Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
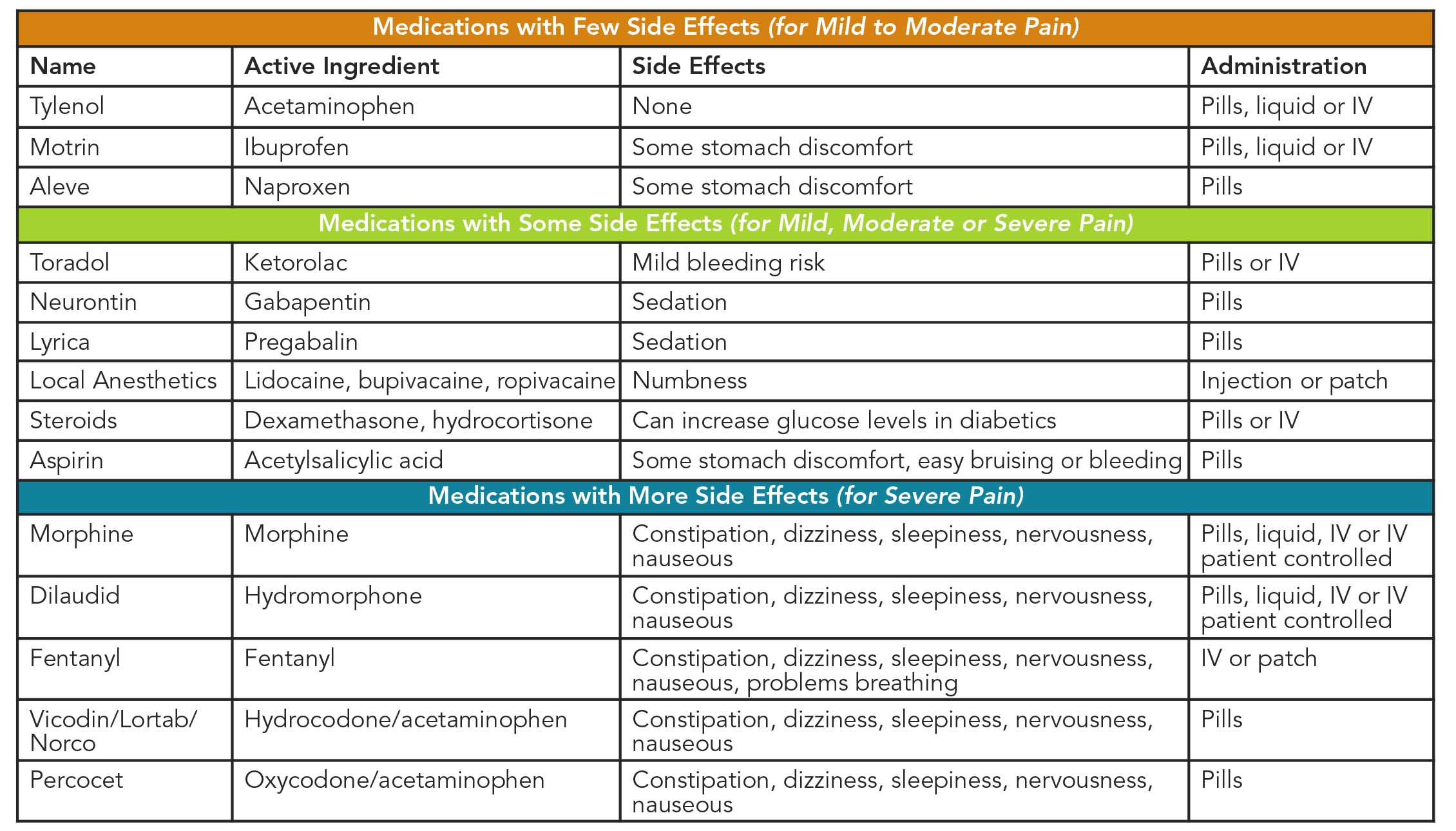
This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. • Gabapentinoids such as gabapentin and pregabalin are often included in perioperative multimodal analgesia regimens in an attempt to reduce acute, subacute, and chronic pain after surgery • Current American Pain Society and European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy guidelines offer conflicting recom- We recommend being selective with regard to using gabapentinoids for acute postoperative pain management after careful consideration of the potential side effect profile based on patient comorbidities as well as the expected severity of postoperative pain. Perioperative gabapentin, 1200 mg, administered preoperatively plus 600 mg every 8 hours continued for 72 hours after surgery did not affect time to pain cessation, the rate of pain resolution, or the proportion of patients with chronic pain at 6 months or 1 year following surgery. Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study In addition, because pain intensity may be an unmeasured confounder of the association between gabapentin use and delirium, we examined how the RR estimate would change under various scenarios: (1) the prevalence difference in severe pain between gabapentin users and nonusers and (2) the relative risk between severe pain and delirium from the The use of gabapentin before surgical incision showed an overall cumulative reduction of pain score, in the first 24 hours after surgery, by an average of 1.04 (0-10 pain scale) in comparison to placebo (MD, –1.04; 95% CI, –1.45 to –0.63; P < .00001). Hah et. al. reported that in a randomized clinical trial of 410 patients undergoing a variety of surgeries (294 of which were orthopedic surgeries), patients given 1200 mg gabapentin preoperatively and 600 mg three times daily postoperatively for three days, demonstrated a 24% increase in the rate of opioid cessation after surgery. 27 Menigaux Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. A combination of therapies and medications will be used together for better pain control after your surgery. Reduce pain from sensitive nerves. Gabapentin Gabapentin 250 mg is statistically superior to placebo in the treatment of established acute postoperative pain, but the NNT of 11 for at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours with gabapentin 250 mg is of limited clinical value and inferior to commonly used analgesics. Surgeons have made substantial efforts to decrease postoperative opioid prescribing, largely because it can lead to prolonged use. These efforts include adoption of non-opioid pain medication including gabapentin. Gabapentin appears safe and well tolerated when used for persistent post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients, although minor side effects do occur. Gabapentin may relieve refractory chest wall pain in some of these patients, particularly those with more severe pain. Furthe Pain management after total hip arthroplasty (THA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. This Know that your prescription is good up to 7 days after it is issued. Check if you were given a long-acting anesthetic (stops pain at the wound or surgical site). This may help control your pain for several days, and you may need fewer or no opioids. Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic The findings contradict guidelines published by the American Pain Society (APS) in 2016, which advocate “around the clock” use of gabapentin, pregabalin and other nonopioid drugs both before and after surgery. In summary, the administration of gabapentin was effective in decreasing postoperative narcotic consumption and the incidence of pruritus. There was a high risk of selection bias and a higher heterogeneity of knee flexion range in this analysis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |