Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
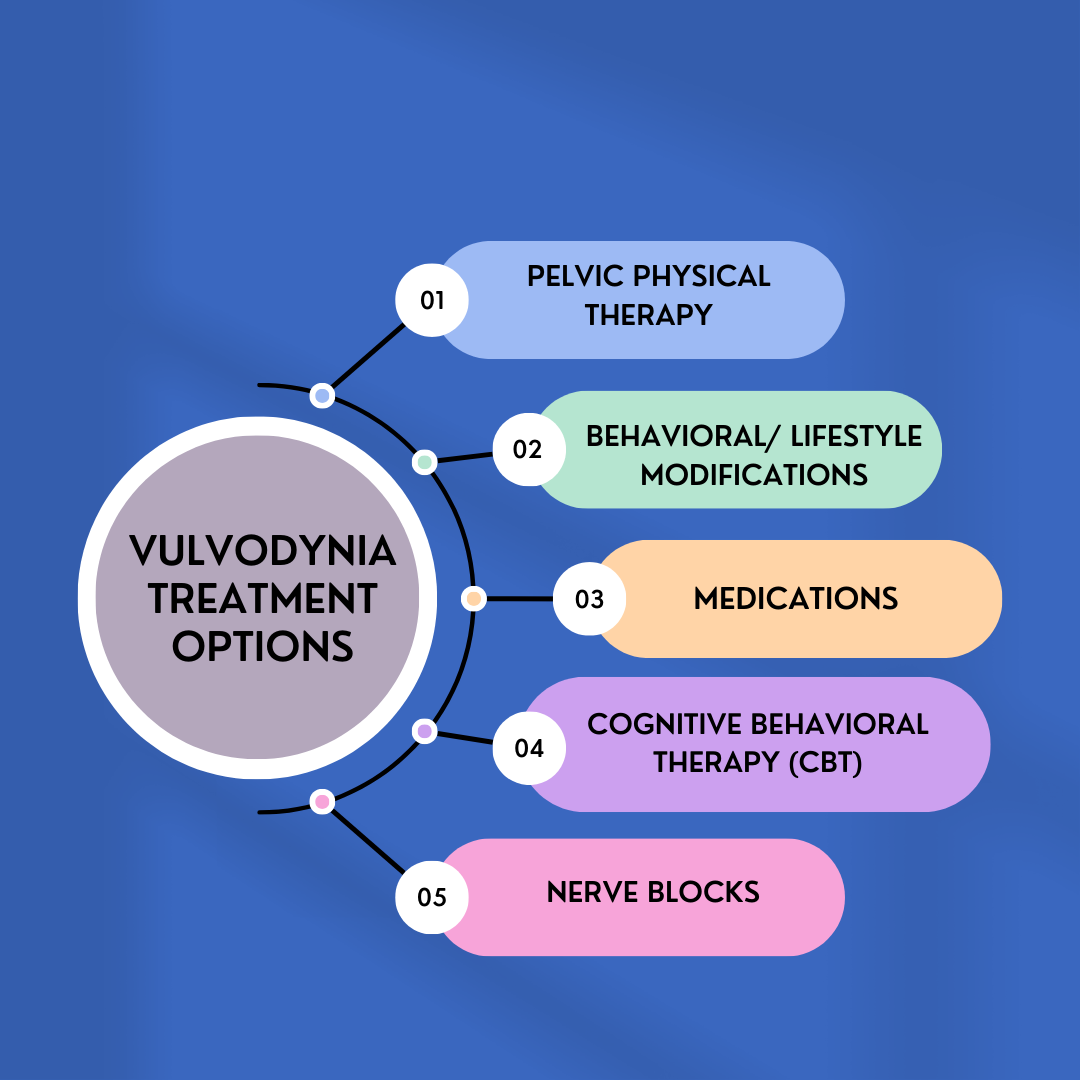
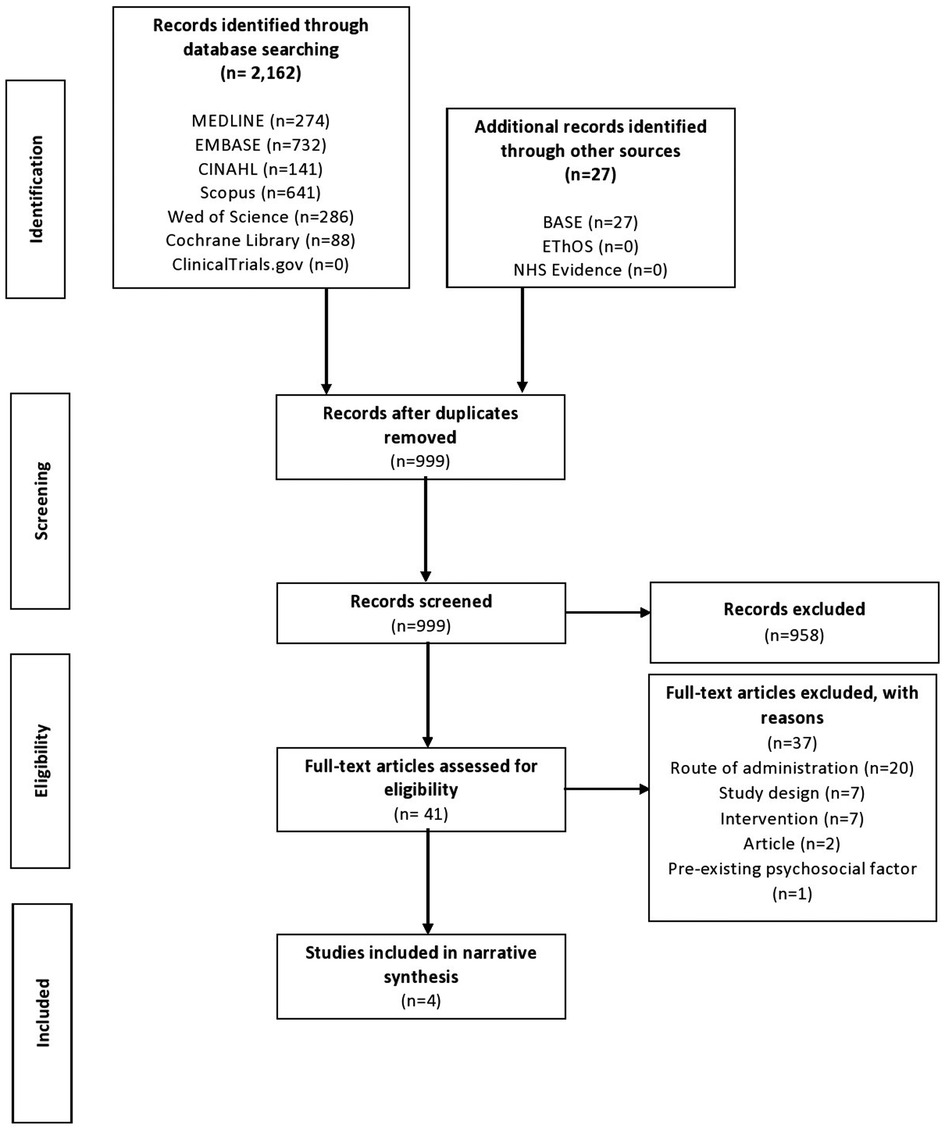
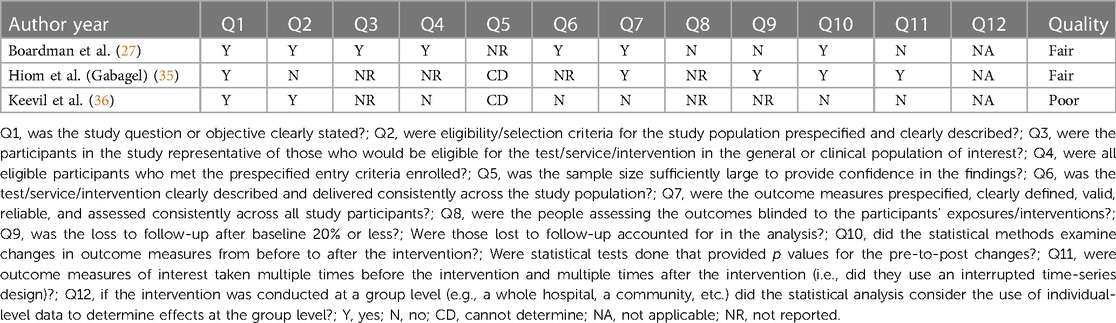
Vulvodynia can affect people of all ages, but it’s more common in younger women aged between 18 and 25. Vulvodynia describes unexplained pain in your vulva, which many women describe as a soreness, burning or stinging. It is usually diagnosed when another cause can’t be found. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the treatment of vulvodynia. Topical formulations of gabapentin have shown promise in animal models and case reports investigating its use in other pain conditions. The most frequently used treatments are medications that may include antidepressants, anticonvulsants like orally administered gabapentin, and local anesthetics. Since vulvodynia is a chronic condition, treatment usually needs to be continued indefinitely. Many women prefer a treatment with less systemic effects like a gabapentin topical cream. Medications used to treat vulvar pain include topical, oral, and intralesional medicinal substances, as well as pudendal nerve blocks and botulinum toxin. Tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants also can be used for vulvodynia pain control. to benefit vulvodynia include topical corticoste roids, topical testosterone, and topical antifungal medications. Table 1. Topical Medications Used to Treat Vulvodynia Topical medication Dosage Side effectsa 5% lidocaine ointment Apply to skin as needed; dispense 30-g tube. Do not use .20-g of ointment in a 24-h period. Erythema or edema. Rare Gabapentin: Highest tolerable oral dose between 1200 and 3000 mg per day for 8 weeks: Oral gabapentin, 1200–3000 mg per day for 8 weeks: Anti-inflammatory agents: Submucosal methylprednisolone (1, 0.5, 0.3 mL) once per week for 3 weeks: Corticosteroids: 0.05% Clobetasol propionate or 0.5% topical hydrocortisone ointment for 28 nights Antiepileptics treat vulvodynia by calming the central nervous system and are used to treat neuropathic pain conditions. 89, 90 In a multicenter double‐blind crossover RCT, oral gabapentin did not reduce dyspareunia. 90 There is no evidence to support the use of oral gabapentin for vulvodynia. Since oral gabapentin is frequently used for neuropathic pain, Boardman et al 23 hypothesized that topical gabapentin could be effective in treating vulvodynia. Records were gathered of pre- and postmenopausal women diagnosed with localized or generalized vulvodynia over a 6-year period and were narrowed to those treated with topical gabapentin. Vulvodynia is a leading cause of dyspareunia in premenopausal women, causing considerable morbidity and sexual dysfunction. A multimodal approach is used to treat vulvodynia. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the treatment of vulvodynia. Although gabapentin is recommended and commonly prescribed for vulvodynia, its value in such cases is usually associated with complaints that have neuropathic components, such as dynamic allodynia. Gabapentin rating summary. 6.6 average rating out of 10. 10 ratings from 10 user reviews. Compare all 14 medications used in the treatment of Vulvodynia. Twenty-five trials explored the use of oral and topical medications in the treatment of vulvodynia. Data Synthesis: Vulvodynia is a poorly understood disease with an unknown etiology. Oral tricyclic antidepressants and gabapentin continue to be the most commonly used treatments for vulvodynia pain. Vulvodynia is a diagnosis of exclusion, meaning that we first have to rule out other causes of vulvar pain. • We will do a pelvic exam, and we may use a small swab or Q-tip® to collect a sample to rule out a yeast infection or bacterial infection. We will also use the soft side of a Q-tip® and touch your vulva in different Tricyclic antidepressants should be considered for the treatment of vulvodynia. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and gabapentin (Neurontin) should be considered for symptomatic relief Different Vulvodynia Medications. Gabapentin. This is a well known anticonvulsant (anti-epileptic drug). It also affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in some types of pain. Gabapentin is also used to: “treat adult neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster). Results: Between January 2001 and December 2006, 51 women with vulvodynia (19 or 37% with generalized vulvodynia, 32 or 63% with localized) were treated with 2% to 6% gabapentin. After a minimum of 8 weeks of therapy, the mean pain score among the 35 evaluable women was significantly reduced from 7.26 to 2.49 (mean change -4.77, 95% confidence Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Lyrica have been used to treat chronic pain conditions, including vulvodynia Gabapentin tends to have fewer side effects than the tricyclic antidepressants. Physical therapy of the pelvic floor muscles is commonly employed in the treatment of vulvodynia, for both local and generalized pain. This page gives you information about the medication gabapentin which you have been prescribed to reduce the pain of vulvodynia. Vulvodynia is pain in the vulva (area around the outside of the vagina) that lasts at least 3 months and does not have a specific cause. We evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin, in an extended release formulation, in women diagnosed with localized provoked vulvodynia, defined as superficial vulvar vestibular pain that is provoked by touch, in a demographically diverse sample. Objective: To evaluate whether extended-release gabapentin is more effective than placebo among women with vulvodynia. Methods: In a multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized crossover trial, gabapentin (1,200-3,000 mg/d) was compared with a placebo.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |