Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
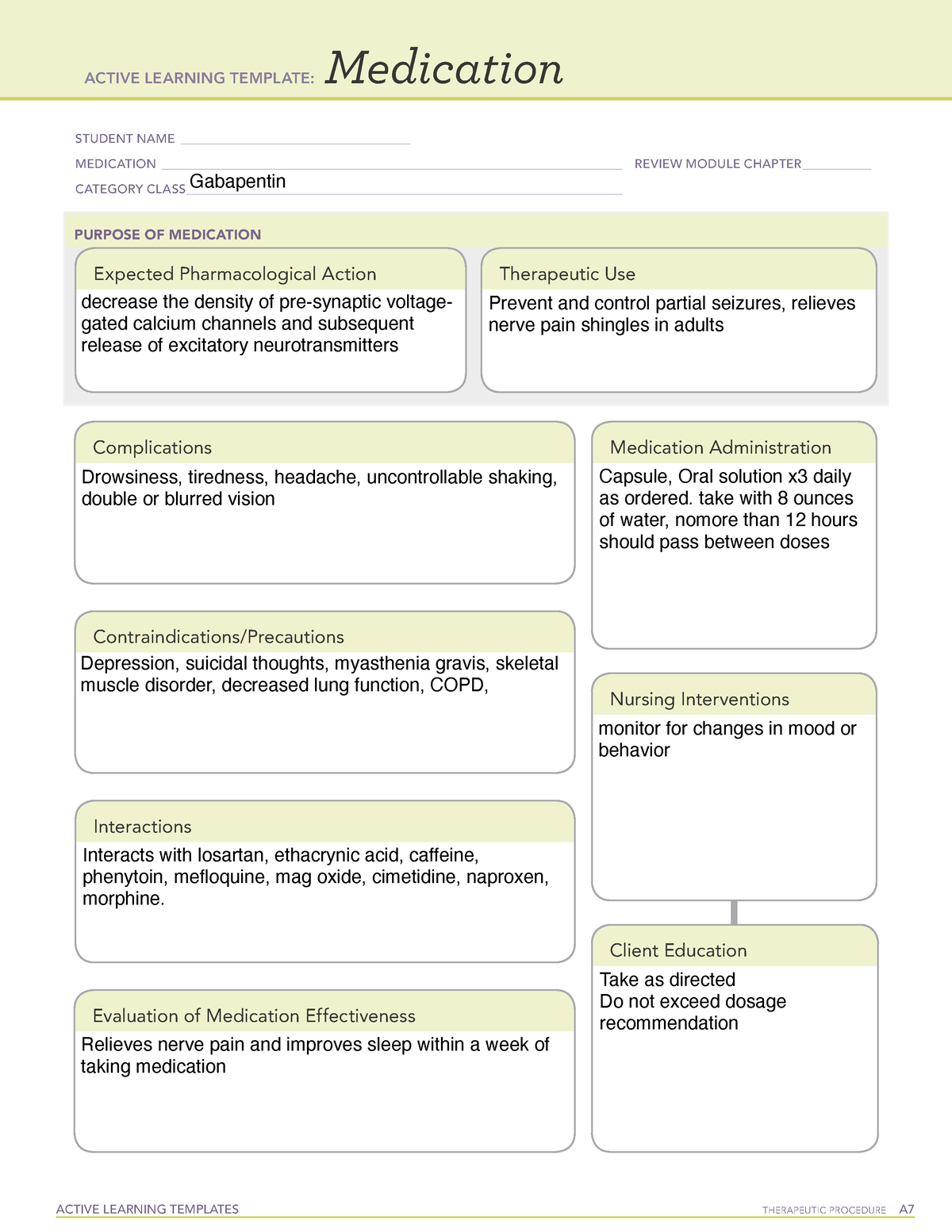 |  |
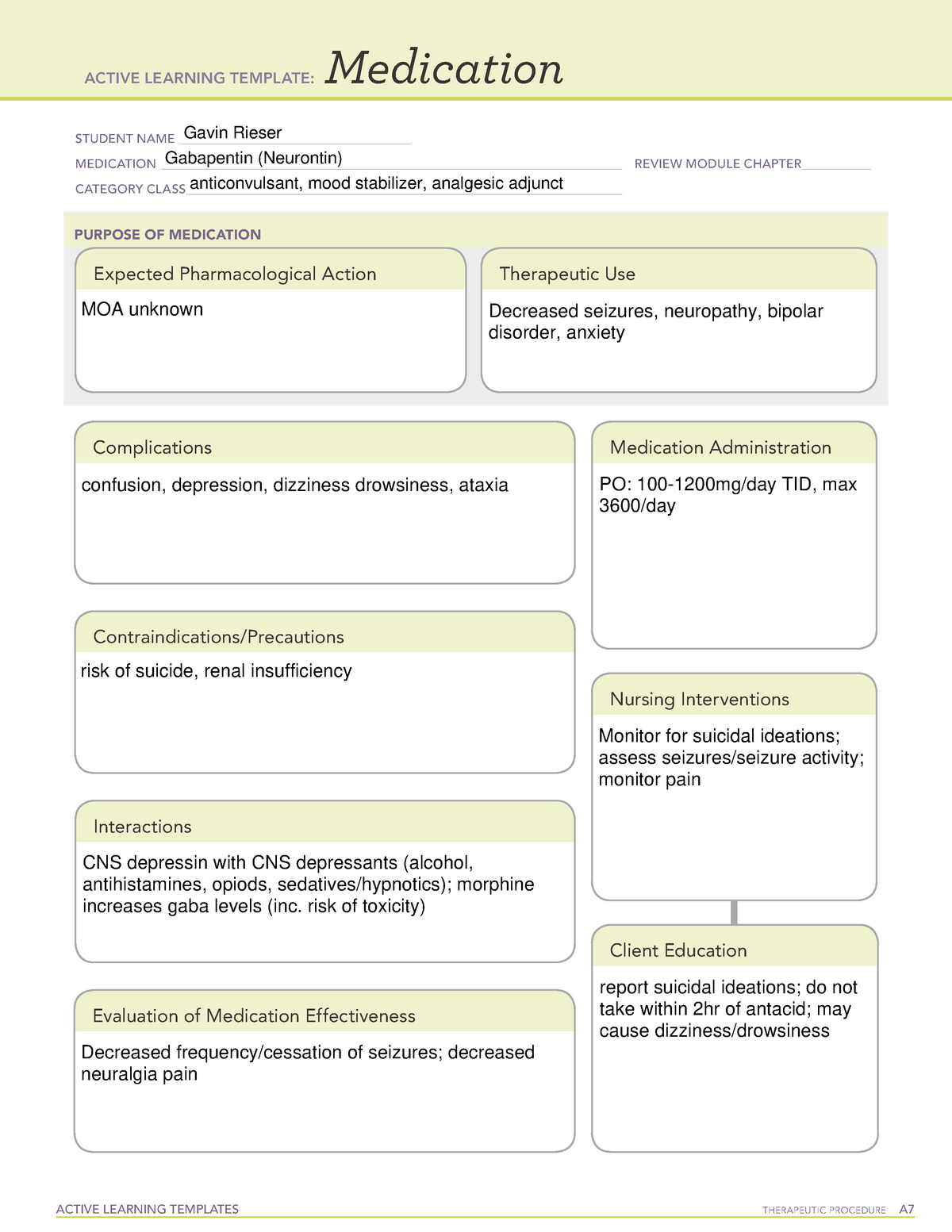
Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM Gabapentin is used for partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan. This drug can cause harm to the fetus of pregnant women. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients with epilepsy 3 to 12 years of age is associated with the occurrence of central nervous system related adverse events. Learn about gabapentin, a GABA analogue used for postherpetic neuralgia and seizures, and its nursing process considerations. Find out how to assess, calculate, and monitor gabapentin dosage, and what adverse effects and interactions to watch for. nursing considerations As needed, open gabapentin capsules and mx contents with water, fruit juice, apple sauce or pudding before administration. Give drug at least 2 hours after an antacid. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Nursing Considerations Therapeutic Effects Side/Adverse Effects; Anticonvulsant: gabapentin: Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Taper dose; do not stop abruptly: Decreased neuropathic pain or seizures Nursing considerations Assessment. History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy; Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output; Interventions. Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with Monitor closely for notable changes in behavior that could indicate the emergence or worsening of suicidal thoughts or behavior or depression. Assess location, duration, and characteristics of seizure activity. Assess location, characteristics, and intensity of pain periodically during therapy. Monitor frequency and intensity of pain on pain scale. Pregnancy considerations: A cohort study utilizing the US Medicaid dataset investigated gabapentin exposure during pregnancy from January 2000 to December 2013. While no significant associations were observed with major malformations, multiple administration of gabapentin was correlated with an increase in the risk of cardiac defects. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity Learn about gabapentin, an anticonvulsant used for seizures and neuropathic pain, and its nursing implications. Find out the indications, precautions, adverse effects, dosages, and patient instructions for gabapentin. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. gabapentin (Neurontin) Disease Spotlight: Epilepsy. Nursing Considerations. Here are important nursing considerations when administering this drug: Nursing Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents It is thought that Gabapentin may play a role in neural membranes. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. However, gabapentin is often used off-label for a variety of conditions. In fact, one study revealed that 83% of gabapentin prescriptions were for off-label use. Some of the common reasons gabapentin is prescribed are: Neuropathic pain and diabetic neuropathy (this is very common) Bipolar disorder and anxiety; Migraine prevention Mechanism of action is not known. May affect transport of amino acids across and stabilize neuronal membranes. Therapeutic Effects: Decreased incidence of seizures. Decreased postherpetic pain. Nursing Implications Monitor of therapeutic effectiveness; may not occur until several weeks following initiation of therapy, in those treated for seizure disorders , assess frequency of seizures: In rare cases, the drug has increased the frequency of partial seizures, Monitor dizziness and CNS depression, monitor for changes in behavior that
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |