Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 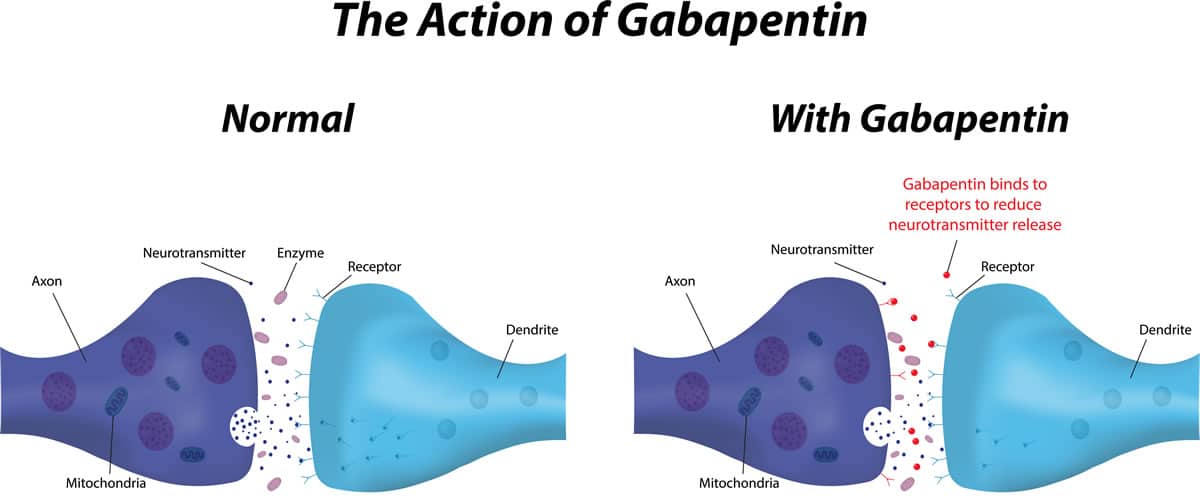 |
treating your condition and the risks of untreated illness during pregnancy. I take gabapentin. Can it make it harder for me to get pregnant? It is not known if gabapentin can make it harder to get pregnant. Sexual dysfunction (including loss of desire to have sex and loss of ability to have an orgasm) has been reported among women who take Does taking gabapentin increase the chance of birth defects? Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. Small, controlled studies on gabapentin have not suggested an increased chance of birth defects. Studies have not been done to see if gabapentin can increase the chance of miscarriage in human pregnancy. Animal studies reported an increased chance for miscarriage. Does taking gabapentin increase the chance of birth defects? Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. Five studies reported significant findings with increased risks of overall congenital anomalies, specific anomalies (nervous system, eyes, oro-facial clefs, urinary and genital system), miscarriage, stillbirth and specific neurodevelopmental outcomes after exposure to pregabalin during pregnancy. Ideally, women planning a pregnancy should speak to their GP or specialist to determine whether gabapentin is still the best medicine for them. Women with an unplanned pregnancy while taking gabapentin should be reviewed at the earliest opportunity by their GP or specialist. While gabapentin (Neurontin) is now used in a wide variety of clinical settings — for epilepsy, pain management, restless leg syndrome, anxiety, and sleep disturbance – there is relatively little information regarding its reproductive safety. Most recently, a prospective study from researchers at the Motherisk program reports on the outcomes of 223 pregnancies exposed to gabapentin treating your condition and the risks of untreated illness during pregnancy. I take gabapentin. Can it make it harder for me to get pregnant? It is not known if gabapentin can make it harder to get pregnant. Sexual dysfunction (including loss of desire to have sex and loss of ability to have an orgasm) has been reported among women who take In our study, only 28% of the women continued taking gabapentin throughout pregnancy as two-thirds of the women (66%) discontinued in the first trimester, most following pregnancy confirmation between 6 and 8 weeks’ gestation. There was an increased risk of preterm birth among women exposed to gabapentin either late (RR=1.28 [CI 1.08-1.52], p < 0.01) or both early and late in pregnancy (RR=1.22 [1.09-1.36], p < 0.001). There was a higher risk of preterm birth among women exposed to gabapentin either late (RR, 1.28 [1.08-1.52], p < 0.01) or both early and late in pregnancy (RR, 1.22 [1.09-1.36], p < 0.001), SGA When treating neuropathic pain in a woman who is pregnant, the use of gabapentinoids (e.g. gabapentin) or an antiepileptic drug (AED) (e.g. levetiracetam, lamotrigine) is a last line option. This is due to the limited availability of data for safe use during pregnancy. Other options should be trialled first. Advice and warnings for the use of Gabapentin during pregnancy. FDA Pregnancy Category C - Risk cannot be ruled out If you are taking gabapentin for epilepsy, it is important that this is well treated during pregnancy as seizures can harm both mother and baby. Gabapentin might lower levels of folic acid. Some professional organisations recommend that people taking this type of medication take a higher dose of folic acid, while others do not. In this large population-based study, we did not find evidence for an association between gabapentin exposure during early pregnancy and major malformations overall, although there was some evidence of a higher risk of cardiac malformations. Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking gabapentin tablets, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. Pregnant women and their physicians should weigh the benefits of treatment with gabapentin with the risks of potential adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with its use. Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog with GABA agonist activity. T1 exposure was defined as pregnancies with at least one filled prescription for gabapentin during the first 90 days of pregnancy (starting from the date of LMP), independently of exposure to gabapentin later in pregnancy. Exposure early in pregnancy was defined as at least one gabapentin dispensing in the first 140 days of pregnancy and no UK guidelines state that women who take any anti-epileptic medication should be prescribed high dose folic acid (5mg), although it is currently not known whether high dose folic acid supplementation offers any additional benefit or protective effects over standard dose regimes when taking gabapentin preconceptually or during pregnancy. If you're trying to get pregnant or have become pregnant while taking gabapentin, it is recommended to take a high dose of folic acid (5mg a day). You can get this from your doctor or midwife. Ideally you'll take high dose folic acid for 3 months before you start trying to get pregnant and for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |