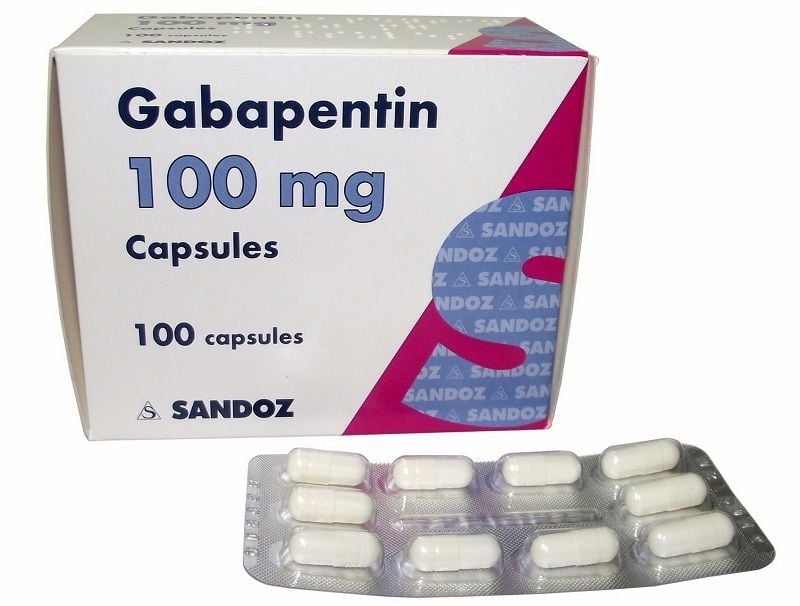
Background Gabapentin is often used to manage pain in children with dystonic cerebral palsy, however the evidence for its effectiveness in this population is limited. Gabapentin has been used in the management of neuropathic pain, epilepsy and occasionally movement disorders. A four-year retrospective, observational study analysed the use of gabapentin for severe dystonia in children at the Evelina London Children's Hospital. Spastic cerebral palsy, the most common type of cerebral palsy, is characterized by muscle spasms and muscle tightness that can cause pain, limb rigidity and limitations in range of motion and joint function over time. One of the goals of supportive treatments for spastic cerebral palsy is managing spasticity. This clinical practice guideline provides evidence‐based clinical recommendations for the use of pharmacological and neurosurgical management options for individuals with dystonia and cerebral palsy (CP), alongside practical considerations and suggestions for future research priorities. Introduction: Gabapentin has been used in the management of neuropathic pain, epilepsy and occasionally movement disorders. Methods: A four-year retrospective, observational study analysed the use of gabapentin for severe dystonia in children at the Evelina London Children's Hospital. Motor severity was classified according to the Gross Motor Objective: To compare the efficacy of gabapentin as add-on therapy to trihexyphenidyl in the treatment of children with dyskinetic cerebral palsy (CP). Methods: An open-labelled, randomized, controlled trial was conducted among children aged 3-9 y with dyskinetic CP [Gross Motor Functional Classification System (GMFCS) 4-5]. Doctors prescribe several medications to treat cerebral palsy and its symptoms. They use medications to control seizures or muscle spasms, for pain relief, to aid digestion, and more. Medicines can improve the symptoms of cerebral palsy, as well as associated conditions, but they also come with the risk of side effects. The American Academy of Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine (AACPDM) Care Pathway for Dystonia in Cerebral Palsy recommends baclofen first line and trihexyphenidyl second line as pharmacologic treatment. 10 Specific indications for other medications included consideration of gabapentin for people with dystonia and pain and clonidine for Dyskinetic cerebral palsy (DCP) is the second most common type of cerebral palsy after spastic forms. DCP is typically caused by non-progressive lesions to the basal ganglia or thalamus, or both, and is characterised by abnormal postures or movements associated with impaired tone regulation or movement coordination. Phenol injections have been used in the pediatric population but are poorly tolerated because of the adverse side effects of long-term pain and parasthesia. 30 One study showed that oral baclofen increased voluntary movement in children with cerebral palsy by initially reducing spasticity. 51 A weight-adapted dose of ITB has been used for Many children with cerebral palsy have seizures. Seizure medications can be helpful but also have some risks and side effects. Anti-epileptic medications work by reducing excessive brain stimulation. They calm hyperactivity in the child’s brain, which reduces and controls seizure activity. Gabapentin (Neurontin)-currently remains untested in cerebral palsy but has been used to treat spasticity in other populations; Dyskinetic CP Medications (dystonia, chorea and athetosis) Dyskinetic cerebral palsy medications for dystonia are prescribed to help reduce pain and the person’s spontaneous and unintended muscle movements. Some This rare but treatable cause of dystonia in childhood is a distinct entity from cerebral palsy . Perhaps in part due to the profound success of l-dopa therapy in reducing the impairments in Segawa’s disease, it has also gained use in children with cerebral palsy who have prominent dystonia. This is despite a limited understanding of the A wide assortment of medications is utilized to treat Cerebral Palsy. Some reduce symptoms, while others address complications. Drug therapy is used to control body movements, prevent seizures, treat depression, relax muscles, assist digestion, and manage pain. dotal evidence exists for gabapentin use in adult movement disorders (RLS & Wilson's Disease) but use in childhood, including severe dystonic cerebral palsy (CP) has not been reported. This study aims to: 1. Evaluate the use of gabapentin in a cohort of children with dystonia at the Evelina London Children's Hospital (ELCH) 2. Gabapentin is often used to manage pain in children with dystonic cerebral palsy, however the evidence for its effectiveness in this population is limited. Gabapentin has shown benefits for a variety of pain etiologies in adult patients, with off-label use as an adjunctive agent in pediatric patients occurring more frequently. To summarize the studies which evaluate safety and efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of pediatric pain. Evidence exist to support their use, however, it is not without risk and further research is required to highlight proper dosing, co-treatments and patient selection. Keywords: cerebral palsy, chronic pain, spasticity, dystonia, baclofen, diazepam, tizanadine, cyclobenzaprine, dantrolene. Background: Gabapentin is often used to manage pain in children with dystonic cerebral palsy, however the evidence for its effectiveness in this population is limited. Gabapentin is often used to manage pain in children with dystonic cerebral palsy, however the evidence for its effectiveness in this population is limited. The primary objective of this feasibility pilot study was to assess the factors which might impact on a future randomised controlled trial including the ability to recruit and retain participants, assess adherence/compliance to the
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-605377259-de566072ac9a44c3a9ae688a8c6027c4.jpg) |