Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
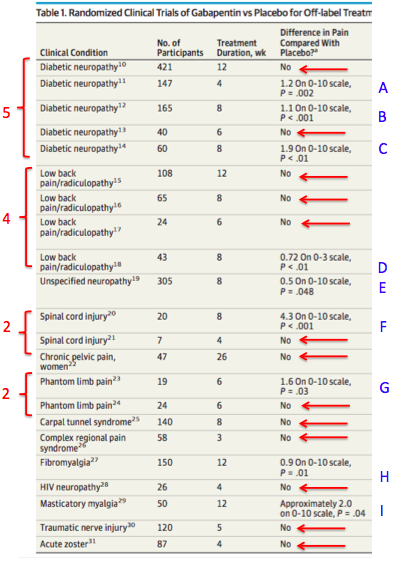
Gabapentin is prescribed frequently for chronic back pain syndromes in both primary care and specialty pain clinics, particularly when there is a ‘radicular’ or neuropathic component with pain radiating into the upper or lower legs [6]. Gabapentin could be an option in the conservative management of acute or chronic radicular pain. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). : You say medication, I know I've been reading a lot about gabapentin. Can you explain what they use for that is? Can you explain what they use for that is? Dominic Pelle : Yeah, so gabapentin is that type of medication I talked about that relaxes the nerve, so it's a specific medication used to just ease nerve pain, okay. Mean age ± SD: gabapentin group 57.6 ± 8.8 yr; placebo group 54.6 ± 11.4 yr. Flexible dosing of gabapentin up to 3600 mg/d for 12 wk, v. matching placebo. Add-on therapy with NSAIDs permitted. Pain, disability and adverse events at wk 1–5, 7, 9 and 12. Baron et al. 27: 217 participants with chronic (≥ 3 mo) radiculopathy. Pharmaceutical treatments for radiculopathy include opioid, antiinflammatory (steroidal and nonsteroidal), neuromodulating, topical, and adjuvant treatments. These medications act locally, peripherally, or centrally on the neural axis. Is gabapentin (Neurontin) effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain? Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in neuralgia. eHealthMe is studying from 322,822 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Herniated nucleus pulposus (slipped disk)? This review finds good evidence that these drugs are not an effective treatment for low back pain with or without radiculopathy, and are associated with an increased risk of adverse events. Methods: Thirty-five patients with radicular pain and diagnosed as L4, L5 or S1 radiculopathy were treated with oral gabapentin from a total of 300 mg per day once up to a total of 1800 mg per day divided in 3 doses for eight-week trial period. Cervical radiculopathy is pain and neuropathy in the neck that results from a pinching or inflammation of a cervical nerve at the point where it exits the spine, called the foramen or neuroforamen. The name radiculopathy is derived from a combination of the Latin word radicula (small root) and the Greek word pathos (disease). Abstract. Lumbar radiculopathy can be presented as low back pain and radiating pain. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has been used to treat radicular pain, and after the injection, additional medications such as gabapentinoids including pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) can be administered to relieve remnant pain. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in neuralgia. eHealthMe is studying from 322,815 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Cervical radiculopathy? The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). We investigated a single epidural steroid injection compared with gabapentin in patients with lumbosacral radicular pain in a double blinded fashion. Despite the specific indications of gabapentinoids, there is a notable increase in the off-label prescription of, which has raised the concern about the misuse of these drugs since the benefits remain unclear. 17, 18, 19 To our knowledge regarding their use on sciatica, pain relief only has been reported in one trial comparing gabapentin with placebo 20 and in no one of those investigating When it comes to neck pain, gabapentin is commonly prescribed for conditions such as cervical radiculopathy, in which the nerves in the neck become compressed or irritated, causing pain, numbness, and weakness. By taking gabapentin, patients can experience significant relief from these symptoms. Yildirim, K, Deniz, O, Gureser, G, et al. Gabapentin monotherapy in patients with chronic radiculopathy: the efficacy and impact on life quality. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2009;22:17-20 Crossref Lumbar radiculopathy can be presented as low back pain and radiating pain. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has been used to treat radicular pain, and after the injection, additional medications such as gabapentinoids including pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) can be administered to relieve remnant pain. With regards to use in radiculopathy, in one placebo controlled study of 50 patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy found that when compared to placebo, those who received Gabapentin had improved motor and sensory function, lumbar flexion range of motion, and pain . Compare risks and benefits of common medications used for Radiculopathy. Find the most popular drugs, view ratings and user reviews.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |