Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
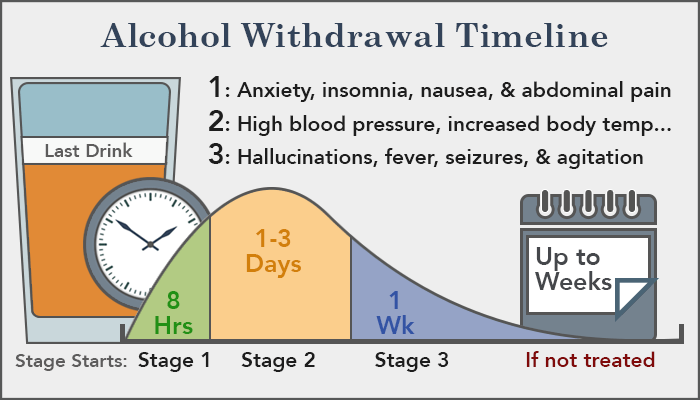 |  |
The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Some doctors use gabapentin and other medications to help treat alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication used for epilepsy seizures, restless leg Gabapentin can help relieve neuropathic pain when alcohol-related nerve damage is the cause. Reducing discomfort is vital to the entire recovery process. Is Gabapentin Addictive? Given gabapentin’s potential use in addressing disorders like alcohol withdrawal, the issue of whether it is addictive is an important one. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and neuropathic pain. However, when used excessively or misused, it can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Some common questions you might have include: How long does gabapentin withdrawal last? Does stopping gabapentin cause withdrawal, or can you just quit cold turkey? Gabapentin may be used to treat alcohol dependence, addiction, and withdrawal. It can help with managing the anxiety, insomnia, headaches, or pain that often occurs in substance withdrawal. Add-on gabapentin with a dose of 1600 mg/d is effective in reducing some of the withdrawal symptoms in patients addicted to opiate undergoing methadone-assisted detoxification. Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4. What Are the Symptoms of Gabapentin Withdrawal? The main symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal are nausea, anxiety, headaches, and seizures. According to the study titled “Gabapentin Withdrawal Syndrome” by Tran et al., published in Pharmacotherapy in 2005, gabapentin withdrawal occurs in patients who abruptly discontinue the medication, particularly after long-term use or high doses. Typically, a doctor will advise gradually tapering gabapentin to avoid dangerous side effects and withdrawal symptoms. This advice applies to both generic gabapentin and brand name versions of How quickly gabapentin withdrawal symptoms come on depends on several variables, including how long you have been using, dosage, and whether you are using gabapentin with other substances of abuse. The example case study above shows that gabapentin withdrawal can surface in 2–3 days and then intensify. Withdrawal symptoms can start from 12 hours to 7 days after stopping the medication. Gabapentin is prescribed off-label for several conditions including: Gabapentin is also used off-label alcoholics. Gabapentin is a potentially efficacious treatment for reducing the risk of relapse to harmful drinking patterns in outpatient management of alcoholism. Gabapentin's ease of use, rapid titration, good tolerability, and efficacy in both the withdrawal and chronic phases of treatment make it particularly appealing. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. The safest way to stop using gabapentin is to taper off the medication under the supervision of a doctor. Are You Covered For Treatment? al is necessary. Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other be aware of gabapentin’s limitations for treating alcohol use disorder and be attentive to emerging data on risks and benefi ts. KEY POINTS Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. A double-blind trial of gabapentin 900mg/d in 40 subjects concomitantly treated with methadone did not significantly reduce severity of opiate withdrawal relative to placebo, perhaps as a function of the relatively low dose of gabapentin used (900/mg/d); when gabapentin was given as an add-on to methadone in an open-label study, greater When gabapentin use is suddenly reduced or stopped, withdrawal symptoms can emerge because the brain struggles to readjust to functioning without the medication’s influence. One major factor driving these withdrawal symptoms is how gabapentin alters the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Gabapentin withdrawal can begin within 12 hours and last up to 7 days. As of 2023, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has not classified gabapentin as a controlled substance because experts have always believed it showed little potential for abuse or dependence. When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |