Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
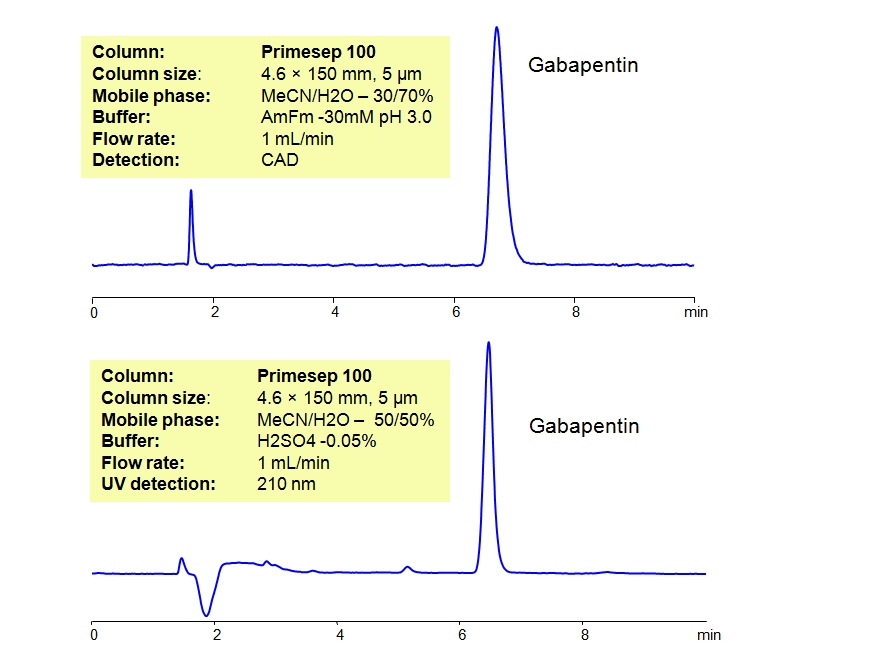
What non-hormonal medicines are used to reduce hot flushes? The non-hormonal medicines used to reduce hot flushes in women include gabapentin, clonidine, venlafaxine or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The treatment option depends on the individual. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® available as 100mg, 300mg, Gabapentin is effective in the control of hot flashes at a dose of 900 mg/day, but not at a dose of 300 mg/day. This drug should be considered for treatment of hot flashes in women with breast cancer. earched the PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases for English-language articles published until June, 2018. The following search terms were used: “menopause,” “hot flushes,” “vasomotor symptoms,” “gabapentin,” and “non-hormonal therapy.” Primary outcomes were frequency, duration, and composite score of hot flushes. Secondary outcomes were adverse effects and Examining individual trials, the two trials that evaluated 900 mg/d of gabapentin reported that hot flashes were decreased by 45% to 50% (Fig 1E). 15,16 In the individual patient trial that studied 2,400 mg/d, hot flashes were reported to be reduced by approximately 80% (Fig 1E). 17 In this last trial, however, there was a much more substantial Gabapentin, known by its brand name Neurontin, is primarily used to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. However, it has been found to be effective in alleviating hot flashes. Gabapentin works by mimicking the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The mechanism of action is not well established, and preliminary trials suggest that it may be useful in bipolar disorders. The central nervous system neurotransmitter effects of gabapentin may be responsible for reducing the frequency of hot flashes. Gabapentin has been approved for use in France for postherpetic neuralgia. Based on the anecdotal information, the current phase 2 clinical trial was developed to more definitively evaluate gabapentin's efficacy against hot flashes and its associated toxicity. Fortunately, a new treatment option may be able to treat hot flashes without the risk. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, may be effective for the treatment of hot flashes. Often sold as Neurontin, gabapentin is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of epilepsy. In studies, gabapentin reduced hot flashes from 45%-71% depending on the dose. In one, albeit small, clinical trial 2,400 mg of gabapentin divided three times a day was as effective as 0.625 mg of Premarin a day (which is a standard dose for hot flashes). Other agents that have been used to alleviate hot flashes include belladonna/ergotamine tartrate/phenobarbital combination, dong quai, evening primrose oil, gabapentin, ginseng, mirtazapine The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved the official use of gabapentin for hot flashes. However, clinical studies show it can be effective in reducing their frequency. At doses used to control hot flashes, gabapentin was well tolerated, with drowsiness as its most reported adverse effect. Gabapentin can be considered effective in the treatment of hot flashes and should be considered a reasonable alternative when estrogen therapy is not desired. The use of gabapentin was associated with reductions in the severity and frequency of hot flashes in menopausal women by 20% to 30%, but the high level of heterogeneity across the studies precluded the provision of a reliable summary effect. Gabapentin 300 mg/day could be useful to relieve hot flashes in women for whom hormone therapy is not suitable or when hot flashes do not respond to other therapies. Further researches are needed to determine the efficacy of gabapentin use for longer periods or at higher doses. Other antidepressants that have been used to treat hot flashes include: Venlafaxine (Effexor Xr). Paroxetine (Paxil). Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). Gabapentin Helps Hot Flashes. In BREEZE 3, 600 postmenopausal women (mean age, 54.0 years; mean time since last menstrual period, 114 months; mean body mass index, 29.4 kg/m²) were randomized to Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. Research presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) indicates that an investigational extended release (ER) formulation of gabapentin (Serada, Depomed) is effective for the treatment of hot flashes and sleep Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown that when compared with placebo, gabapentin is effective at reducing hot flash frequency by 54% and hot flash composite score (combined hot flash frequency and severity score) by 31% to 51%. A 2005 study by Pandya et al. randomized 420 women with breast cancer and experiencing at least 2 hot flashes in 24 hours to one of three groups: gabapentin 300 mg daily, gabapentin 900 mg daily, or placebo 23. After 8 weeks, the 300 mg dose group showed a modest 20% reduction in hot flashes, but the 900 mg dose group showed a reduction of Objective: Gabapentin is used to treat vasomotor symptoms (VMS) in postmenopausal women with contraindications to hormonal therapy or who prefer alternatives. We investigated the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin for treating menopausal hot flushes via a meta-analysis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |