Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 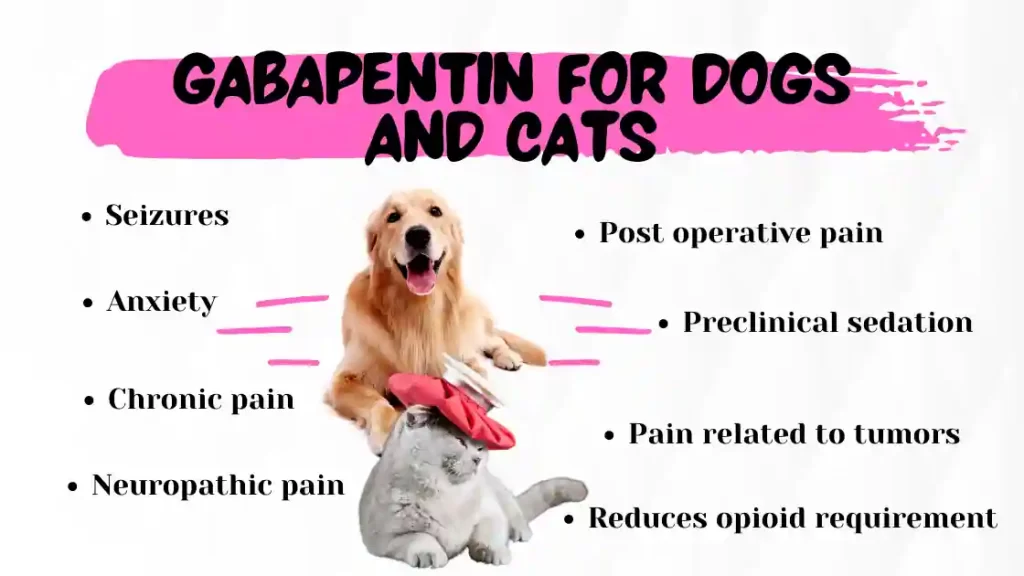 |
Gabapentin is used “off-label” for several conditions. Examples include anxiety, pain, and nerve pain from diabetes (diabetic nephropathy). It can also help treat alcohol use disorder (AUD). As with all medications, gabapentin has possible side effects you should know about. But do these side effects include harm to your liver and kidneys? As with most medication, high doses of gabapentin can be dangerous and potentially fatal. Gabapentin has known CNS (central nervous system) depressant effects and large doses could induce coma or respiratory depression. Safe Use Of Gabapentin It should be noted that the studied medicinal dose range of gabapentin is quite large. Recent research suggests that although gabapentin isn’t typically effective for regular back pain, it may work for back and leg pain that comes from the nerves. If you’re considering gabapentin to treat sciatica, talk to a healthcare professional. It may be an option for you. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. To learn more about gabapentin, join the Drugs.com gabapentin Support Group and Q&A Section where you can ask questions, share experiences and keep up with the latest news. This is not all the information you need to know about gabapentin for safe and effective use and does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your treatment. Different brand names and formulations of gabapentin are available, each with specific uses and dosing instructions. Neurontin: Treats pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) and, when combined with other seizure medications, treats partial-onset seizures in adults and children over 3 years old. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. Tell your healthcare provider if you are also taking opioids. Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping suddenly can cause serious problems. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Neurontin is a prescription medicine used to treat: Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults. Partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older with seizures. Both men and women were almost equally likely to overdose on gabapentin. What Happens if You Take Too Much Gabapentin? Gabapentin works by slowing down the central nervous system. It does so by mimicking the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which slows down activity in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin’s effect does help to calm and provide mild sedation, but it does not address underlyling causes of stress, fear, anxiety, etc. If your kitty is calmer, this may be the most you can expect from gabapentin. Just like it can be used as a long-term pain medication, it can be used longterm to help with calming if it has a visible benefit. Neurontin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain. Neurontin is used in adults to treat neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster). Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Neurontin is a brand (trade) name for gabapentin which may be used for the treatment of some seizure disorders or to relieve nerve pain. Experts aren't sure exactly how Neurontin (gabapentin) works, but research has shown that gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels. Gabapentin is one of the top non-opioid alternatives that was prescribed to people for pain management. It was thought to be a safer alternative to opioids that is why doctors prescribe gabapentin to people who are experiencing pain but do not want the risk of opioid addiction. Can gabapentin get you high? Yes, gabapentin can get you high. Gabapentin belongs to the class of medications called anti-epileptics. It is used in combination with other seizure control medications to manage and prevent seizures associated with epilepsy. Gabapentin does not cure epilepsy and only works to control seizures as long as the medication is taken.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |