Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
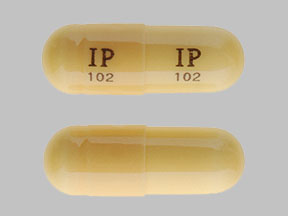
Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Remember, your health and safety are paramount. Avoid mixing gabapentin with alcohol to minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of this medication. Gabapentin Withdrawal. Abruptly stopping neurontin after long-term use can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. This study showed that gabapentin is efficacious in promoting abstinence and reducing drinking in individuals with alcohol use disorder and especially so in those with more alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Although an estimated 30 million people meet criteria for alcohol use disorder (AUD), few receive appropriate pharmacotherapy. Background: Gabapentin is an antiepileptic medication with evidence of benefit in alcohol use disorder patients. The mechanism of action of gabapentin may also benefit patients suffering from acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Treatment with gabapentin may benefit alcohol withdrawal inpatients based on its use in Alcohol Use Disorder outpatients and mechanism of action. Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat hospitalized alcohol withdrawal syndrome patients, but are associated with several adverse drug events. Gabapentin in Treating Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal. Withdrawal symptoms, which are common among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD), may be emotionally and physically draining, adding to the difficulty of navigating the long and winding road to recovery. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Future studies evaluating gabapentin's effect on long-term safety and hospital readmissio Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4 Gabapentin is an off-label medication for alcohol use disorder, sold under the brand names Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant, among others. The medication was originally developed to treat epilepsy and is now FDA-indicated for a variety of additional uses, including the treatment of conditions like postherpetic neuralgia and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that may help reduce symptoms and cravings of alcohol withdrawal, but it can also cause serious side effects. Learn how gabapentin works, how it compares with benzodiazepines, and why it is not advisable to mix it with alcohol. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Benzodiazepines are considered the drugs of choice for treating alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been studied as a potential treatment for acute alcohol withdrawal, based on its modulatory action on brain excitatory (i.e., glutamergic) and inhibitory (i.e., GABAergic) pathways. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. The prestudy high-alcohol withdrawal group had positive gabapentin effects on no heavy drinking days (P < .02; NNT, 3.1) and total abstinence (P = .003; NNT, 2.7) compared with placebo, while within the low-alcohol withdrawal group, there were no significant differences. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |