Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
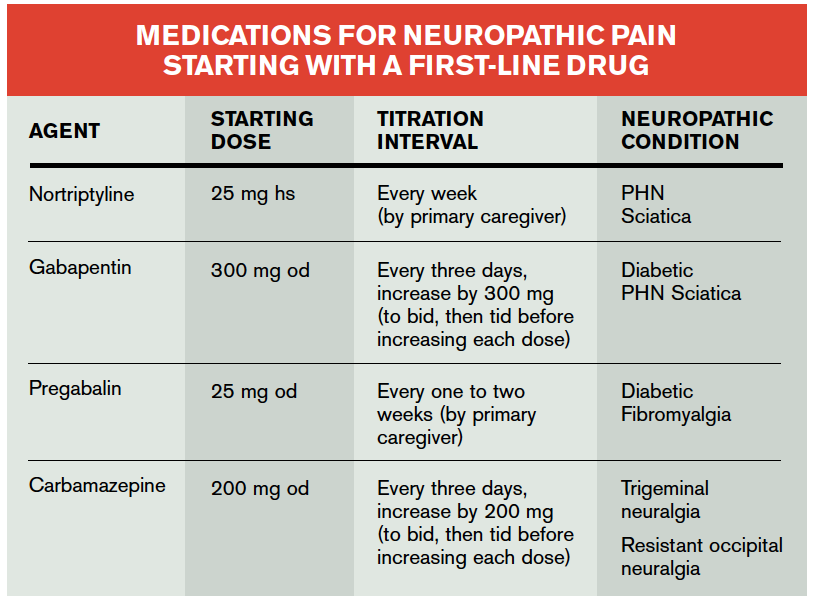
Anti-convulsant drugs such as gabapentin have demonstrated evidence of effectiveness in providing pain relief in acute and chronic neuropathic are commonly used as part of the pharmacological management of CRPS [64, 65]. Medications that are commonly used and/or have some clinical data in CRPS are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen or ibuprofen; tramadol; antidepressants such as amitriptyline, doxepin, or trazodone; anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin), clonidine, clonazepam, baclofen, topical capsaicin cream, the 5% lidocaine patch There are indications that gabapentin administered at doses of 600 to 1800 mg every 24 hours in the first eight weeks can cause some reduction in pain symptoms suffered by patients with CRPS-I. There is limited evidence that gabapentin reduces sensory abnormalities such as hyperaesthesia and allodynia. There is mixed evidence that vitamin C reduces the risk of CRPS after a fracture. 22, 23 Medications often used to treat neuropathic pain, such as anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin Neurotin (or Gabapentin, originally developed to treat epilepsy) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Low-dose Naltrexone (used to treat opioid dependence) Calmare Therapy; Ketamine; Pain (Drug) Pumps; Neridronate; Marijuana *Please note that my opinion of any treatment is often based upon my own research only. Despite its widespread use in treating CRPS, very low-quality evidence suggests that gabapentin is ineffective in the treatment of CRPS I. In 2016, a study compared amitriptyline and gabapentin for CRPS I and pediatric neuropathic pain. Both the medications were found to reduce pain intensity and disability significantly. While there is evidence from case series suggesting its efficacy in CRPS, gabapentin is widely empirically used for various neuropathic pain syndromes. Pregabalin, a closely related drug with the same mode of action, can be used as well, although there are currently no data evaluating pregabalin specifically for CRPS [ 12 ]. Gabapentin has been a great advance in treating CRPS/RSD and neuropathic pain. In addition to its effectiveness, it is very safe, with no reports of fatal overdose or organ This type of therapy uses a mirror to help trick the brain. Sitting before a mirror or mirror box, you move the healthy limb so that the brain perceives it as the limb that is affected by CRPS. Research shows that this type of therapy might help improve function and reduce pain for those with CRPS. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation neuropathy (DPN). Pregabalin has a chemical structure similar to gabapentin (Neurontin'), a medication originally developed to treat seizures that is now widely used to treat many varieties of neuropathie pain including CRPS/RSD (Compound Regional Pain Syndrome/Reflex Sympathy Dystrophy). Both medications reduce pain by nor- Lastly, prevention of CRPS following injury or trauma is an area currently being studied with evidence for vitamin C showing potential efficacy.⁵⁻⁷. Non-Conventional Treatments for CRPS: What the Data Reveal Gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug used for chronic pain management, specifically neuropathic pain. While the Physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT) can improve outcomes in CRPS, when started early (symptoms for less than 1 year). 3 Objectives of PT and OT in CRPS are to improve range of motion, desensitization, minimize swelling, promote normal positioning, decrease muscle guarding, and increase functional use of the extremity. 4 CRPS meds: Gabapentin and Lyrica (pregabalin) are the most widely used AEDs for treating CRPS. Another commonly used adrenergic drug is clonidine, which stimulates alpha 2 receptors and inhibits the release of NE. Gabapentin had a mild effect on pain in patients CRPS I. It significantly reduced the sensory deficit in the affected limb. A subpopulation of CRPS patients may benefit from gabapentin, but then for each individual patient the benefit has to be weighed against the frequently occurring side effects. Competing interests Gabapentin had a mild effect on pain in CRPS I. It significantly reduced the sensory deficit in the affected limb. A subpopulation of CRPS patients may benefit from gabapentin. Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition often involving hyperalgesia and allodynia of the extremities. CRPS is divided into CRPS-I and CRPS-II. Type I occurs when there is no confirmed nerve injury. Type II is when there is known associated nerve injury. Female gender is a Gabapentin and pregabalin are the most widely used anticonvulsants for treating CRPS. Common side effects of anticonvulsants include drowsiness, dizziness and weight gain. There's also a small increased risk of suicidal thoughts, which may occur as early as a week after starting treatment. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Overall, evidence is considered insufficient for use of gabapentinoids for CRPS-related pain. However, three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) did find gabapentin to result in significant improvement in pain whereas one RCT reported use of amitriptyline to be equally as effective as gabapentin. [90, 91] A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that gabapentin was mildly beneficial for pain and sensory symptoms in CRPS type I. Gabapentin has been shown to be effective in treating other neuropathic pain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |