Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/things-to-stop-if-you-love-an-alcoholic-67300-final-89a3850658ec4525a3bc45721f526fb4.png) |
 |  |
 | 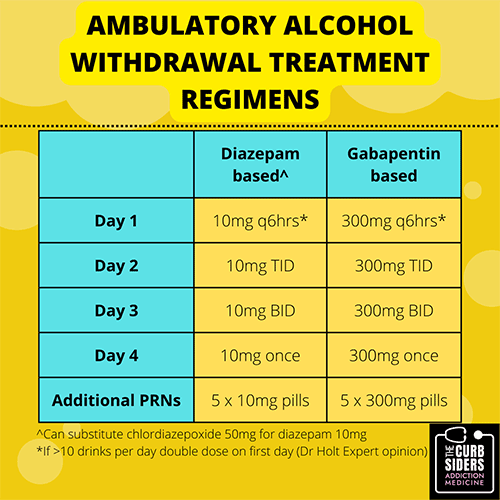 |
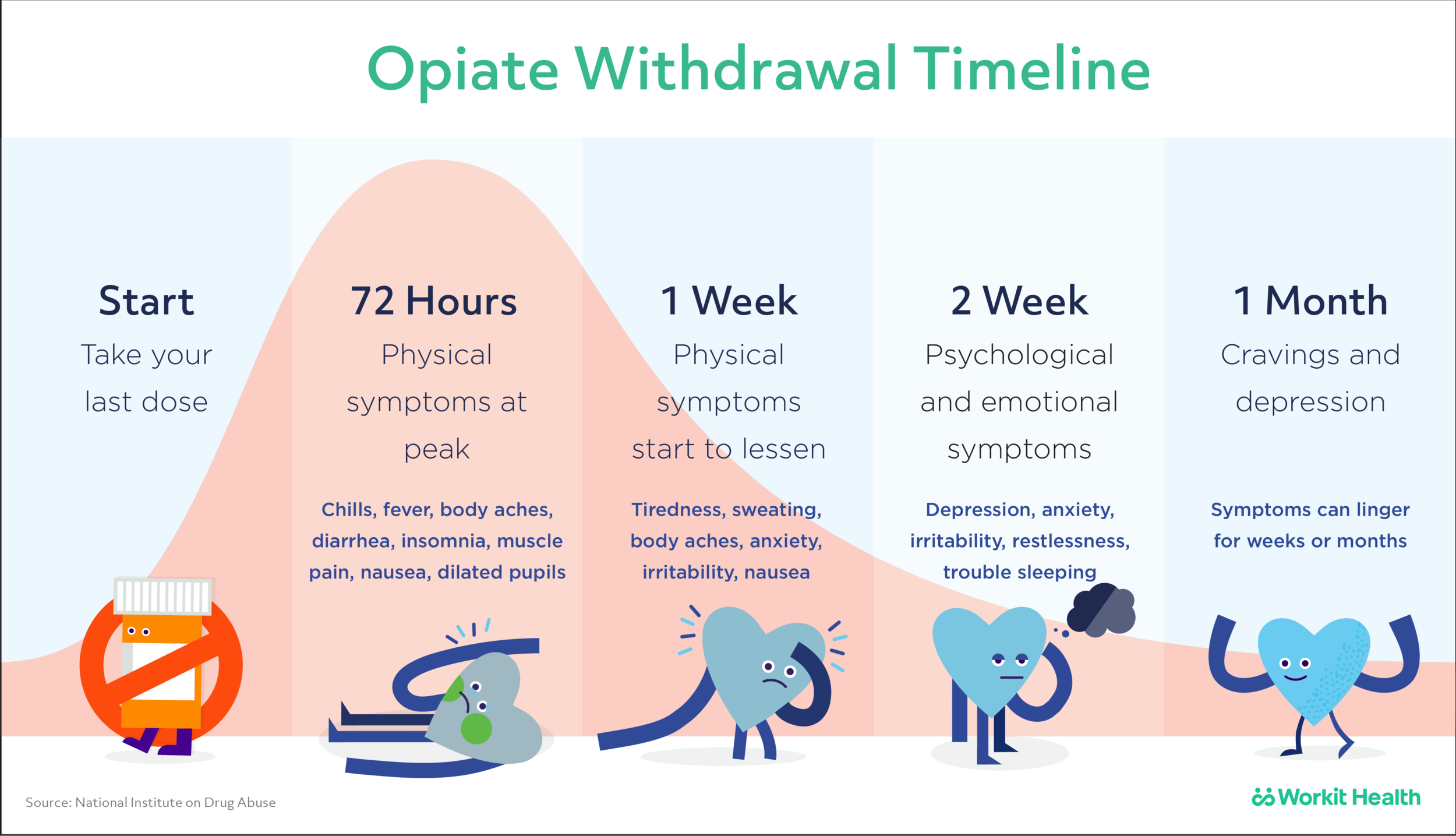
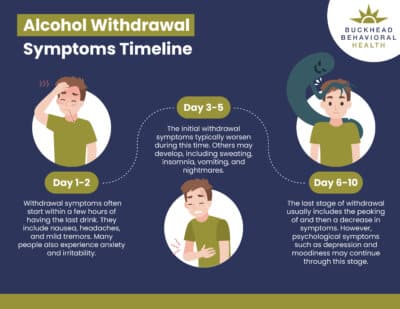
Prior withdrawal is a risk factor for future episodes. Prior alcohol withdrawal seizures is a risk factor for more severe alcohol withdrawal. 50% of persons with history of long term, heavy alcohol use will have mild alcohol withdrawal. 10% of symptomatic individuals will progress. Generalized tonic clonic seizures. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder in patients with a history of withdrawal found that gabapentin was associated with lower rates of returning to drinking as compared to placebo with a greater benefit experienced by patients reporting more withdrawal symptoms at the beginning of the study Go to the nearest emergency room or call 911 (or your local emergency service number) if you or a loved one has any concerning symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol withdrawal symptom timeline. The severity and length of alcohol withdrawal varies based on many factors. But a general timeline includes: Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, A double-blind trial of gabapentin 900mg/d in 40 subjects concomitantly treated with methadone did not significantly reduce severity of opiate withdrawal relative to placebo, perhaps as a function of the relatively low dose of gabapentin used (900/mg/d); when gabapentin was given as an add-on to methadone in an open-label study, greater Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4 Experiments in 1955 demonstrated that alcohol-naïve volunteers given continual alcohol for longer periods developed more severe withdrawal than those who drank for shorter periods . These results imply that most people are vulnerable to the effects of the abrupt cessation of prolonged, sustained ethanol intake. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Future studies evaluating gabapentin's effect on long-term safety and hospital readmissio A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. In the context of alcohol withdrawal, Gabapentin helps by stabilizing neural activity, reducing the risk and intensity of withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, restlessness, and the potential for seizures. This study showed that gabapentin is efficacious in promoting abstinence and reducing drinking in individuals with alcohol use disorder and especially so in those with more alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Although an estimated 30 million people meet criteria for alcohol use disorder (AUD), few receive appropriate pharmacotherapy. Gabapentin may have benefits in terms of decreased daytime sedation and decreased alcohol craving. 12 However, alcohol withdrawal seizures in patients treated with gabapentin have been reported in several studies. 13,14 Therefore, gabapentin monotherapy should not be used in severe AWS or in those with a history of AWS seizures or who are at Given gabapentin’s effectiveness for acute alcohol withdrawal problems, a research team at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) explored whether AUD patients who exhibit more severe withdrawal symptoms might experience greater improvements with gabapentin than those who experience fewer symptoms. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from reduced How Does Gabapentin Affect Alcohol? It is important to note that gabapentin does not tackle the underlying reasons for alcohol addiction. However, it can help with some alcohol withdrawal symptoms, making detoxification easier to handle. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. ⚠️ Be careful about over-diagnosing patients with alcohol withdrawal, because the treatment for alcohol withdrawal can be disastrous in a patient who actually has hepatic encephalopathy: Patients with hepatic encephalopathy have excess GABA stimulation, so they are very sensitive to GABAergic medications (e.g., benzodiazepines or barbiturates). Gabapentin was well tolerated and effectively diminished the s ymptoms of alcohol withdrawal in our population especially at the higher target dose (1200 mg) used in this study. Gabapentin reduced the probability of drinking during alcohol withdrawal and in the immediate postwithdrawal week compared to lorazepam. Full paper available at:
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/things-to-stop-if-you-love-an-alcoholic-67300-final-89a3850658ec4525a3bc45721f526fb4.png) |
 |  |
 |  |