Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 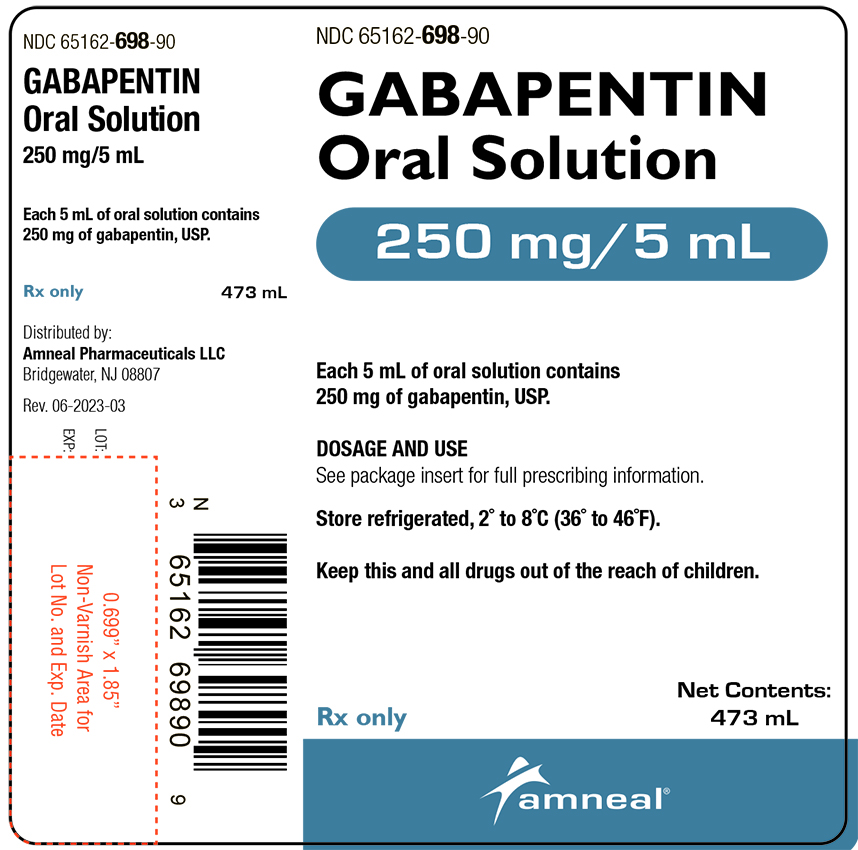 |
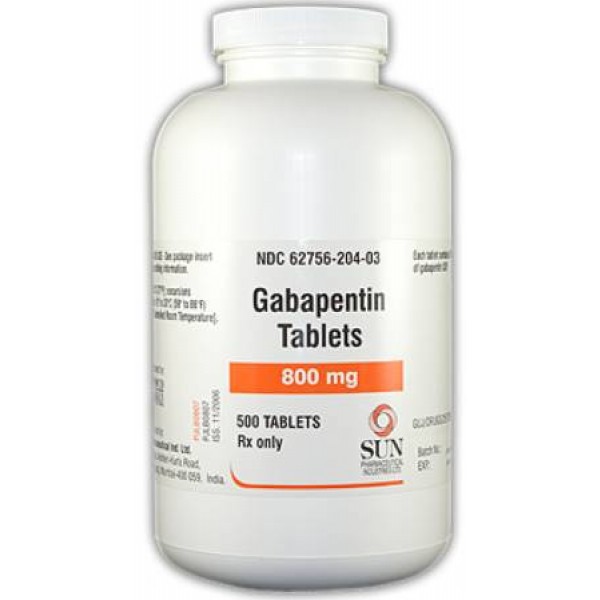
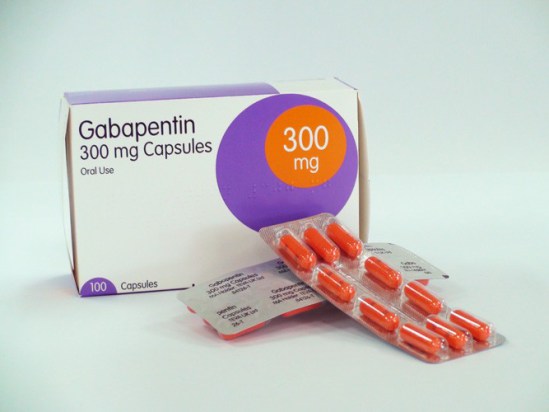
Gabapentin use in elderly patients. Gabapentin can be used in elderly patients, but caution should be exercised due to age-related changes in renal function. A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients Keep gabapentin and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of gabapentin. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use gabapentin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. I have a 17-ish year old kitty who weighs about 7 lbs. For some months now, she has been meowing constantly, keeping me awake at night, night after night. She takes two 50 mg. tabs of gabapentin daily but it does nothing (and costs me $100/mo.). She also takes .50 mg. of Xanax a day, and large doses of CBD oil. GABAPENTIN (GA ba pen tin) treats nerve pain. It may also be used to prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. It works by calming overactive nerves in your body. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin, originally developed as an anti-seizure medication, has found widespread use in treating various forms of neuropathic pain. Among its many dosages, Gabapentin 100mg is often prescribed for its effectiveness and relatively mild side effects. A Cochrane review reported that 3 to 4 patients out of every 10 with either of these conditions experienced at least a 50% reduction in pain intensity when prescribed gabapentin at dosages of 1800mg-3600 mg/day (gabapentin encarbil: 1200mg-3600 mg/day). This compared with only 1 or 2 out of every 10 given a placebo (an inactive treatment). Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin Uses. Gabapentin is a versatile medication with a range of therapeutic applications. Its primary uses include treating seizures, managing neuropathic pain, and addressing anxiety and insomnia. In addition, ongoing research is exploring its potential in managing other conditions, such as restless leg syndrome and migraine headaches. Gabapentin is a prescription medication commonly used to manage conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and anxiety disorders. It works by altering the way nerves communicate with the brain. Gabapentin is available in various forms and strengths, so it’s essential to follow your doctor’s dosing instructions carefully. Gabapin 100 MG Tablet is a prescriptive drug primarily used to prevent seizures.It belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants. Aside from seizures, Gabapin 100 MG Tablet is also used to cure hot flashes, restless legs syndrome (RLS) and postherpetic neuralgia. What Is Gabapentin and How Does It Work? Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults, treating the pain of post herpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs known as anti- seizure drugs. Gabapentin is available in 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules, and in 600 mg and 800 mg tablets. The dose of gabapentin to treat epilepsy with partial onset seizures in patients 12 years of age and older is up to 600 mg three times daily. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Off-label use means there is some evidence to show that a drug may be medically appropriate to treat conditions other than those for which it was approved. Gabapentin is sold under the brand name Neurontin and is available as a generic product as well. Gabapentin oral capsule is commonly used to treat the following conditions: Seizures: Gabapentin is used to treat partial (focal) seizures. It’s taken together with other seizure medications in What is gabapentin used for? Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Each hard gelatin Coni-Snap capsule with white opaque body and cap printed with "PD" on one side and "Neurontin/100 mg" on the other contains 100 mg of gabapentin. Nonmedicinal ingredients: cornstarch, lactose, and talc; capsule shell: FD&C Blue No. 2, gelatin, red iron oxide, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and yellow A 100 mg/mL suspension may be made with tablets (immediate release) and either a 1:1 mixture of Ora-Sweet® (100 mL) and Ora-Plus® (100 mL) or 1:1 mixture of methylcellulose 1% (100 mL) and Simple Syrup N.F. (100 mL).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |