Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
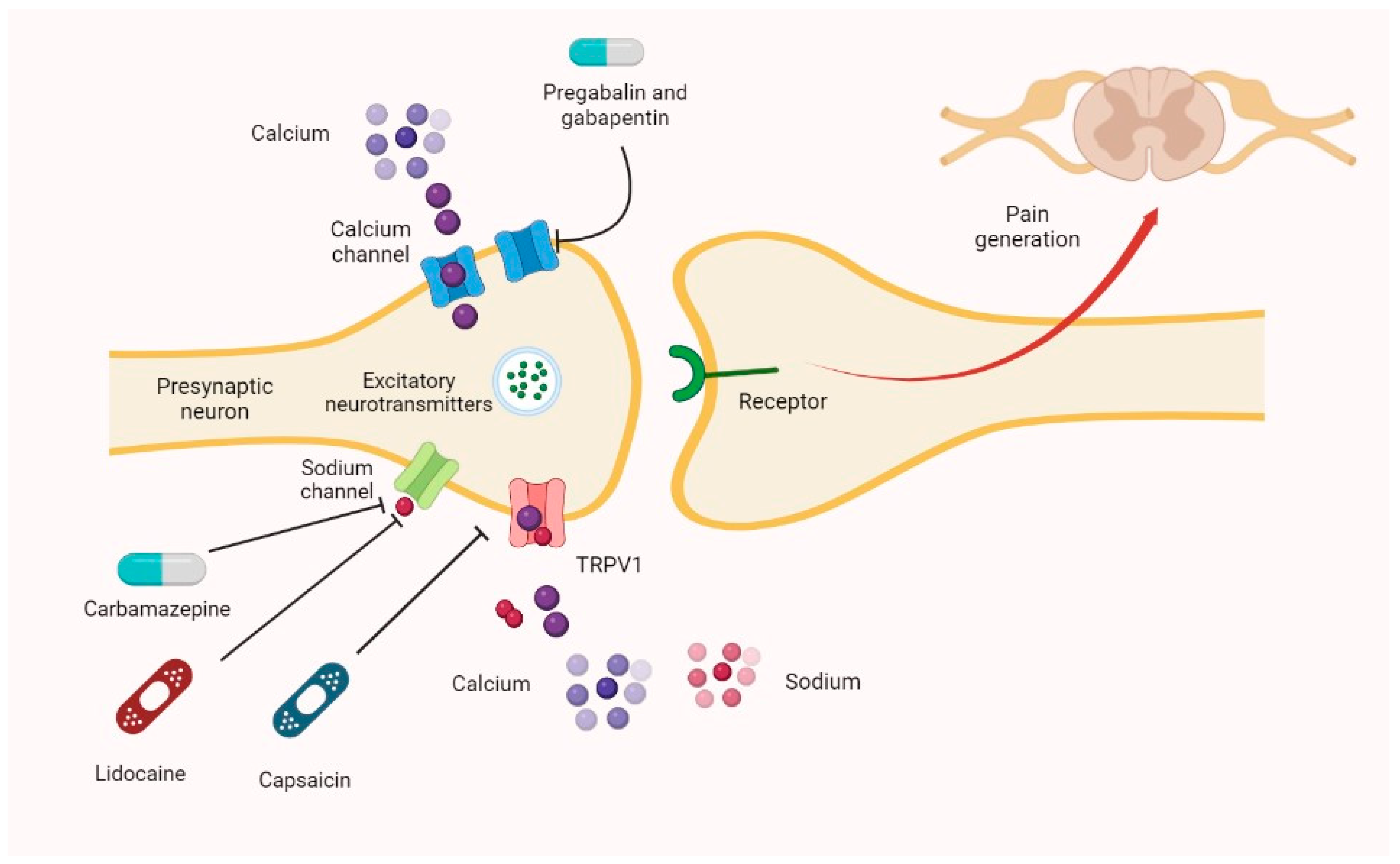
Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Onset of action may be seen as early as the second week of treatment with rapid titration, but the peak effect usually occurs about 2 weeks after a therapeutic dosage is achieved; therefore, an adequate trial may be 2 months or longer. If gabapentin is not effective or not tolerated, discontinue treatment gradually over a minimum of 1 week. The onset of action can vary based on the dosage and the condition being treated, but gabapentin is generally well tolerated and effective for both neuropathic pain and seizure management. The short answer is: generally, no, gabapentin does not provide immediate pain relief in the way that an opioid might. While some individuals may experience subtle effects soon after taking a dose, the significant benefits, such as pain reduction or anxiety relief, usually take time to manifest. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with m Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Although the mechanism of action of gabapentin is not fully established, there is strong evidence to suggest a novel mechanism of action. ONSET, PEAK AND DURATION OF COMMON PAIN MEDICATIONS Medication Onset of Action (minutes)* Peak Effect (hours)* Duration of Action (hours)* Route of Admin. Comments Methadone 30 -60 1 -2 4 -6 Full analgesic effects, are not attained until 3 to 5 days after initiation of dosing. Drug is known to eliminate slowly causing high risk of overdose 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Mechanism of action. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Key Takeaways: Gabapentin Onset of Action: Gabapentin usually starts working in 1-2 hours. Dosage Matters: Higher doses can lead to quicker effects but may increase side effects. Consistency is Key: Regular dosing is essential for optimal pain relief. Individual Variation: Metabolism and conditions affect how quickly relief is felt. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the When used to treat a type of seizure disorder, called a partial onset seizure, gabapentin decreases the abnormal activity in the brain that causes the seizures. When used to treat nerve pain, or neuralgia, following a herpes zoster (shingles) infection, gabapentin may reduce the response to painful stimuli. Best titrated up slowly to reduce the risk of side effects; however, this may delay the onset of an effect. Similar to other anticonvulsant medicines, gabapentin may increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts, particularly in young adults under the age of 24. Seizures, focal (partial) onset: Immediate release: Oral: Initial: 300 mg 3 times daily; increase dose based on response and tolerability. Usual dosage: 300 to 600 mg 3 times daily; doses up to 2.4 g/day and 3.6 g/day have been tolerated in long-term and short-term clinical studies, respectively. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. This timeframe aligns with the typical onset of action for gabapentin, which can range from 30 minutes to 2 hours after ingestion. Several factors can influence the absorption and onset of action of gabapentin. Food intake, for instance, can affect how quickly the medication is absorbed. Factors Influencing Gabapentin’s Onset of Action The time it takes for gabapentin to work in dogs is influenced by several factors, including: H3: Dog’s Individual Characteristics: Each dog’s metabolism, age, weight, and overall health can affect how quickly the medication is absorbed and processed. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |