Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
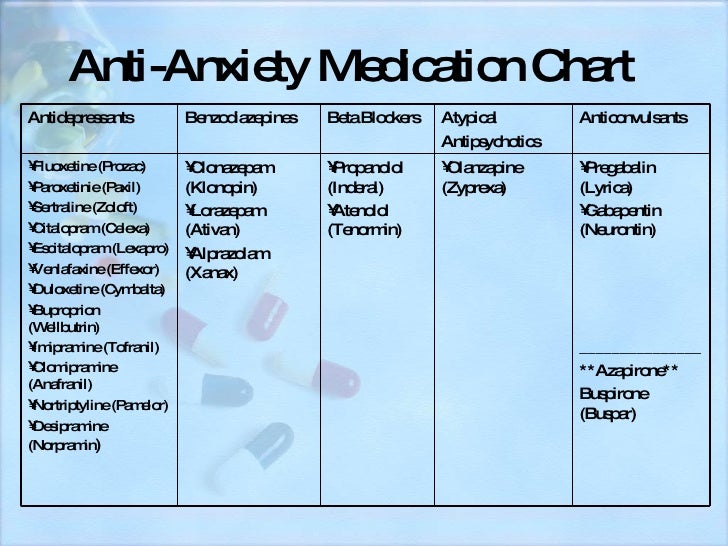 |  |
People with generalized anxiety disorder who take Gabapentin have been shown to be less irritable, reduce the use of alcohol as self-medication, have fewer depression symptoms, feel less anxious anticipating the future, improve in phobic avoidance (going out in public more, and experience a significant decrease in panic disorder and reduction There is mounting evidence that Gabapentin may be an effective intervention for various types of anxiety including: generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. There is considerable research documenting the efficacy and safety of Gabapentin for anxiety disorders. In this review, the author examines the evidence for psychopharmacologic treatments among adults for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder derived from clinical trials. For each disorder, major categories of drugs are reviewed, and then the evidence-based medications in each category are discussed. The author reviews key safety and tolerability Gabapentin can be used in adults and children age 3 and older who have partial seizures. panic attacks, feelings of aggression or anger, impulsive behavior Pregabalin tends to act more potently and with faster onset, making it potentially more effective for acute anxiety relief, like in the case of panic attacks. In cases of generalized anxiety disorder, pregabalin may also be preferred due to its stronger evidence base and quicker symptom relief. While gabapentin is increasingly being used to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), little is known about its effectiveness on GAD symptoms. The patient presented here has a relatively straightforward psychiatric history, with GAD playing a prominent role. Research also indicates that gabapentin works better than disorders like bipolar illness, panic disorder, or panic attacks to lessen the effects of alcohol withdrawal and some forms of anxiety. The precise mechanism of gabapentin’s action is not entirely understood. Evidence also suggests gabapentin is more effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and certain types of anxiety than conditions like bipolar disorder, panic disorder, or panic This review will focus on the comparative properties of gabapentin and pregabalin, specifically the available evidence on their use in the treatment of primary anxiety disorders — GAD, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Neurontin (gabapentin) "Neurontin has changed my life dramatically. I suffered from high anxiety with panic and anxiety attacks. I started this medicine at about 19 and had been off and on it the past 13 years. It literally has made me a new person. When I don't use it, I notice a lot of fatigue, worry, anxiety, etc. Gabapentin and Xanax (alprazolam) are used to treat anxiety. Gabapentin is primarily an anti-seizure (anticonvulsant) drug used also used for treating post-herpetic neuralgia, the pain that follows an episode of shingles. Xanax belongs to a different drug class called benzodiazepines, and is used to treat anxiety disorders and panic attacks. Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Some research suggests that Gabapentin can effectively alleviate anxiety symptoms in some people. That said, the efficacy of this prescription medication can vary from person to person. It’s important to know that Gabapentin is not FDA-approved specifically for the treatment of anxiety. Pande et al, 2000 55 Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for add-on gabapentin in panic disorder Jadad score = 3: 103 patients with panic disorder randomized to treatment or placebo: Gabapentin 600–3,600 mg/d in add-on group for 8-wk trial: PAS Our preliminary observations suggest a role for gabapentin as monotherapy or for adjunctive use in patients with panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder. The promising preliminary results encourage further clinical exploration and systematic study of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety disorders. One hundred three patients were randomly assigned to receive double-blind treatment with either gabapentin (dosed flexibly between 600 and 3,600 mg/day) or placebo for 8 weeks. No overall drug/placebo difference was observed in scores on the Panic and Agoraphobia Scale (PAS) (p = 0.606). Off-label uses include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) [2*] , post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and social anxiety disorder (SAD). Gabapentin can also be prescribed for depression and bipolar disorder [3*] if a patient does not respond to or cannot tolerate antidepressant medications. Gabapentin is used to treat symptoms of anxiety disorder. Read more to learn everything you need to know about anxiety and how gabapentin works. How does Gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by mimicking a neurotransmitter in the brain called GABA. GABA has a calming effect on the brain and impaired functioning of GABA has been linked to various mental health conditions such as panic disorder and depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |