Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |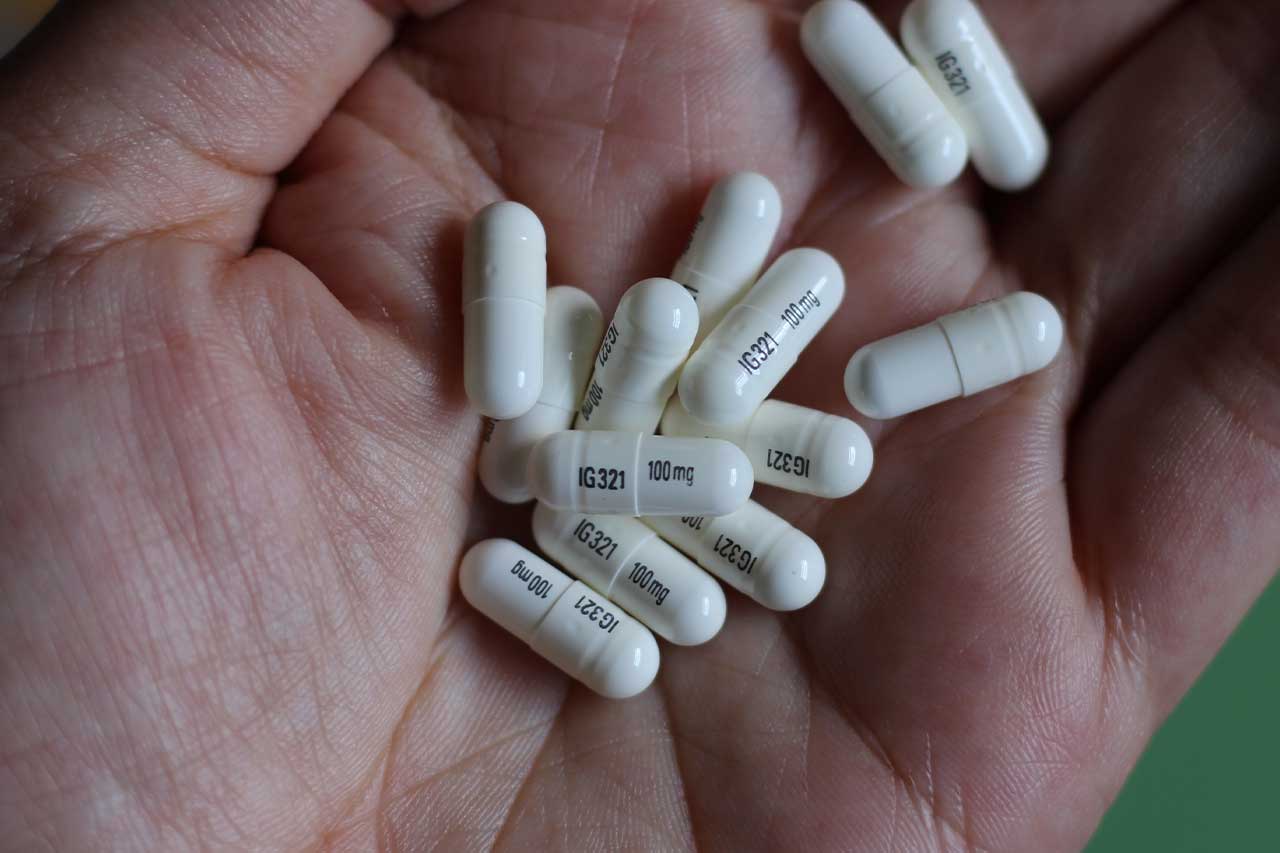  |
For nerve pain, it is usually started at a low dose of 100-300 mg per day. The dose is then increased gradually over several weeks, up to 1200-3600 mg per day. Taking gabapentin with food can help minimize side effects. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). The results showed a statistical benefit of gabapentin compared to placebo, at all end points, for pain improvement.⁴ The gabapentin dosing regimen used in this study was 900 mg/d for week 1; 1,800 mg/d for week 2; 2,400 mg/d for week 3; and 3,600 mg/d for week 4. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. If you are experiencing prolonged pain after a shingles infection has resolved, you may have postherpetic neuralgia. Consult with your doctor about the treatments available to help you manage this condition and whether gabapentin is an option that can help you improve your quality of life and lessen the pain after a shingles infection. Gabapentin is a versatile medication used to treat various conditions, including seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. It works by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain and calming overactive nerves. Gabapentin is taken by mouth and is available either as a capsule (100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg) or a tablet (600 mg and 800 mg). Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. When used for pain, gabapentin is prescribed at a lower "loading dose" and gradually increased to the optimal "therapeutic dose." Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have diabetic neuropathy benefit the most from using gabapentin. This relief is due to the medication’s Another reason gabapentin takes time to work is that the dose is usually started low and gradually increased over time to reach an effective dose. For example, when used to relieve nerve pain, the initial dose may be started at 300 mg and increased by 300 mg daily over several days, gradually reaching up to 600 mg three times per day. Studies Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. In general, Gabapentin may alleviate nerve pains and improve the quality of life. It comes in handy for alleviating pain in the following situations: For relieving inflammatory postherpetic neuralgia, which is the pain from shingles. In nerve compressions, especially if correcting whatever is pinching the nerve takes a long time. In this prospective randomized clinical trial we evaluated the effects of low dose gabapentin (100 mg and 300 mg) in controlling pain and improving symptoms of patients with CTS. Following treatment with gabapentin 100 and 300 mg per day, patients reported significant decrease in pain severity and BCTQ subscores (p < 0.001). One of the most common uses of Gabapentin 100mg is treating neuropathic pain. This type of pain often results from nerve damage caused by conditions such as diabetes, shingles (postherpetic neuralgia), or spinal cord injuries. A 100mg dosage can provide relief for mild to moderate nerve pain, making it a viable option for many patients. Nerve pain is unfortunately difficult to treat. For Gabapentin, about 20% will get excellent pain relief, 40% will get around 30% pain relief, and about 40% will get minimal pain relief and a lot of side effects. This is true of all nerve pain medications. The maximum dose of Lyrica (or pregabalin is the generic name) is 600. Dosage for nerve pain. The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. Changes to your dose. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same. How to take it Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower The exact way that gabapentin works for nerve pain or seizures is unknown. Gabapentin may block certain signals from nerves. Seizures are caused by electrical activity in the brain that is
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |