Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
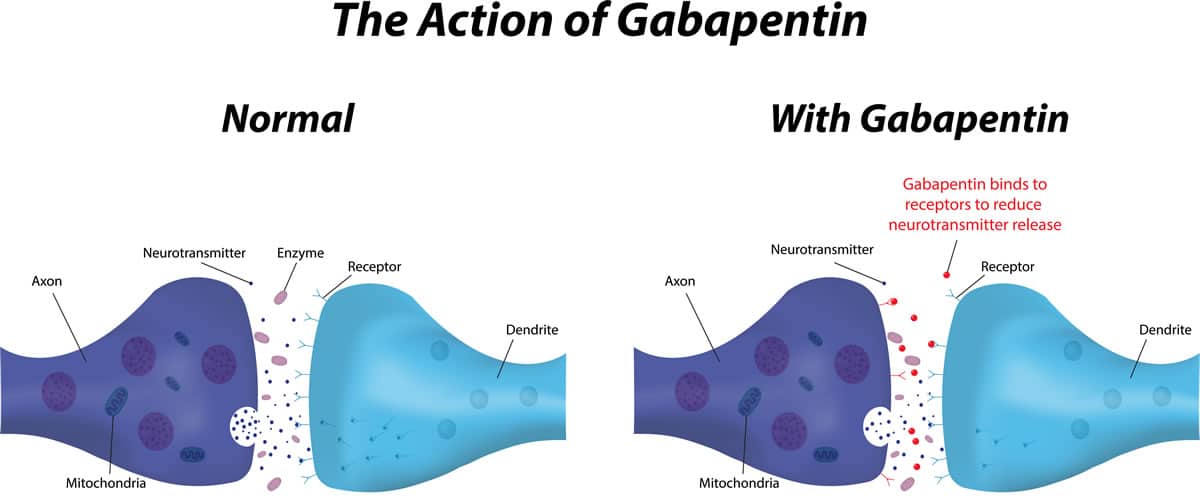
Patients should be informed of the potentially fatal risks of interactions between pregabalin and alcohol, and with other medicines that cause CNS depression, particularly opioids. MHRA/CHM advice: Antiepileptic drugs in pregnancy: updated advice following comprehensive safety review (January 2021) See Epilepsy. Further evidence supporting the use of pregabalin for the treatment of withdrawal symptoms comes from randomized controlled studies of gabapentin, another α2δ subunit ligand. These studies have shown the potential of gabapentin for the treatment of opioid [57, 58], alcohol [59, 60], and cannabis dependence . Understanding the risks linked to combining Gabapentin and alcohol is crucial for ensuring safety and avoiding severe health complications. This article assesses the impacts of Gabapentin and alcohol on the body, the possible dangers of their interaction, and strategies for using them safely. No, it is not advised to drink alcohol while taking Gabapentin. Drinking alcohol can increase the side effects of Gabapentin, such as drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. In addition, Gabapentin and alcohol can interact to cause increased sedation, coordination difficulty, and increased risk of falls. Mixing gabapentin with alcohol can lead to dangerous side effects and can potentially magnify existing issues like alcohol addiction. It's essential that patients using gabapentin avoid drinking alcohol to maintain their safety and wellbeing. Pregabalin and gabapentin both come as oral capsules and are available as a liquid solution. Gabapentin also comes as an oral tablet. Pregabalin is taken 2 to 3 times a day and gabapentin is usually taken 3 times a day. If you have kidney problems, your pregabalin or gabapentin dose may need to be lowered. Gabapentin (also called Neurontin) is a medicine that works in a similar way to pregabalin. Like pregabalin, it can be taken to treat epilepsy and nerve pain. It can also be taken for migraines. However, there are other differences between pregabalin and gabapentin. Gabapentin is taken in different doses to pregabalin. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally similar drugs acting via the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. The mechanism by which the drugs may induce dependence is not well worked out. Gabapentin and pregabalin are associated with significant euphoric effects. pregabalin, gabapentin and clonazepam are widely misused. They should liaise with consultant addictions psychiatrists where available. Accurate alcohol histories should be obtained, and breath alcohol levels measured. Altered blood parameters such as raised ferritin, triglycerides, gamma-glutamyl trans- Individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions may find that the combination of gabapentin and alcohol worsens their symptoms. Gabapentin can affect mood and emotional states , and when alcohol is added to the mix, it can lead to heightened anxiety, depression, or other mood disturbances. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol can amplify these effects, leading to increased drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, more dangerous health risks. Although gabapentin and alcohol are both legal substances, their combined use can be harmful, especially without medical supervision. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric Gabapentin and alcohol should never be mixed. If you have taken a dose of gabapentin, wait at least 24 hours before consuming alcohol to give your body time to cleanse the drug out of your system. Combining gabapentin with alcohol creates a dangerous synergistic effect that intensifies the central nervous system (CNS) depression. This interaction amplifies the sedative properties of both substances, leading to severe impairments in physical and mental function. Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, shingles, restless leg syndrome, and alcohol use disorder. However, it can be dangerous to drink alcohol while taking gabapentin. Both substances are depressants that slow down the body and brain. How do gabapentin and alcohol affect my breathing? Both substances can depress the central nervous system, which includes the brain's respiratory center. Together, they might dangerously reduce respiratory function, leading to shallow breathing or even respiratory failure in extreme cases. Like gabapentin, it's taken for epilepsy and nerve pain. It can also be taken for anxiety. But there are differences between pregabalin and gabapentin. Pregabalin can be taken less often and in different doses to gabapentin. If you need to change to pregabalin, your doctor will explain how to swap safely from gabapentin. While safe to take as prescribed, mixing gabapentin and alcohol can have potentially serious side effects and possible interactions. Drowsiness, dizziness, and a hard time concentrating are just a few of the side effects that can occur when drinking alcohol while taking gabapentin. Combining gabapentin with alcohol poses significant risks. Understanding these dangers is crucial for anyone considering using gabapentin alongside alcohol. The interplay between gabapentin and alcohol can amplify each other's effects, leading to heightened side effects. drug or alcohol addiction; or. a severe allergic reaction . Do not give this medicine to a child without medical advice. Pregabalin is not approved for use by anyone younger than 18 years old to treat nerve pain caused by fibromyalgia, diabetes, herpes zoster, or spinal cord injury.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |