Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
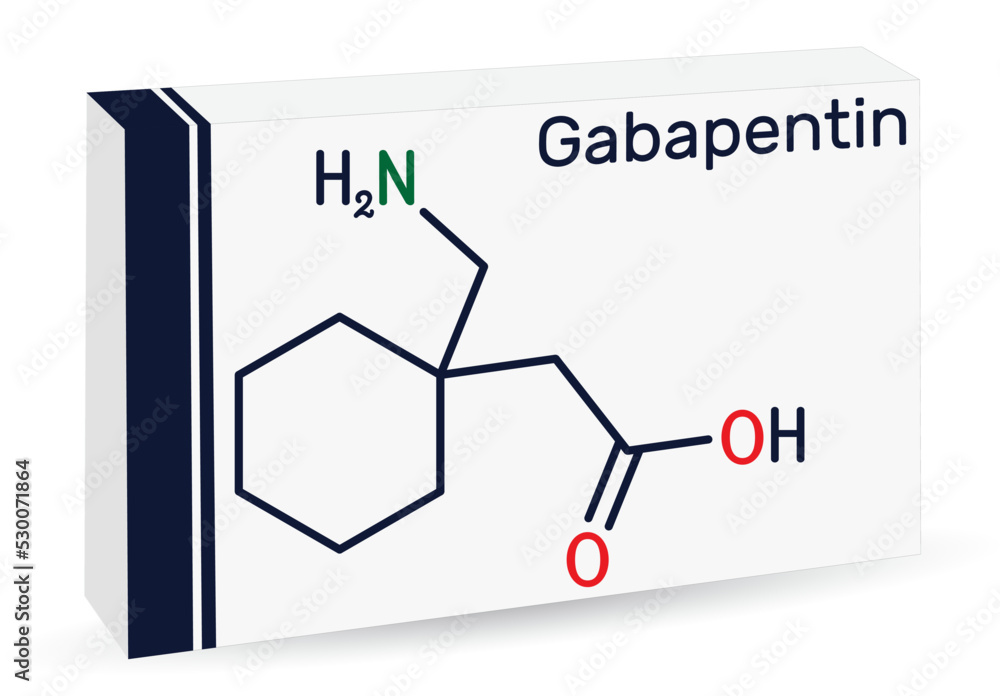
Affecting more than 300 million people worldwide, osteoarthritis (OA) is common and difficult to manage. Although OA can involve any joint, the knee, hip, and hand are most commonly affected. Gabapentin is used off-label for the treatment of severe knee osteoarthritis and typically when all other treatment options have failed to provide adequate relief. The rationale behind its use is based on the types of pain that OA causes, namely nociceptive pain (pain caused by damage to tissues) and nociplastic pain (pain caused by altered Evidence-based guidelines recommend the anticonvulsant gabapentin as a first-line analgesic for the treatment of neuropathic pain (pathologic pain that results from abnormal processing of stimuli Objective: Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed to treat nociplastic pain. Some patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) suffer from both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. We examined the cost-effectiveness of adding gabapentin to knee OA care. We used the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of knee OA, to examine the value of gabapentin in treating knee OA by comparing three strategies: 1) usual care, gabapentin sparing (UC-GS); 2) targeted gabapentin (TG), which provides gabapentin plus usual care for those who screen positive for nociplastic pain on the modified PainDETECT questionnaire (mPD-Q) and Objective: Gabapentin can treat neuropathic pain syndromes and has increasingly been prescribed to treat nociplastic pain. Some patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) suffer from both nociceptive and nociplastic pain. We examined the cost-effectiveness of adding gabapentin to knee OA care. Osteoarthritis (OA) affects tens of millions of Americans and is a leading cause of disability and reduced quality of life across the globe. Other than joint replacement surgery, there is no known "cure" for OA, and most treatments focus on relief of symptoms such as pain. Gabapentin shows promise in managing arthritis pain, particularly in knee osteoarthritis and potentially in postoperative settings. Its efficacy is linked to its ability to modulate pain pathways and reduce inflammation. Gabapentin’s Role in Osteoarthritis Treatment. Some studies suggest that gabapentin, in its oral form, may help alleviate OA symptoms. By targeting specific nerve pathways, gabapentin could potentially reduce pain and inflammation in the joints. Average use of acetaminophen as rescue medication was much lower in the pregabalin and duloxetine groups than in the placebo group . The use of rescue medication in the placebo group was higher, amounting to 56 days. Per protocol analysis. There was a reduction in reporting pain in all three groups at the end of the trial. Also, many of the medicines used to treat fibromyalgia work by boosting the amount of serotonin in your body. Taking two or more of these drugs together could lead to a potentially life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. We used the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of knee OA, to examine the value of gabapentin in treating knee OA by comparing three strategies: 1) usual care, gabapentin sparing (UC-GS); 2) targeted gabapentin (TG), which provides gabapentin plus usual care for those who screen positive for nociplastic pain on the modified PainDETECT questionnaire (mPD-Q) and We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. While gabapentin is generally not prescribed to treat arthritis symptoms, one randomized clinical trial showed that gabapentin, when paired with duloxetine, was shown to have promising effects in pain reduction and improved functional status in patients with knee osteoarthritis over a three-month period, with gabapentin’s effects manifesting Researchers compared the efficacy of gabapentin in treating knee OA using the Osteoarthritis Policy Model, a validated Monte Carlo simulation of the disease. Background Pain is the major complication of osteoarthritis (OA) patients and is a decisive symptom for medical intervention. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) derivatives are optional painkillers but not widely used in pain management of OA patients. We synthesized the efficacy and safety of GABA derivatives for OA pain management. Methods We searched Medline, Cochrane CENTRAL, Embase, and Gabapentin (generic for Neurontin), is commonly prescribed for neuropathy. Neuropathy is pain felt along the nerve endings. Many diabetics suffer from neuropathy. • Gabapentin and duloxetine are both effective in reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis. • Medical treatment is used for releiving pain in knee osteoarthritis. Efficacy of duloxetine and gabapentin in pain reduction in patients with knee osteoarthritis Gabapentin is not specifically approved for osteoarthritis but may help some patients manage their pain. It is primarily an anticonvulsant medication, and its effectiveness for OA-related pain varies among individuals. Gabapentin shows promise in managing arthritis pain, particularly in knee osteoarthritis, by reducing pain severity and improving functional status over time. Its mechanisms involve both central and peripheral actions, including modulation of pain-related growth factors and nerve sensitivity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |