Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
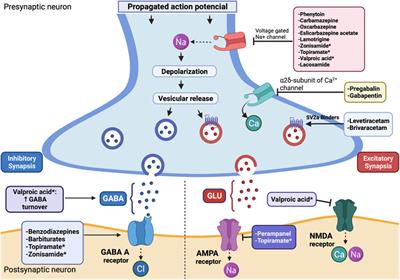
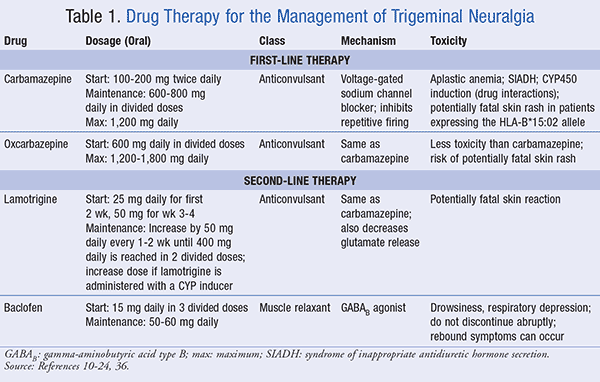
Keppra is known for its fast onset of action and high bioavailability, making it an effective choice for acute seizure management. In contrast, Gabapentin is often used to treat neuropathic pain and has a more gradual onset of action. However, when it comes to effeciency, Keppra often takes the lead. Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Nerve pain due to diabetic peripheral neuropathy in adults. Partial seizures in children (age 1 month and older) who have epilepsy. Doctors may also prescribe Pregabalin and Gabapentin for other uses besides the conditions specified by the FDA. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Levetiracetam (Keppra) are both antiepileptic medications, but they have some key differences. Gabapentin is used to treat certain seizures and nerve pain, while Levetiracetam is used for various types of seizures, including partial-onset, myoclonic, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is one of the most common causes of facial pain seen in dental and neurologic practices. This classic neuropathic pain disorder has been known for centuries.1 The International Headache Society (IHS) defines TN as a “unilateral disorder characterized by brief electric shock-like pains, abrupt in onset and termination, and limited to the distribution of one or more The current study tested the antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of the anticonvulsant drug, levetiracetam compared with the standard drug, gabapentin, in a model of streptozotocin-induced peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Use Gabapentin for ongoing pain, Tramadol for short-term use. Mechanism of Action: Targets nerve pain by affecting calcium channels in the brain: Opioid-like medication, modifies pain perception in the brain: Consider Tramadol for post-op pain, Gabapentin for long-term. Sedation Risk: Moderate, more likely with higher doses Keppra vs Gabapentin: Keppra (levetiracetam) is primarily used to treat seizures, while Gabapentin targets nerve pain and some seizure types. Keppra has fewer drug interactions, but Gabapentin may cause more sedation. Their uses often depend on the specific condition being treated. I don't know if gabapentin provides as much anti-seizure effect as Keppra. Gabapentin has helped with nerve pain for me, but hasn't really improved numbness in my feet. I also recently started Vimpat as my focal seizures were becoming more frequent. We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gabapentin and Keppra. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 565,459 people who take Gabapentin and Keppra, and is updated regularly. In patients with chronic neuropathic pain, does levetiracetam (Keppra) effectively treat pain symptoms? Based on low-quality evidence, levetiracetam was found to be ineffective for the Neurontin (gabapentin) and Keppra (levetiracetam) are two such drugs that are often prescribed for these conditions. They each impact different aspects of neuronal excitability, but both have effects in reducing seizure frequency in patients with epileptic disorders. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Keppra is an anticonvulsant that is used in conjunction with other medications for the treatment of certain types of seizures. Keppra was given as a stand-alone treatment or in combination with gabapentin, another antiepileptic drug (AED) used to treat pain, to 400 patients experiencing migraine headaches, neck, back Levetiracetam compared with placebo for neuropathic pain: Patient or population: neuropathic pain (6 studies in central neuropathic pain due to multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, polyneuropathy, central post‐stroke pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and post‐mastectomy pain) Intervention: levetiracetam 2000 mg to 3000 mg daily Comparison Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may View more. Prescription only. Prescribed for Seizures, Epilepsy. Trileptal may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide. · Postherpetic neuralgia in adults · Nerve pain due to diabetic peripheral neuropathy in adults · Fibromyalgia in adults · Nerve pain due to spinal cord injury in adults · Partial seizures in adults and children (ages 1 month and older) who have epilepsy (seizure disorder), when used along with other seizure medications
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |