Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
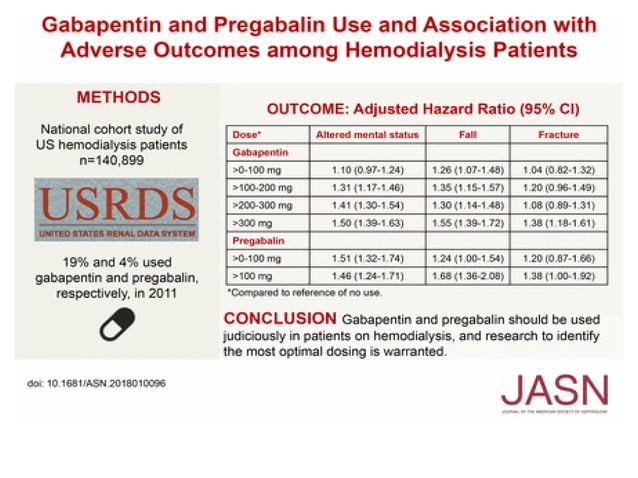
%PDF-1.7 %µµµµ 1 0 obj >/Metadata 867 0 R/ViewerPreferences 868 0 R>> endobj 2 0 obj > endobj 3 0 obj >/ExtGState >/XObject >/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC Treatment with gabapentinoids in patients with inflammatory arthritis (IA) appears to increase the risk of fractures, according to findings of a UK study published in BMC Medicine. The case-case-time-control study, which included 28,293 patients hospitalized for hip fractures in Australia, found that gabapentinoid use was associated with an increased risk of hip fracture, especially in patients who were frail and had chronic kidney disease. Examining associations by gabapentinoid type revealed stronger increased risks of fragility fractures with recent gabapentin use in all models (fully adjusted OR 1.79 [1.21, 2.64]) than for recent pregabalin use (fully adjusted OR 1.33 [0.82, 2.14]). A study published in JAMA Network earlier this month investigated the relationship between the use of gabapentinoids, a class of drugs that includes pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin), and the risk of hip fractures. Similar to previous studies linking antidepressant and benzodiazepine use to hip fractures, the research showed that After adjusting for comorbidities and the use of other medications, researchers estimate that people over age 50 have a 30% higher risk of hip fractures within 60 days of gabapentinoid dispensing. The risk is even higher for patients with chronic kidney disease (141%) and those with high scores for frailty (75%). Gabapentin (Neurontin) can also be utilized in the multimodal treatment of rib fractures, but there is no consensus on its proven benefit. A recent randomized control trial of gabapentin The researchers used a case–crossover design (i.e., patients served as their own controls over time) to examine the temporal relation between gabapentin exposure and hip fracture. After adjusting for comorbidities, relevant medication use (e.g., benzodiazepines, opioids), and increased gabapentinoid prescribing over time, the odds ratio for In this case-case-time-control study of Australian residents hospitalized for hip fracture, gabapentinoid use was associated with an increased risk of hip fractures, especially in patients who were frail or had chronic kidney disease. A new study reveals that current gabapentinoid use in inflammatory arthritis patients increases fracture risk by 36%. With no proven efficacy for pain management in IA, experts call for safer prescribing practices. Achieving adequate pain control for rib fractures remains challenging; prescription of alternatives to narcotics is imperative to curtail the current opioid epidemic. Although gabapentin has shown promise following elective thoracic procedures, its efficacy in patients with rib fractures remains unstudied. We hypothesized that gabapentin, as compared to placebo, would both improve acute pain In this population-based case-case-time-control study of Australian adults hospitalized for first hip fracture, the use of gabapentinoids was associated with a higher risk of hip fractures, especially in patients who were frailer or with chronic kidney disease. The link between gabapentinoids and hip fractures existed across different age groups, but the odds of hip fracture were higher among patients who were frailer or had chronic kidney disease. Gabapentinoid use increased eightfold in Australia between 2012 and 2018, with one in seven Australians aged 80 and older prescribed a gabapentinoid during Observational studies in non-IA populations suggest gabapentinoids are associated with fractures but are limited by methodological heterogeneity/potential residual confounding. Patients with IA generally have an increased risk of fracture so may be particularly vulnerable. Gabapentin’s use as in multimodal pain regimens for controlling acute pain secondary to rib fractures remains common [32], and recent consensus guidelines recommend consideration of gabapentin as part of multi-modal analgesia [32, 33]. However, these recommendations were assigned a low grade in recognition of poor data on the topic. Although gabapentin has shown promise following elective thoracic procedures, its efficacy in patients with rib fractures remains unstudied. We hypothesized that gabapentin, as compared to placebo, would both improve acute pain control and decrease narcotic use among critically ill patients with rib fractures. Researchers found that gabapentinoids were linked to a 30% increased hip fracture risk after adjusting for concurrent medications and time trends. The risk was higher among frail individuals (1.75 times) and those with CKD (2.41 times). Forty patients were randomized. The groups were well matched with respect to age, gender, prior narcotic use, tobacco use, and prior respiratory disease.Although the median RibScore did not differ between groups, the gabapentin group had a higher median number of ribs fractured as compared to the placebo group (7 vs. 5, respectively). In comparison, previous case-crossover studies on hip fractures demonstrated 124% increased odds with antidepressant use, 42 47% increased odds with antipsychotic use, 43 55% to 75% increased odds with benzodiazepine use, 44 and 62% increased odds with opioid use. 43 However, these case-crossover studies did not include any control case Gabapentin is an example of an extensively studied antiepileptic drug which can be used to treat neuropathic pain in SCI. Neuropathic pain occurs frequently in SCI patients and is difficult to treat due to complex nervous system changes. Neuropathic pain following an injury of the spinal cord can present above or below the level of injury.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |