Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
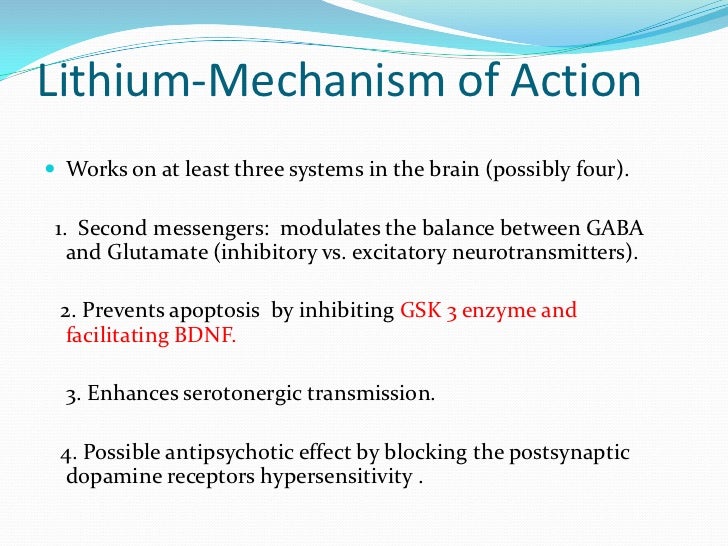 |  |
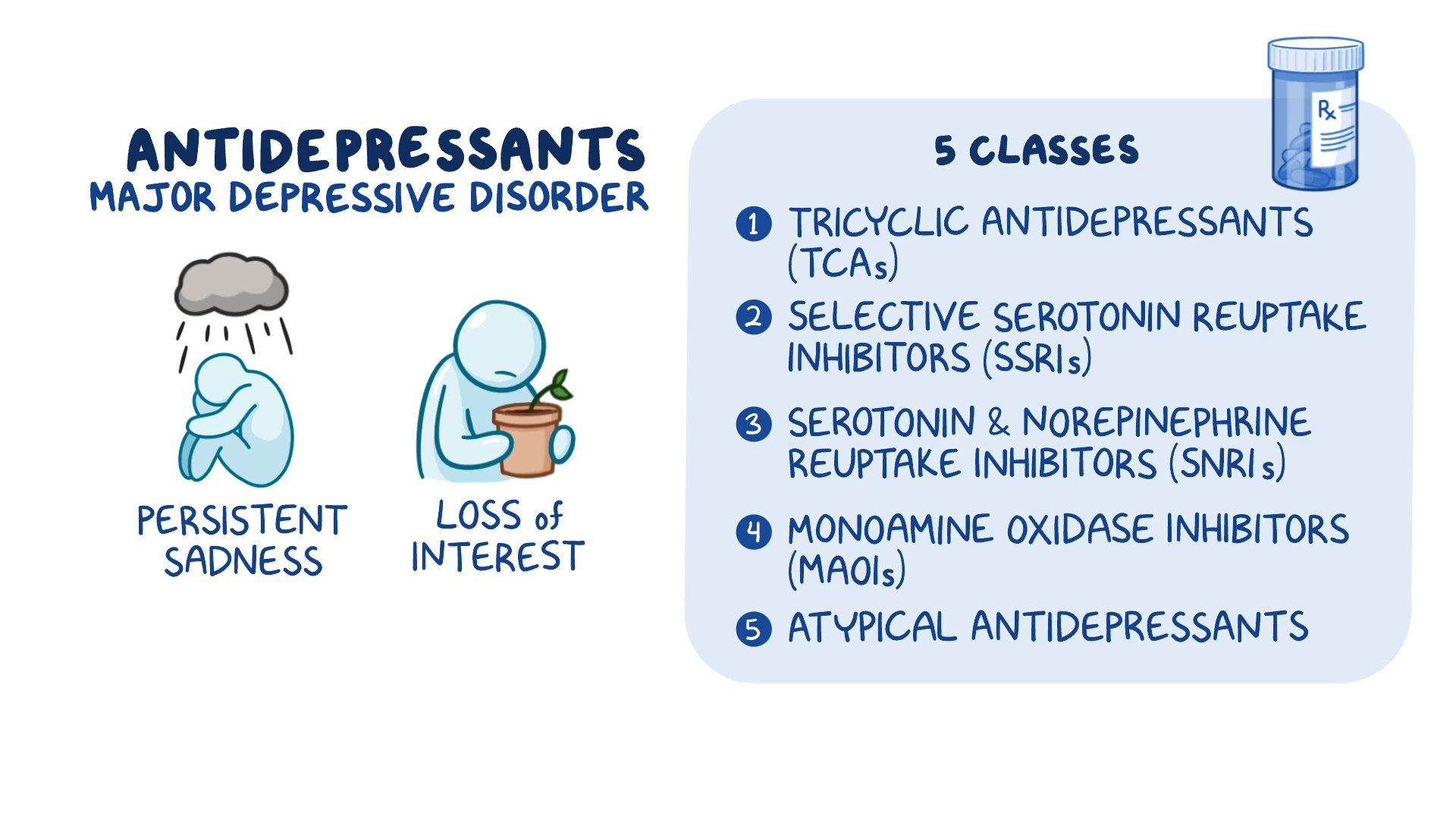
American Psychological Association: Gabapentin has been “largely discredited as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.” Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance: Gabapentin “was used frequently for treatment of bipolar disorder, but controlled studies found it was no more effective than a placebo.” Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Neurontin is also referred to by its drug name, Gabapentin. Neurontin is an anticonvulsant, or drug that controls seizures. In cases of depression, Neurontin works as a mood stabilizer. How do I take it? Prescribing information states that Neurontin should be taken three times a day. Neurontin comes in tablet, capsule, and liquid solution forms. Adjunctive therapy of gabapentin to stable doses of mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics, initiated at 300 mg at bedtime and increased by 300 mg every four nights until symptom relief or adverse effects were noted. Final GBP dose was clinically determined. Maximum dose 3600 mg per day in divided doses (range 600 mg to 3300 mg). Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding ( 84 ). medications, mood stabilizer use and dosage, evidence regarding poor response to standard mood stabilizers be-fore gabapentin use, evidence regarding whether during gabapentin treatment mania or hypomania occurred, ad-verse events, maximum and maintenance gabapentin dose and duration of treatment, indications for treatment There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. The results suggest that gabapentin may be of benefit to bipolar patients who only partially respond to other mood stabilizers. A favorable side-effect profile and rapid action make this drug an attractive choice as an adjunctive therapy. For 1 year, 13 patients received adjunctive gabapentin with standard mood stabilizers and 12 patients received adjunctive placebo. On the basis of the CGI-BP, gabapentin-treated patients showed significant improvement from baseline to month 12. Patients frequently express an interest in using gabapentin rather than standard mood-stabilizing agents (like lithium carbonate, divalproex sodium, or carbamazepine) due to its limited side effect profile. Thus, clinical interest regarding its use in mood disorders has grown. A large number of peer-reviewed but noncomparative studies and reviews 23 – 25, 27 – 31, 33 – 37, 39, 40 also support gabapentin’s role either as monotherapy after first-line treatment failure or as adjunctive therapy to mood stabilizers, antidepressants, or neuroleptics. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Some research suggests that gabapentin might have mood-stabilizing properties, potentially helping with conditions like bipolar disorder. It’s like the medication is acting as an emotional shock absorber, smoothing out the highs and lows. Gabapentin is not reliable on its own in bipolar disorder, but two placebo-controlled trials suggest it may have a role as adjunctive therapy. It augmented lithium in acute mania and had mild preventive effects over a year when added to various mood stabilizers. Other medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases when other treatments haven’t worked. How do mood stabilizers work for bipolar Mood Stabilizing Medications. Lithium (Eskalith or Lithobid) Valproate/Valproic Acid/Divalproex Sodium (Depakote or Depakene) Carbamazepine (Equetro or Tegretol) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) Gabapentin (Fanatrex, Gabarone, Horizant, or Neurontin) Topiramate (Topamax or Topiragen) Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) Side Effects of The relatively low frequency of bipolar disorder diagnoses in the sample of off-label gabapentin visits suggests that use of gabapentin as a mood stabilizer has declined, which corresponds with more recent psychopharmacology literature concluding that gabapentin’s mood-stabilizing effects are minimal to negligible (13, 32). We found few Mood Stabilizing Medications. Lithium (Eskalith or Lithobid) Valproate/Valproic Acid/Divalproex Sodium (Depakote or Depakene) Carbamazepine (Equetro or Tegretol) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) Gabapentin (Fanatrex, Gabarone, Horizant, or Neurontin) Topiramate (Topamax or Topiragen) Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) Side Effects of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |