Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
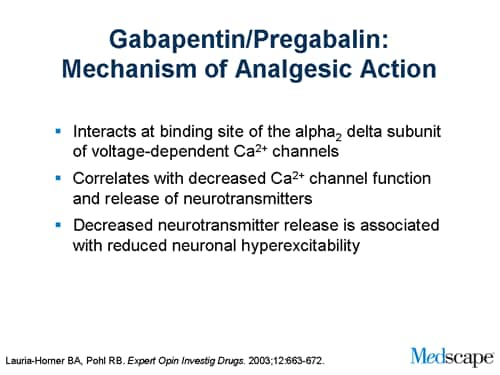
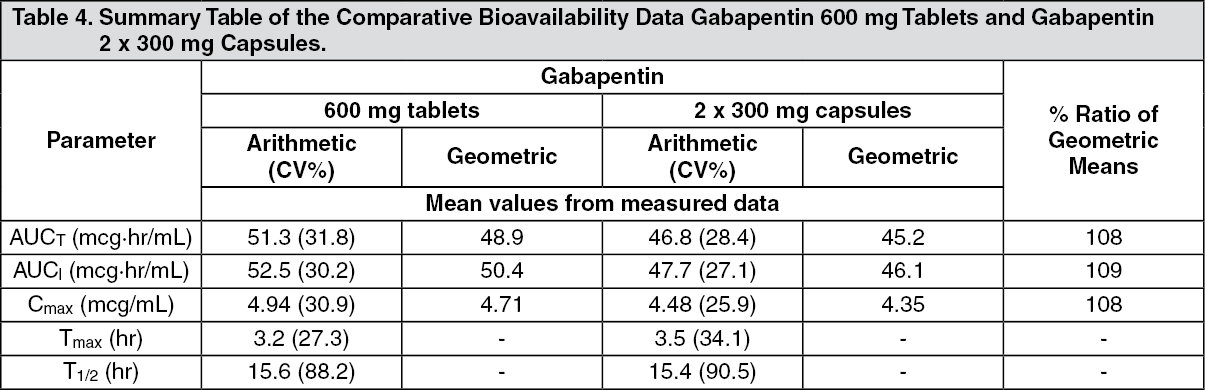
mechanism unknown, but does bind to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, which may modulate synaptic transmission through alteration of vesicle fusion, and may indirectly modulate GABA Gabepentin Mechanism of action of pregabalin and gabapentin. Reproduced with permission from []Brainstem structures, from which descending modulatory fibers originate, may be a key target of the analgesic action of gabapentinoids, because alpha-2/delta-1 expression is very high in these areas. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Gabapentin's mechanism in RLS is unclear, but it is known to bind strongly to α2δ-subunits of voltage-activated calcium channels. This binding likely inhibits calcium entry, normalizing neurotransmitter release, including excitatory glutamate; however, the precise mechanism remains unknown. Pharmacokinetics Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. Gabapentin prevents neuronal death in several models including those designed to mimic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This may occur by inhibition of glutamate synthesis by branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (BCAA-t). Gabapentin is a drug that modulates calcium channels and is used for various conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. Learn about its dosage forms, pharmacokinetics, indications, contraindications, and adverse reactions. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gaba Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce different actions responsible for pain attenuation Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The interaction of gabapentin and pr Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific bindin Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. While sharing a common property of suppressing seizures, antiseizure medications have many different pharmacologic profiles that are relevant when selecting and prescribing these agents in patients with epilepsy and other conditions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |