Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
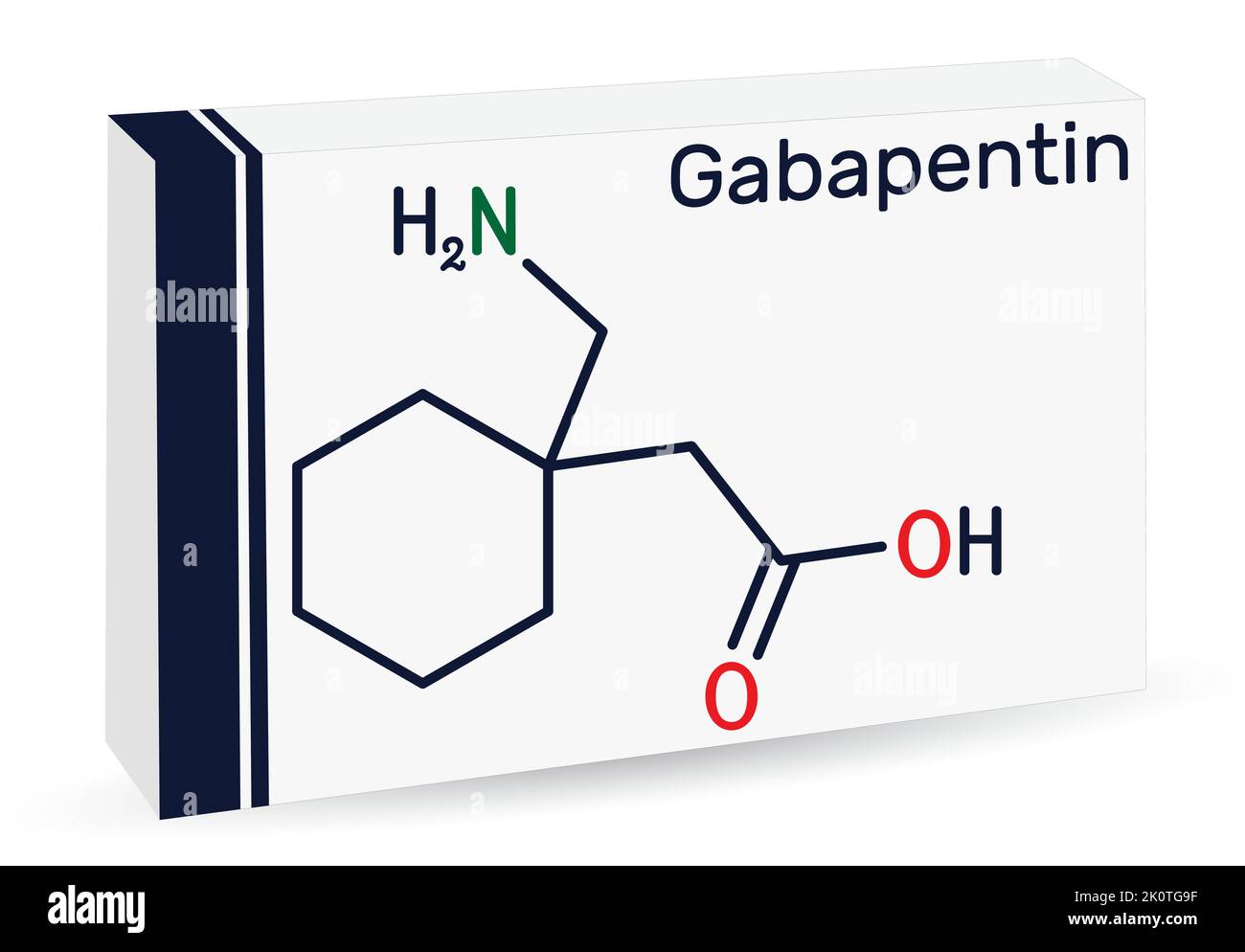
Gabapentin: A single retrospective study of gabapentin in patients with PTSD showed a marked or moderate improvement in sleep, as well as a decreased frequency or intensity of nightmares. 28. I myself.have been using gabapentin 600mg every morning. I started having nightmares within two weeks. I contacted my primary care physician and told her about the nightmares. She stated gabapentin will not give you nightmares. I stopped taking gabapentin on my own, nightmares went away. Gabapentin can cause a number of side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. nightmares are a rare side effect of gabapentin, but it is possible that the medication could cause them. If you experience nightmares while taking gabapentin, you should talk to your doctor. Consider alternative treatments beyond prazosin for managing PTSD-related nightmares. This retrospective study suggests that gabapentin may improve in particular sleep difficulties and also other symptoms associated with chronic PTSD. Prospective, controlled studies are needed to further investigate the effects of gabapentin on insomnia, nightmares, and other core PTSD symptoms. PTSD-associated nightmares, but the data are low grade and sparse: trazodone, atypical antipsychotic medications, topi-ramate, low dose cortisol, fluvoxamine, triazolam and nitraz-epam, phenelzine, gabapentin, cyproheptadine, and tricyclic antidepressants. Nefazodone is not recommended as first line Recently, some drugs have shown promise for treating nightmares, such as terazosin, clonidine, trazodone, some antihistamines, and gabapentin. What medications cause nightmares? Medications belonging to a variety of classes of drugs may cause nightmares and bad dreams. These medications may be prescribed to treat common conditions including hypertension or depression, and medications used to treat less common conditions such as Parkinson’s Disease. Why do some medications cause Nightmares is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 50-59 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Migraine. Gabapentin Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia and also is used to treat neuropathic pain. When 300 to 3,600 mg/d (mean dosage, 1,300 mg/d) of gabapentin was added to medication regi-mens, most patients reported decreased fre - quency or intensity of nightmares. 9 Monitor patients for sedation, dizziness, mood Nightmares often improve with successful treatment of the primary psychiatric disorder (eg, anxiety, depression, PTSD). (See 'Treatment of co-occurring psychiatric disorders' above.) Severe and chronic nightmares – Treatments include psychotherapy and medication. The choice can be individualized according to patient preferences and access to Sir: Gabapentin is a newer anticonvulsant approved for use as an adjunct agent in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization. 1 Recent publications indicate that gabapentin has been useful in a wide array of psychiatric conditions including anxiety disorders, 2 alcohol withdrawal, 3 bipolar disorder, 4 behavioral disorders, 5, 6 and even antidepressant-induced The following medications may be considered for treatment of PTSD-associated nightmares, but the data are low grade and sparse: trazodone, atypical antipsychotic medications, topiramate, low dose cortisol, fluvoxamine, triazolam and nitrazepam, phenelzine, gabapentin, cyproheptadine, and tricyclic antidepressants. Moved Permanently. The document has moved here. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Limited evidence was available to support the use of anticonvulsants for PTSD-related sleep disturbances at the time of the van Liempt et al. (2006b) and Maher et al. (2006) reviews, with the exception of small open label trials of gabapentin and topiramate. Only two studies to report effects of anticonvulsants on sleep outcomes in a PTSD Level C The following medications may be considered for treatment of PTSD-associated nightmares, but the data are low grade and sparse: trazodone, atypical antipsychotic medications, topiramate, low dose Cortisol, fluvoxamine, triazolam and nitrazepam, phenelzine, gabapentin, cyproheptadine, and tricyclic antidepressants. I started on gabapentin last Friday 100mg before bed. First night I had a migraine so bad I couldn’t even sleep and since then I’m having such vivid nightmares I can’t tell when I’m awake or sleeping. Gabapentin: Gabapentin does a few different things. It’s an anticonvulsant, but it can also help with neuropathic pain, anxiety, and sleep. Only one small study was reported to support its use for nightmares. Vivid dreams and nightmares can be an unexpected side effect of several medications and supplements, such as melatonin, beta blockers, and antidepressants. And while they don’t happen to everyone, it’s helpful to be aware of some of the most common offenders.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |