Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
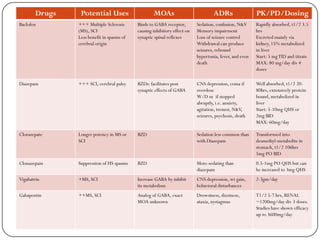 | 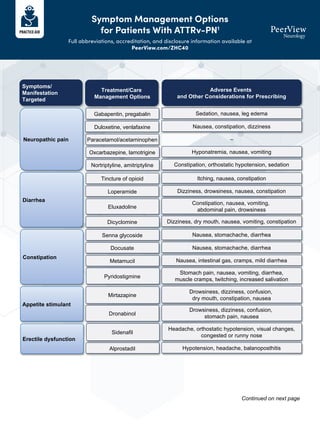 |
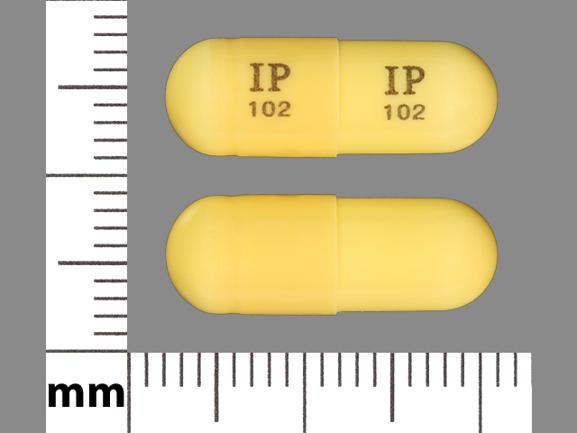
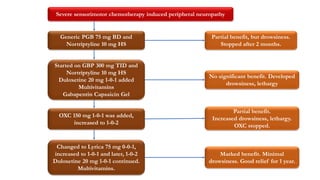
Gabapentin For Sleep. Gabapentin, also referred to as Neurontin, is a medication that’s often prescribed by doctors for quite a few different purposes. Primarily, it’s known as an anticonvulsant, a medication that helps prevent or stop seizures resulting from epilepsy. Research has shown that gabapentin can have significant effects on sleep architecture, the pattern and structure of sleep stages throughout the night. Gabapentin and REM Sleep: Effects, Benefits, and Potential Risks is a topic of particular interest to researchers. Gabapentin is considered highly effective for the treatment of insomnia for a few reasons. First and foremost, it improves sleep quality by reducing spontaneous arousal in the brain. It also increases total sleep time thanks to fewer awakenings and its ability to help individuals go to sleep faster. Gabapentin Sleep Effects. Gabapentin is part of a class of medications known as anticonvulsants, which means it can decrease abnormal excitement in the brain.This medication is often prescribed for seizures but can also help with restless legs syndrome (RLS), insomnia, and even neuropathic pain caused by conditions like diabetes. Lyrica(Pregabalin) is a prescription medication used to treat nerve pain caused by diabetes, shingles, or spinal cord injury, as well as certain types of seizures. It works by reducing the number of pain signals sent out by damaged nerves. Side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, and blurred vision. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. Research suggests that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical recovery and memory consolidation. This effect could be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to achieve restorative sleep due to pain or anxiety. Potential Benefits of Gabapentin for Sleep Disorders. Despite the uncertainties surrounding its impact on REM sleep, gabapentin has shown promise in treating various sleep disorders. Its use in managing insomnia, particularly in patients with chronic pain or anxiety, has garnered attention from sleep specialists. Taking gabapentin can make you sleepy. According to studies, about 20% of people taking gabapentin experience drowsiness or fatigue. It may be even more likely, affecting 20% to 30% of people, with Horizant. However, tiredness is less common with Gralise, occurring in about 5% of people taking it. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to help manage certain epileptic seizures. It also is used to relieve pain for some conditions, such as shingles. Dizziness and drowsiness are common side effects of gabapentin. Neurontin may cause serious side effects including: see "What is the most important information I should know about Neurontin?” problems driving while using Neurontin. See "What I should avoid while taking Neurontin?" sleepiness and dizziness, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury, including falls Gabapentin (Neurontin) enhances sleep by calming overactive brain activity. It reduces neuronal activity and nerve transmission, helping to relax the brain and promote drowsiness. This process improves sleep quality, especially for those experiencing sleep disturbances. Understanding Gabapentin’s Effects on Sleep. To appreciate how gabapentin influences sleep, it’s essential to delve into the intricate architecture of our nightly rest. Sleep is not a uniform state but rather a complex cycle of different stages, each playing a vital role in physical and mental restoration. Neurontin/Gabapentin comes as a capsule to take by mouth. Neurontin is taken three times a day. To minimize Neurontin side effects, take the very first Neurontin dose at bedtime. Then take this Neurontin medication at evenly spaced times throughout the day and night to ensure a constant level of Neurontin/gabapentin in your body. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is prescribed for epilepsy and nerve pain, but some people may take gabapentin for sleep. Learn about whether off-label gabapentin works for sleep disorders. Never take double doses of Neurontin (gabapentin) that’s an adamant rule whereas on Neurontin (gabapentin) medication. However, if you missed a dose on that point and promptly remembered it hours before consequent dose, you will take one to catch up. however if it’s close to the time for consequent dose, higher forego that missed dose and proceed to consequent one. Several studies have been conducted on the safety and effectiveness of taking gabapentin for sleep issues. The results of these studies are listed below: According to a 2010 study, gabapentin can improve sleep quality and slow-wave sleep (deep sleep), lower your risk of spontaneous nighttime wake-ups, and prevent premature morning awakenings Can gabapentin help you sleep? Yes, it can. As reported in a small study that was published in the March-April 2010 edition of the journal Clinical Neuropharmacology, “Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal.” Gabapentin can cause several common side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. Other commonly reported side effects include headache, nausea, and blurred vision. These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication.In rare cases, gabapentin may cause more serious side effects
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |