Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
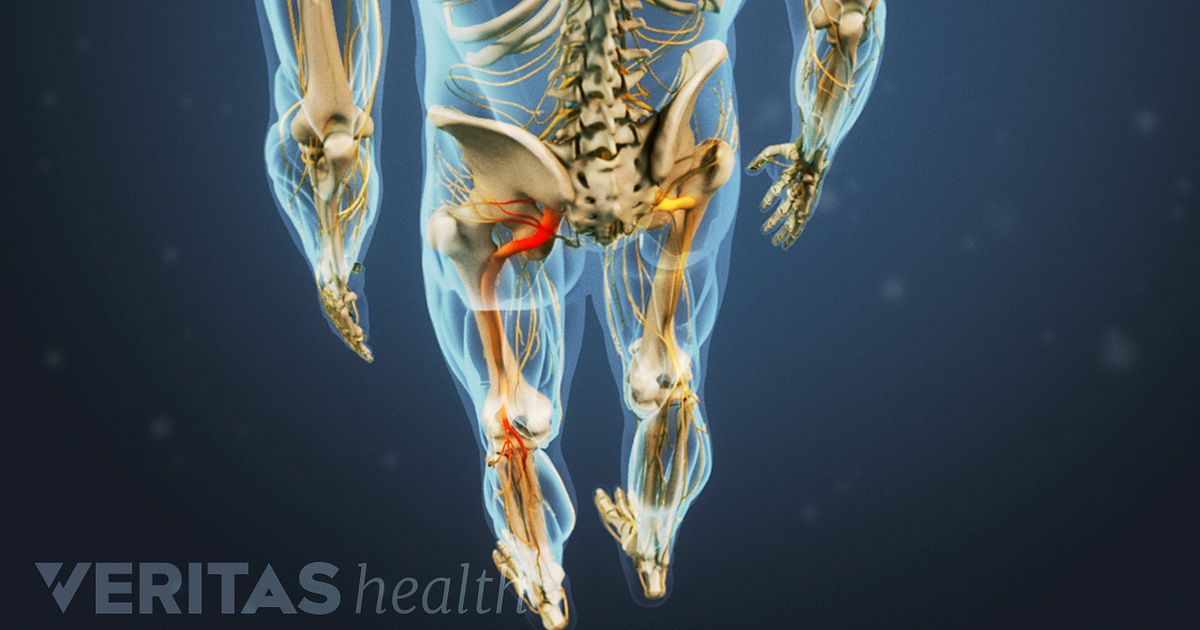
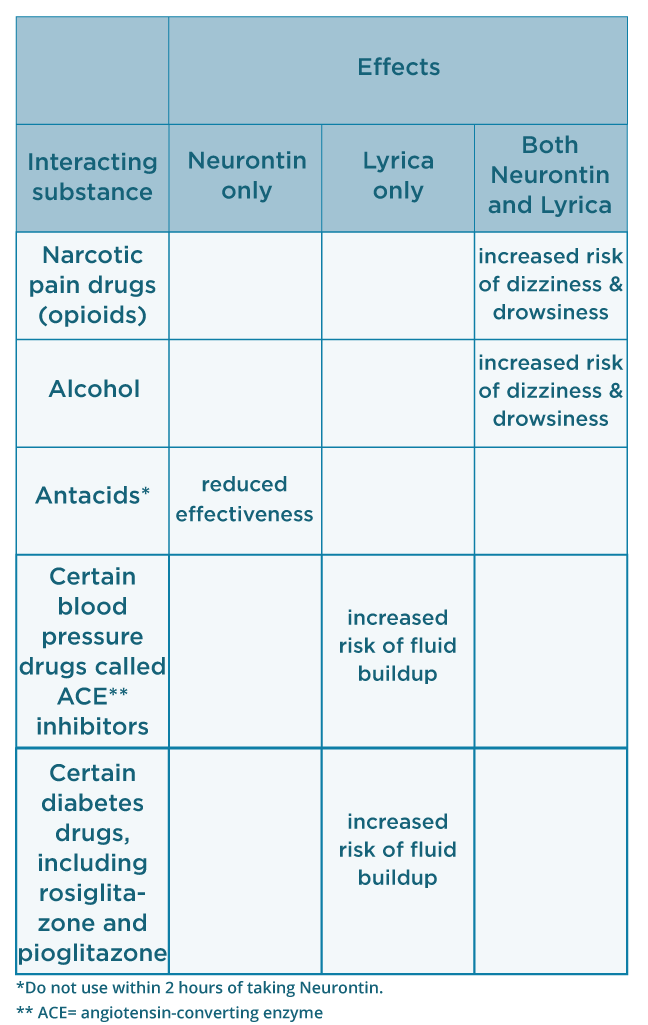
Despite the specific indications of gabapentinoids, there is a notable increase in the off-label prescription of, which has raised the concern about the misuse of these drugs since the benefits remain unclear. 17, 18, 19 To our knowledge regarding their use on sciatica, pain relief only has been reported in one trial comparing gabapentin with placebo 20 and in no one of those investigating Conclusions and relevance: Pregabalin and GBP were both significantly efficacious. However, GBP was superior with fewer and less severe adverse events. Gabapentin should be commenced before PGB to permit optimal crossover of medicines. Trial registration: anzctr.org.au Identifier: ACTRN12613000559718. PubMed Disclaimer. Is gabapentin or pregabalin the more optimal pharmacological treatment for chronic sciatica? Findings. This randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. Meaning. Gabapentin was Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are both used to treat neuropathic pain, but their precise role in sciatica has been under-explored. The amount and quality of evidence for their use is low. Weak evidence suggests efficacy and side effect profiles of PGB and GBP in sciatica are similar. Findings This randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. When it comes to sciatica, there is limited evidence on the effectiveness of these drugs, with only one trial reporting pain relief for gabapentin compared to a placebo. No studies have specifically investigated the pain relief effects of pregabalin for sciatica. Impact Of Pregabalin On Leg Pain And Disability Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have diabetic neuropathy benefit the most from using gabapentin. This relief is due to the medication’s There is currently an absence of high-grade evidence regarding the treatment of chronic sciatica (CS). Whilst gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are both currently used to treat CS, equipoise exists regarding their individual use. In particular, no head-to-head study of GBP and PGB in CS exists. Sciatica is a disabling condition characterized by radiating posterior or posterolateral leg pain that is sometimes accompanied by back pain, sensory loss, weakness, or reflex abnormalities. Evidence regarding medical treatment is limited. Both gabapentin and pregabalin have been widely used to treat neuropathic pain including sciatica. Note: it is expected that the NICE guidance [NICE, 2019a] will be updated and focus on whether gabapentin and pregabalin are suitable treatments for sciatica. The NICE guideline development group (GDG) was unable to recommend one drug as clearly superior to the others because of the variations between the included studies that led to Robertson K, Marshman LAG, Plummer D, Downs E. Effect of Gabapentin vs Pregabalin on Pain Intensity in Adults WIth Chronic Sciatica: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3077. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 30326006 Pregabalin was once thought to be a useful treatment for sciatica because of the coexisting neuropathic pain component with nociceptive pain. However, despite increasing prescription rates of pregabalin for back and neck pain, for example, a six-fold increase in Australian primary care between 2003/4 and 2013/4, there was no robust evidence for We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pregabalin in patients with sciatica. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either pregabalin at a dose of 150 mg per In this review, no evidence has been found to support the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for sciatica pain or low back pain, since the effect is not superior to placebo. In addition, adverse effects of different considerations associated with their use have been reported. A small study comparing gabapentin to pregabalin for chronic sciatica found that gabapentin might be the better option. The study showed that treatment with gabapentin resulted in more pain relief and had less risk of side effects when compared to pregabalin. Gabapentin (GBP) and pregablin (PGB) are GABA analogs often used to treat sciatic pain, but is one superior to the other? Pregabalin is newer and available as a branded product only, but is it more effective than generically available GBP? What’s Known. DailyMed. Label: pregabalin capsule.. DailyMed. Label: gabapentin capsule.. Baldwin DS, den Boer JA, Lyndon G, Emir B, Schweizer E, Haswell H. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in generalised anxiety disorder: a critical review of the literature. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Whilst pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are both used to treat neuropathic pain, their relative role in sciatica is unclear. Our aim was to extensively review the roles of PGB and GBP in treating sciatica. Sciatica is commonly seen in primary care. Its prevalence in the general population varies between 3% and 14%, depending on the definition used. 1 The prognosis of acute sciatica is generally favourable: data from a prospective study of 183 patients with a median disease duration of 16 days show that in approximately one third of patients, symptoms improve greatly (ie, measured on a 4 point
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |