Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
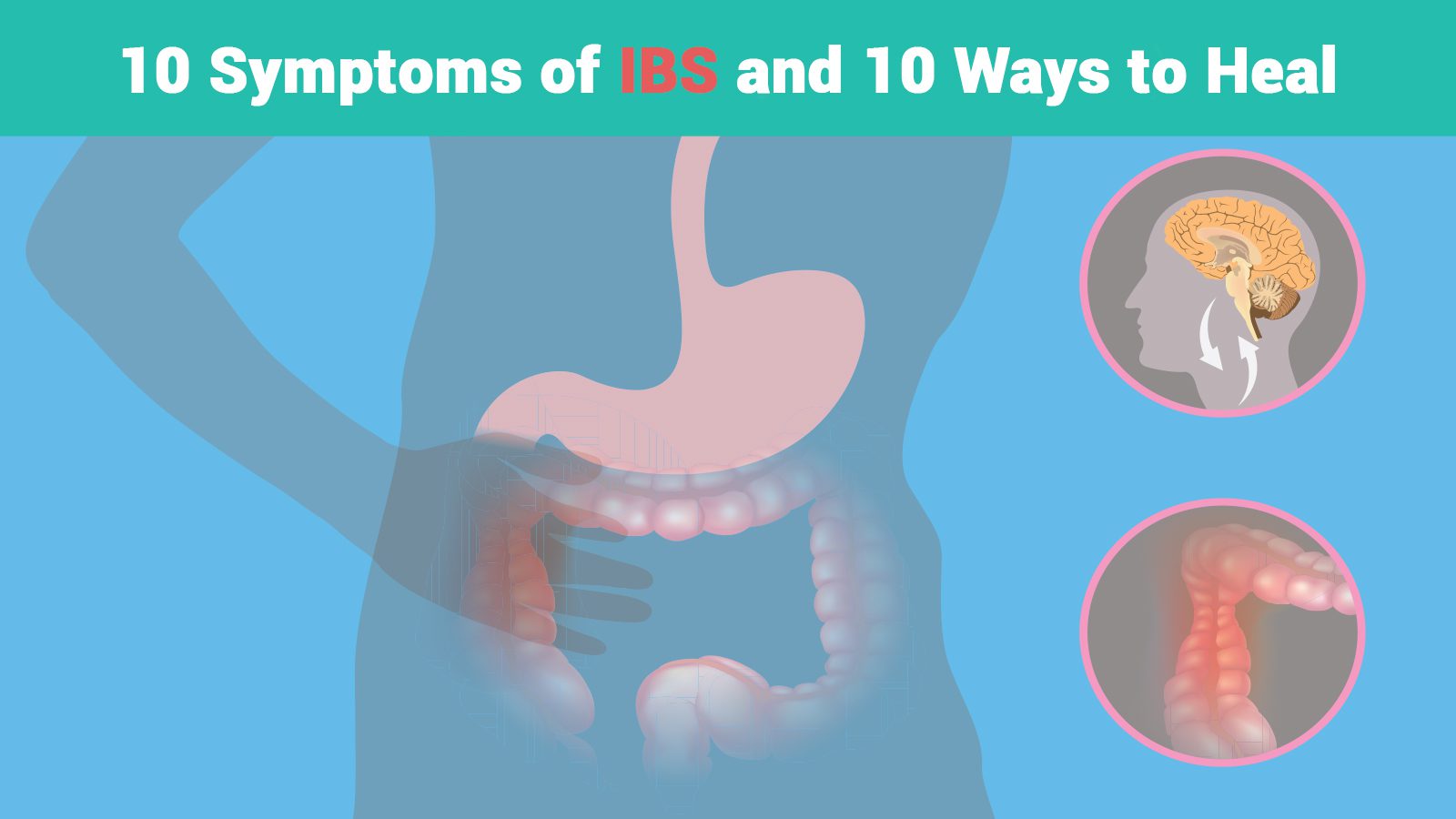
A forum community dedicated to Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Digestive Health Support. Come join the discussion about treatment, diet, health, lifestyles, spirituality, medication, research, recovery, and more! IBS-D and Gabapentin/Neurontin. Tags gabapentin ibs diarrhea neurontin. Jump to Latest Follow 2K views Context: Visceral pain is a leading symptom for patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that affects 10% - 20 % of the world population. Conventional pharmacological treatments to manage IBS-related visceral pain is unsatisfactory. Lastly, psychosocial, pharmacological, and procedural pain management techniques will be discussed. An extensive review of the existing literature reveals a paucity of data regarding pain management specific to IBD. In addition, there is growing consensus suggesting a spectrum between IBD and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms. Our results show that gabapentin reduces rectal sensory thresholds through attenuating rectal sensitivity to distension and enhancing rectal compliance in diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. For the purpose of treatment, IBS can be divided into four types, based on symptoms: constipation-predominant, diarrhea-predominant, mixed or unclassified. A healthcare professional also will likely explore whether you have other symptoms that might suggest another, more serious condition. These include: Onset of symptoms after age 50. Weight loss. Central neuromodulators (antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other central nervous system−targeted medications) are increasingly used for treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), now recognized as disorders of gut−brain interaction. A 2014 study indicated that gabapentin can not only be used for the treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with IBS, but it can significantly tone down the systemic anxiety that can be a problem caused by IBS. Intraperitoneal injection of NB001, an adenylyl cyclase 1 (AC1) inhibitor, reduced spontaneous pain but had no significant effect on behavioral anxiety. In contrast, gabapentin reduced both spontaneous pain and behavioral anxiety. Although all patients with IBS have symptoms of abdominal pain and disordered defecation, treatment needs to be individualized and should focus on the predominant symptom. This paper will review therapeutic options for the treatment of IBS using a tailored approach based on the predominant symptom. Abstract. Background: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a complex syndrome that is difficult to manage. Here we present the evidence supporting medication treatments for specific IBS symptoms, discuss evidence-based management of IBS with medications including dose regimens and adverse effects and review progress on research for new IBS treatments. Summary: Currently, there is evidence to Background: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a highly prevalent and economically burdensome condition; and pain is often the most unpleasant, disruptive, and difficult-to-treat symptom. Visceral hypersensitivity is a common feature driving pain in IBS, suggesting that neuropathic mechanisms may be implicated. Gabapentin reduces rectal mechanosensitivity and increases rectal compliance in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:981–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02685.x. How severe was Irritable bowel syndrome and when was it recovered: Irritable bowel syndrome in Gabapentin; Expand to all the drugs that have ingredients of gabapentin: Irritable bowel syndrome and drugs with ingredients of gabapentin (1,051 reports) More studies by gender and age: Female: 0-1 2-9 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60+ Gabapentin can significantly impact bowel function and lead to diarrhea or constipation in some individuals. These effects are thought to occur due to gabapentin’s actions on calcium channels, opioid receptors, and serotonin in the GI tract. Older adults, higher gabapentin doses, and certain underlying conditions seem to increase risk. Keywords: Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Clinical Trial, Visceral Pain, Visceral Hypersensitivity, Hyperalgesia, Diarrhea, Constipation. 1. Introduction. Visceral pain, i.e., pain arising from the viscera is the cardinal symptom of patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a prevalent disease afflicting 10% - 20 % of the world population (1-3). In the present study, we have demonstrated that gabapentin reduces symptom thresholds in IBS patients through the enhancement of rectal compliance and the attenuation of rectal sensitivity to distensions without altering postprandial tonic response of the rectum. Clonidine, gabapentin and pregabalin can moderately improve IBS symptoms. Lubiprostone relieves constipation predominant IBS (IBS-C) while loperamide improves diarrhea predominant IBS (IBS-D). Gabapentin is a medication that has been shown to be effective in treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) by reducing rectal mechanosensitivity and increasing rectal compliance. It is also used to relieve painful bowel spasms and treat diarrhea. GABA agonists or analogues such as pregabalin or gabapentin could be useful for IBS treatment. As Zhang et al. proved, gabapentin improves pain and anxiety-like behaviours in mice, although the pharmacological use of this drug for the treatment of IBS should be limited due to its serious side effects (hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |