Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | 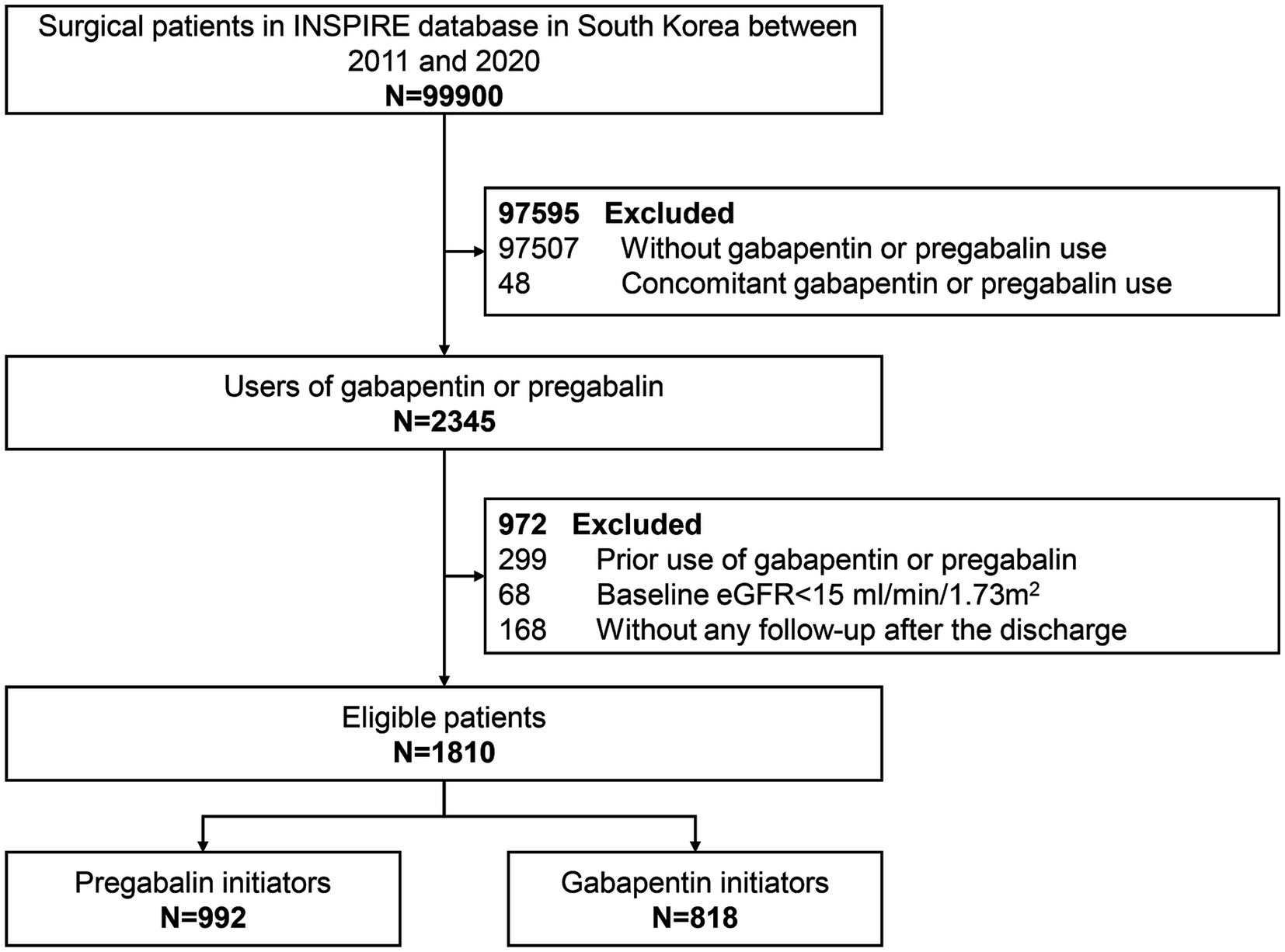 |
 | /male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
The standard doses of gabapentin prescribed for people with normal kidney function are not suitable for those with CKD. Typically, healthcare providers will significantly reduce the dose of gabapentin based on a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) , a measure of kidney function. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Height However, previous kidney function, as well as factors such as hydration levels, can all influence renal function recovery. What are the signs of kidney damage from pain meds? Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. This accumulation can increase the Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Tests showed normal renal function (creatinine 0.9mg/dl, urea 30mg/dl and no pathological findings in urinary sediment. His normal treatment consisted of paroxetine, mianserin, disulfiram, eprosartan, bisoprolol, and, during the last 48 hours, gabapentin. How they can affect the kidneys: If you have kidney disease, understand what your kidney function is before you take an antibiotic. That will help you and your doctor determine the dosage. Owen says that some medications used to treat viruses can cause kidney injury. Notably, gabapentin is exclusively excreted through the kidneys, making its dose reduction essential when given to patients with impaired renal function. The appropriate dosing based on the patient’s actual creatinine clearance is imperative to prevent severe adverse side effects and drug-related toxicity. This will help prevent any negative effects from the medication, including further kidney damage. You can determine your level of kidney function with a blood test for serum creatinine to calculate an eGFR measurement. An eGFR estimates how well your kidneys are filtering wastes from the blood. Gabapentin and Kidney Health Similarly to the liver, there have been rare cases of kidney damage associated with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions or those taking other medications that can affect kidney function may be at a higher risk.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |