Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
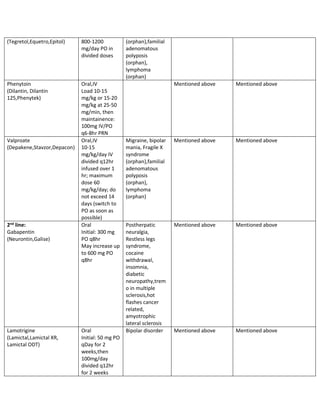
Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that helps to control and reduce severe epileptic seizures. According to a 2020 study, people who took gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal tolerated it well. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, especially Dosage Information. The following dosage information may be useful if you are considering taking gabapentin for withdrawal: Since it is a generic drug, dosage amount may vary depending on the brand and different brand name tablets are not interchangeable. 600-1800 mg per day is typically effective to mitigate symptoms. Benzodiazepines are considered the drugs of choice for treating alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been studied as a potential treatment for acute alcohol withdrawal, based on its modulatory action on brain excitatory (i.e., glutamergic) and inhibitory (i.e., GABAergic) pathways. Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. CIWA protocol adapted from San Francisco General Hospital CIWA protocol form. Dixit D, Endicott J, Burry L, et al. Management of Acute Alcohol In the first double-blind, dose-response, controlled trial of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal, investigators randomized 100 treatment-seeking outpatients with alcohol dependence and moderate alcohol-withdrawal symptoms to 4 days of treatment with one of three gabapentin doses (200, 300, or 400 mg three times daily, tapered to twice daily on Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol alcohol withdrawal.12,14,15 Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal at VAPORHCS Although not currently included in the alcohol withdrawal protocol at Veterans Affairs Port-land Health Care System (VAPORHCS), gaba-pentin has been added to the standard of care in select patients per the discretion of the at-tending physician. Anecdotal reports of patients Currently, three medications are approved by the FDA for treating alcohol dependence: disulfram, an older drug that blocks the metabolism of alcohol and causes nausea; acamprosate, which helps support abstinence and can ease symptoms of withdrawal; and naltrexone, which can help people reduce heavy drinking. gabapentin dose schedule (300 mg capsules four times per day with rapid titration to 600 mg three to four times per day as necessary) in conjunction with an alcohol withdrawal protocol utilizing a symptom-triggered benzodiazepine, versus management with lower dose (or no dose) gabapentin in conjunction with an alcohol Several medications can be used to treat alcohol use disorder, leading to reduced heavy drinking and increased days of abstinence [3]. These outcomes likely reduce the overall risk associated with alcohol use disorder despite total abstinence not being achieved. This topic reviews the pharmacotherapy for treatment of alcohol use disorder. A lcohol withdrawal occurs as a result of cessation of or reduction in alcohol use, particularly after a period of heavy and prolonged drinking. The diagnosis requires the presence of ≥ 2 of a set of 8 criteria: autonomic hyperactivity (eg, sweating or pulse rate > 100 beats per minute); increased hand tremor; insomnia; nausea or vomiting; transient visual, tactile, or auditory Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |