Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
-3-isobutyl-GABA+are+broad-spectrum+anti+consultants..jpg) | |
 | 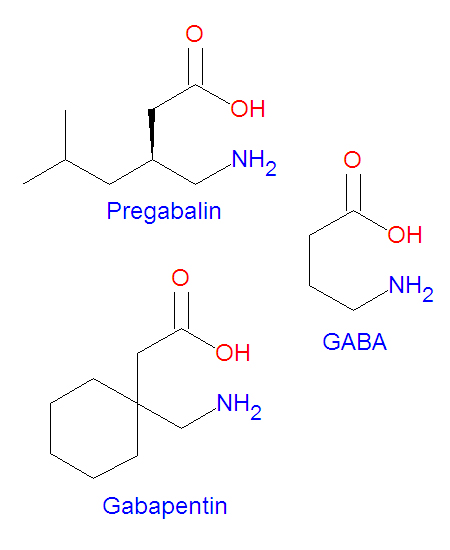 |
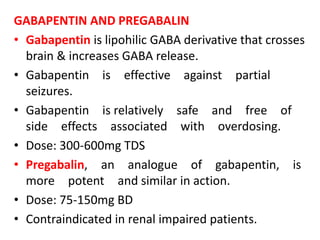
What's the difference between gaba and gabapentin? NT vs Medication: Gaba is a normal neurotransmitter (nt) in the brain and other parts of the nervous system in the body. Gabapentin is a medication that affects GABA in the brain and nervous system. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions While both GABA and gabapentin are related in function, their chemical structures differ significantly: GABA : Simple four-carbon chain, directly interacts with GABA receptors. Gabapentin : Cyclohexane derivative, binds to calcium channels instead of GABA receptors. We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gaba and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 428,042 people who take Gaba and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug but its use has expanded to treat multiple other diseases including post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. The mechanism of action is not fully understood but may be related to gabapentin’s action on calcium channels leading to diminution of excitatory neurotransmitters. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Research about the effects of gabapentin on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter levels has reported inconsistent results, i.e., increase in GABA levels based on human studies, 10 but no effects have been reported in in vitro studies. 11 Moreover, gabapentin affects GABA(A), but not GABA(B) receptor responses, based on in vitro The most common side effects of gabapentin in therapeutic doses are drowsiness, somnolence, dizziness, movement disorders, diarrhea, and weight gain. In addition, cases have been reported of gabapentin-related suicidal acts and aggressive behavior . Table 1. Some researchers highlight an intriguing aspect of GABA's influence on hormone release. They propose its potential usefulness in reducing enlarged prostate problems. GABA stimulates the release of the hormone prolactin by the pituitary gland, potentially alleviating issues related to prostate enlargement. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners. Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: Jennifer shared this: Yes in the vet world, gabapentin is often called gaba. Not surprising since western medicine likes to pretend that supplements Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Gabapentin is a new chemical compound designed as a structural analog of GABA that is effective in the treatment of partial seizures. In contrast to GABA, gabapentin readily penetrates the blood–brain barrier. In man, gabapentin has been demonstrated to increase GABA concentrations [126]. Most probably the mechanism of action is related to However, recent publications challenge the routine use of gabapentin in the perioperative setting due to a potentially unfavorable ratio of benefit vs. adverse side effects. Chronic combined gabapentin and opioid use has been associated with increased opioid-related mortality. While both relate to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), they are fundamentally different in their origin, mechanism of action, and legal status. In short, over-the-counter (OTC) GABA is a dietary supplement, while gabapentin is a prescription medication.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
-3-isobutyl-GABA+are+broad-spectrum+anti+consultants..jpg) | |
 |  |